Posterior Shoulder Flashcards
_____ a common site of humeral fractures
Surgical neck
Lesser tubercle projects anteriorly/posteriorly
anteriorly
Greater tubercle projects laterally/anteriorly
laterally
As one abducts and adducts the humerus- note how the scapula slides along the thoracic wall
This scapular motion occurs at the conceptual ____
Abduction of the arm above the head requires lateral/medial rotation of the scapula
“scapulothoracic joint”; lateral
Action of the serratus anterior
Action: Stabilizes the scapula, laterally rotates the scapula, and protracts the scapula (Boxer’s Muscle)
nerve of the serratus anterior
nInnervated by long thoracic nerve (C5, C6 & C7)

Long thoracic nerve trauma (i.e. surgical procedures [mastectomy] or traumatic knife wound) can render the serratus anterior paralyzed (Step1)
Condition known as “winged scapula”
Unable to clamp or stabilize scapula against thoracic wall
Reduced ability to abduct arm above head because scapula cannot be sufficiently laterally rotated
nLevator scapula- true to its name…
is a “levator” or elevator (“lifter”) of the scapula
Rhomboids _____ the scapula medially/laterally
retract; medially…toward the spine
leavtor scapula and Rhomboids are innervated by
All these muscles innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve (C5) (minor contribution from C4)
Scapulohumeral Muscles
- Deltoid
- Teres Major
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Subscapularis (not shown here)
- Teres Minor
nPrincipal abductor of the arm (supraspinatus muscle initiates the 1st 15° of abduction)
Deltoid
deltoid is innervated by
nInnervated by Axillary nerve (C5 & C6)
_____can be injured in surgical neck fractures of humerus and can result in
Axillary nerve can be injured in surgical neck fractures of humerus
Result in atrophy of deltoid (loss of shoulder contour)
Inability to abduct the arm
Loss of sensation lateral aspect of shoulder
teres major is innervated by
Innervated by the lower subscapular nerve (C5 & C6)
teres major function
Adducts, extends, and medially (internally) rotates the arm
The tendons of the 4 muscles of the rotator cuff insert onto and reinforce the shoulder joint capsule – forming a strong _____
musculotendinous rotator cuff
Supraspinatus Muscle- arises from supraspinous fossa and inserts into the greater tubercle- initiates ______ of arm (~first 15о)
abduction
Infraspinatus Muscle- arises from infraspinous fossa and inserts into the greater tubercle- laterally/medially rotatesthe arm
laterally (externally)
Supraspinatus Muscle- arises from supraspinous fossa and inserts into the greater tubercle- initiates ______ of arm (~first 15о)
abduction
nBoth spinatus muscles are innervated by the
suprascapular nerve (C5 & C6)
Teres Minor- arises from lateral border of scapula and inserts into the greater tubercle- laterally rotates the arm, innervated by _____
axillary nerve
Subscapularis Muscle is innervated by
Innervated by the upper & lower subscapular nerves
(C5 & C6)
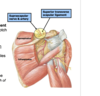
nDeltoid and supraspinatus muscles are separated from the acromion of the scapula by the ______ and ______
subacromial and subdeltoid bursae
the subacromial and subdeltoid bursa- synovial fluid-filled sacks helps reduce friction between the muscles/bone and allows the supraspinatus tendon to glide smoothly beneath the acromion (within the small subacromial space) during shoulder movements
Collectively…these two bursae are often referred to as the ____
Subacromial bursa
nRepetitive movements (weight lifting, baseball, swimming) can inflame the tendons of the rotator cuff causing ____
tendonitis
Of the rotator cuff muscles, it is the ______ that is most commonly diagnosed with tendonitis (due to irritation and impingement within the small subacromial space)
supraspinatus
What do these passageways allow?

These passageways allow neurovascular structures to traverse between anterior and posterior scapular/arm regions

Suprascapular nerve passes through/over the subscapular notch and innervates the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles (suprascapular nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus)
through
what froms the Suprascapular notch
Suprascapular notch is located along the superior border of the scapula
Superior transverse scapular ligament spans the roof of the suprascapular notch forming a foramen
Suprascapular artery passes through/over the ligament (suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk in the neck)
over
Quadrangular Space
Boundaries and Contains
Boundaries:
- Teres major
- Teres minor
- Long head of triceps
- Surgical neck of the humerus
Contains the axillary nerve and the posterior circumflex humeral artery (this artery helps vascularize the head of the humerus)
nRotator cuff muscles are often referred to as the “SITS” muscles:
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis
nDamage to the long thoracic nerve can render the serratus anterior weakened/paralyized resulting in ______
winging of the scapula
______ is the most commonly inflamed tendon of the rotator cuff due to its passage through the small subacromial space
Supraspinatus
Fractures of the proximal humerus (surgical neck) can damage the _____… resulting in deltoid paralysis/weakness
axillary nerve
out of SITS which two produce external (lateral)
rotation of the shoulder
infraspinatus and the teres minor
Which of the following muscles could the surgeon utilize to help reconstruct the breast?
A. Trapezius
B. Erector spinae
C. Latissimus dorsi
C. Latissimus dorsi
Which of the following muscles laterally rotates the scapula?
A.Levator Scapula
B.Rhomboid Major
C.Rhomboid Minor
D.Latissimus Dorsi
E.Serratus Anterior
E.Serratus Anterior
nCC: 38 year-old male presents to the clinic complaining of weakness in his right arm. He relates he is having trouble/difficulty combing his hair and reaching over his head.
nPMH: Dennis denies any medical problems and takes no medications. His only encounter with hospitals and doctors was last year after he fell on the ice and broke his right arm. His medical record indicates he suffered a right proximal humeral fracture
nPE: Exam reveals visually prominent clavicle, acromion, and head of the humerus on the right. Decrease strength on abduction, flexion, and extension of right arm/shoulder
A.Shoulder Separation
B.Shoulder Dislocation
C.Axillary nerve palsy/damage
D.Long Thoracic nerve palsy/damage
E.Rotator cuff tendonitis
A.Axillary nerve palsy/damage
RC Hobbs, a 45 year-old ex-minor league baseball pitcher (currently a successful business man) visits his orthopedist and complains of pain in his right shoulder for the past few weeks. Hobbs relates that he suffered from right shoulder pain off-and-on throughout his 6 year pitching career but has remained pain free for nearly 20 years. He recently joined a local gym and began lifting weights every day in an attempt to get “back in shape.”
Hobbs explains that he has trouble sleeping on his right shoulder and pain when he extends his arm to lift anything. “Ice and aspirin help reduce the pain.”
Which of the following tendons is likely
inflamed and causing the problem?
a. Suprapinatus
b. Infraspinatus
c. Teres minor
d. Teres Major
e. Subscapularis
a.Suprapinatus