Upper Limb Nerve Lesions Flashcards
what are the root nerves for the long thoarcic nerve? What does it innervate?
C5 C6 C7 reach your arm up to heaven; anterior serratus
if the long thoarcic nerve C567 is damaged
winged scapula and the patient has difficulty raising the arm above the head; decreased medial rotation of the scapula










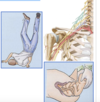
upper brachial plexus damage (C5 and C6)
Upper brachial plexus injuries are called _____
Erb’s- Palsy or Erb’s- Duchenne Palsy

Erb-Duchenne Palsy; Resulting limb is adducted, internally rotated, pronated and extended at the elbow

Lower brachial plexus injuries typically results from upper limb being suddenly pulled superiorly…grasping a limb during a fall or breech birth
This type of trauma can stretch or avulse C8 & T1 (sometimes C7) ventral rami (lower roots)
Lower brachial plexus lesions are referred to as ____
Klumpke Palsy
klumpkes or erbs palsy is more common?
erbs palsy (upper brachial plexus lesions/damage)








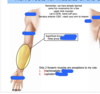

suprascapular nerve roots
C5 C6
If roots C5 and C6 are damaged
supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles are not innervated and cannot laterally move scapula; weak abduction = weakened supraspinatus
thoracodorsal nerve roots
C 678
if thoracodorsal nerve is damaged
decreased innervation of latissimus = decreased rowing climbing and pushing up out of a chair; decreased extension, adduction, and medially rotating arm
axillary nerve roots
C5 and C6
axillary nerve innervates
nInnervates the deltoid and teres minor
if the axillary nerve is damaged
decreaed abduction and loss of rounded contour of deltoid region; weakened lateral rotation of arm (teres minor); Loss of sensation to lateral aspect of arm/shoulder region
axillary nerve damage can be common in
Can occur in surgical neck fractures of the humerus and shoulder dislocations
muscolocutaneous nerve innervates and roots
innervates anterior portion of the forearm
C5 C6 and C7
if the muscoloctaneous nerve is damaged
- weakened flexion of the arm
- weakened suppination of the arm
- sensory loss to the lateral portion of the arm
Brachial plexus lesions affect the ____ rami of several spinal nerves and therefore affect
ventral; motor and sensory
1.Upper brachial plexus injuries… caused by lesions of ___ ventral rami
C5 & C6
Lower brachial plexus injuries… caused by lesions of ___ ventral rami (sometimes C7)
C8 & T1
nUpper brachial plexus injuries typically occur due to excessive ______
lateral stretching between the head & shoulder (motorcycle, equestrian, football injuries- “stinger”); Obstetrical trauma can also injure these roots
Erb’s palsy can also causes a _____ fingers and wrist curl into flexion
“waiters tip hand”
Klumpskys are devastating injuries as they _____ of the hand causing muscle imbalances between the digital flexors and extensors; aka ____ hand and can also lead to horners disease
paralyze the short intrinsic muscles; claw hand
high median nerve damage results in
hand of benediction
1.Weakness/paralysis of many of the anterior forearm muscles
2.Atrophy of thenar muscles (loss of opposition)
3.Sensory deficits in 3½ fingers
4.When these patients attempt to make a “fist”….cannot flex the thumb, 2nd or 3rd digits due to loss of flexion power (FPL, FDS & ½ FDP) – referred to as the Hand of Benediction
____ nerve damage can result in “ape-hand” appearance
median nerve
Sensory testing area for ____ nerve is between the thumb and index finger on dorsum of the hand
radial
nCommon clinical sign is wrist drop- inability to extend wrist or fingers
radial nerve damage
_____ lesions affect most of the intrinsic hand muscles resulting a thin weakened hand (loss of interossei)
Hence, difficulty performing fine motor tasks, open doors, jars….
Ulnar nerve
When these patients attempt to make a “fist”…4th & 5th digits cannot flex properly due to the loss of ____ portion of the FDP and associated lumbricals… resulting in a “claw hand”
ulnar


