Forearm & Elbow Flashcards
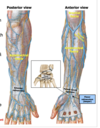
Fibrous membrane connecting the ulna and radius
Serves as attachment for muscles and compartmentalizes the forearm (i.e., separates the anterior vs. posterior compartments)
Collagen fibers originate on the radius and course inferomedially to attach on the ulna
This orientation of fibers assists in transferring forces from the radius to the ulna (i.e. during a FOOSH)
Interosseous
Membrane
colles fracture
Distal radial fractures are the most common fractures of the forearm (>50 years of age)
Typically occurs when patients attempt to “break their fall” by landing on their hand in an extended position (i.e., slip on ice)
Distal radial fracture fragment displaces dorsally (posteriorly) producing a characteristic “jog” in the forearm
This displacement is referred to as the “dinner fork deformity”
nThe wrist consists of 8 _____
carpal bones
____ and ___ are small carpal bones that articulate with the distal radius (wrist joint)
Scaphoid and lunate
nThe hand has 5 _____ bones
metacarpal bones
The hand has 14 _____ : proximal, middle, and distal
phalanges
Cubital fossa (anticubital) is a triangular depression anterior to the elbow for passage of the ____ artery and ______ nerve
brachial; and median
At the wrist level, this antebrachial (continuous with brachial fascia) fascia thickens forming the _____ (posteriorly), and the (anteriorly)
extensor retinaculum; palmar carpal ligament
Just distal (and slightly deeper) to the palmar carpal ligament lies the ______ (which forms the roof of the carpal tunnel)
flexor retinaculum aka the Transverse Carpal Ligament
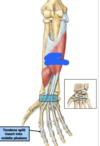
how many superficial anterior muscles are there in the forearm?
- pronator teres
- flexor carpi radialis
- flexor carpi ulnaris
- flexor digitorum superficialis
- palmaris longus
all superficial muscles of the forearm orginate form the _____ of the humerus
medial epicondyle
all superficial flexor muscles are innervated by the ___ nerve except ___ which is innervated by
median; flexor carpi ulnaris; ulnar nerve
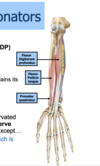
Deep Flexor - Pronators
- Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
- Flexor pollicis longus
- Pronator quadratus
Anterior compartment muscles are _____ muscles
Flexor-Pronator; (i.e., they flex the digits and wrist AND/OR pronate the forearm
Posterior compartment muscles are _____ muscles (i.e., they extend the wrist and digits AND/OR supinate the forearm)
Extensor- Supinator
All these deep flexor- pronator muscles are innervated by the ______ (a branch of the median nerve) except ______ which the medial 1/3 portion is innervated by the ulnar nerve
anterior interosseous nerve (AIN); Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
Two muscles that produce
pronation of the forearm:
- Pronator Teres
- Pronator Quadratus
_____ initiates pronation of the forearm
pronator quadratus
pronator quadratus pulls the distal _____ over the ____
radius; ulna
pronator quadratus is innervated by the
Innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve (C8 & T1)
_____ _ assist the quadratus when more speed/power are required
Pronator teres
protanator teres is innervated by
nInnervated by the median nerve (C6 & C7)
Two muscles that produce
flexion of the fingers:
- FDS
- FDP
FDS muscle belly gives rise to four tendons which pass through the ______ then each splits and then inserts into the middle phalanx of digits 2 – 5
carpal tunnel
FDS is innervated by the
Innervated by median nerve (C7, C8 & T1)
Flexes middle phalanx at the PIPJ
FDS
FDP muscle belly has a dual innervation:
Medial portion via the
Lateral portion via the
Medial portion via the ulnar nerve (C8 & T1) which controls 4th and 5th digits
Lateral portion via the anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve (C8 & T1) which controls the 2nd and 3rd digits
nFlexes distal phalanx at the DIPJ of digits 2-5
FDP
3 functional extensor muscle groups of the forearm are all innervated by the
nAll innervated by (C6, C7 & C8) of the radial nerve (or by a branch of the radial nerve)
Extensors of the Wrist (3), innervation, and function
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
- Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
- Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
All innervated by (C6, C7 & C8) of the radial nerve
these muscles extend and stabilize the wrist
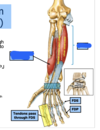
Extensors of the Digits (3)
- Extensor Digitorum
- Extensor Digiti Minimi
- Extensor Indicis
long tendon of the extensors of the digits insert into
Long tendons of these muscles insert into the extensor expansion (“Hood”) of the digits
Extensors/Abductors
of the Thumb
These muscles assist with intricate and precise movements of the thumbs
1.Abductor Pollicis Longus (APL)
●
2.Extensor Pollicis Brevis (EPB)
●
3.Extensor Pollicis Longus (EPL)
All the tendons of these extensor muscles are secured at the wrist by the _______ - a localized thickening of the antebrachial fascia
extensor retinaculum
nThe extensor tendons are compartmentalized into 6_____ within the retinaculum
fibro-osseous tunnels
Ganglion or Synovial Cyst
Thin walled cyst that contain clear mucinous/synovial fluid-are common on the dorsum of wrist
Etiology is unknown-often called “Bible Cysts”
Common site is on the extensor carpi radialis longus/brevis tendons
As cyst enlarge-can cause pain and nerve compression
Treatment often involves surgical excision
Anatomical “Snuff Box”
nBounded by the
- Abductor pollicis longus (APL)
- Extensor Pollicis Brevis (EPB)
- Extensor Pollicis Longus (EPL)
nRadial artery, scaphoid bone, and styloid process of the radius can be palpated in floor of the box
radial nerve divides
- superficial branch (cutaneous/sensory to a portion of the dorsum of the hand)
- deep branch (a motor nerve… i.e. it only innervates muscles):
Deep branch of the radial nerve pierces _____ and enters the extensor compartment where it continues as the posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)- innervating many of the forearm extensors
supinator muscle
Passes posterior to the medial epicondyle in the “cubital tunnel”
Ulnar Nerve
Innervates the flexor carpi ulnaris
Ulnar Nerve
Passes thru a groove “canal of Guyon” on the anterior aspect of the wrist/hand
ulnar groove
Principle nerve of the anterior compartment of the forearm…innervates all anterior compartment forearm muscles except for 1½
Passes between the FDS and FDP
Gives rise to several small muscular branches and the anterior interosseous nerve (AIN)
Gives rise to a small cutaneous nerve- palmar branch which courses superficial to the flexor retinaculum and supplies the skin on the lateral palmar aspect
Median Nerve
Median nerve then passes beneath the ______ (roof of carpal tunnel) and enters the hand
flexor retinaculum
aka…radial head dislocation
Common in toddlers age 1-4
Radial head is small at this age and can sublux out of annular ligament
Principle mechanism of injury is pulling/lifting a child by the arm…partially tearing the annular ligament or dislocating the radial head
Treatment is reduction and sling X 2 weeks
nurse maids elbow
___, _____, and _____ can be palpated in floor of the “snuff box”
Radial artery, scaphoid bone, and styloid process of the radius
Game Keepers Thumb
Rupture of the Ulnar Collateral ligament of the thumb (MCP)
Originated in England when game-keepers strangled small animal between their thumb & index fingers
Today…common skiing injury when the ski pole produces a radially (thumb) directed force which tears the ulnar collateral ligament (“Skier’s Thumb”)
Often associated with a fracture of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
Can require cast and/or surgical repair
golfer’s elbow ____ and tennis elbow ________…
(medial epicondylitis) ; (lateral epicondylitis)
____ nerve passes beneath the flexor retinaculum (roof of the carpal tunnel)- common site of “entrapment”
Median nerve
_____ nerve innervates 1½ forearm muscles then enters the hand coursing beside the ulnar artery
Ulnar
Radial nerve- think “BEST”- innervates the
Brachioradialis, Extensors, Supinator and…Triceps

Colles’ Fracture
























































It is an inflammation of the tendons and synovial sheaths of the EPB and APL tendons at the wrist. Synonyms for the condition include “mom’s wrist” or “housewife’s wrist.”
De Quervian’s Tenosynovitis.


