Vertebral Canal & Spinal Cord Flashcards
Within an isolated vertebra- the body, pedicles, and laminae form the
vertebral foramen
Stacking successive vertebrae foramen together creates the ______ throughout the length of the vertebral column
vertebral canal
Vertebral canal houses and protects the _____ and ______
spinal cord and the meninges (spinal membranes)
In the adult… the cord extends from the base of the skull to
~ L2 vertebral level (sometimes L1)
Spinal cord only occupies the superior 2/3rds of the vertebral canal
In the embryo, the spinal cord occupies ______ of the vertebral column (fig A)
the entire length; This allows the spinal nerves to pass through their associated intervertebral foramen at their level of origin
As a result of this disproportionate growth- the _____ nerve roots must grow the longest
lumbar & sacral/coccygeal
As a result of this disproportionate growth- the lumbar & sacral/coccygeal nerve roots must grow the longest
They descend until they reach their corresponding intervertebral foramen
This collection of nerve roots is referred to as the ______
cauda equina (horse’s tail)
Surrounding the spinal cord and extending from the base of the skull to S2 vertebral level is the _____… a tough protective covering formed by the dura mater
dural sac
_______ extends from the medullary cone to the tip of the dural sac
Internal filum terminale
Spinal cord has two enlargements that provide additional neurons for innervation to the limbs
- Cervical enlargement-innervates the upper limbs
- Lumbosacral enlargement–innervates the lower limbs
there is/isnt a difference between vertebral column levels and spinal cord levels
there is
















It also important to consider the cervical nerves…
There are 8 cervical nerves but only 7 cervical vertebrae
______ exit the vertebral canal superior to vertebra of the same number (i.e. C4 spinal nerve exits between C3 and C4 vertebrae)
_____ exits below the C7 vertebra (i.e. between C7 and T1 vertebrae)
Cervical nerves C1-C7 ; C8 spinal nerve
_____ contains Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) which helps protect the spinal cord and nerve roots
This subarachnoid space
The subarachnoid space is _____ with the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain
continuous
______ is the thin innermost membrane which firmly adheres to the surface of the spinal cord
Pia mater
_____ are lateral extension of pia mater between the dorsal & ventral roots which help to anchor the cord laterally
n
Denticulate ligaments
Between the vertebral canal and dura mater is the ______
epidural space
This epidural space contains ______ and the _____
adipose (fat) tissue; internal (epidural) venous plexus;
Blood supply to the spinal cord is derived from both ______ and ________ components
Both components are necessary to insure adequate blood supply to the cord
vertical (longitudinal) and horizontal (segmental)
These vertical or longitudinal arteries include:
- ________ which arises from the vertebral arteries
- _______ which arise from the vertebral arteries (or the posterior cerebellar artery)
a single anterior spinal artery; Paired posterior spinal arteries
______ are irregularly spaced vessels that communicate (anastomosis) with the longitudinal spinal arteries
Segmental or horizontal arteries
The largest of these segmental vessels is the ______
great anterior segmental artery or “artery of Adamkiewicz”
Venous blood from the spinal cord drains into the anterior and posterior _____ which course along the surface of the cord
spinal veins
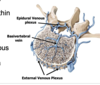
Spinal veins ultimately drain into the within the vertebral canal
internal or epidural venous plexus
The internal or epidural venous plexus connects with the external venous plexus via _____
large basivertebral veins (which drain the vertebrae)
Vertebral Venous Plexuses
These interconnecting vertebral venous plexuses (VVP) run along the length of the vertebral column AND typically have very few valves (if any)…allowing blood to flow unimpeded up and/or down the vertebral column
These interconnecting VVP (Batson’s plexus) have direct venous connections with veins in the pelvis and veins along the posterior thoracic wall
In addition, these VVP communicate with veins inside the cranial cavity (i.e. surrounding the brain) called dural venous sinuses (learn about those later)
These anatomical connections may account for the fact that cancer cells from the prostate (commonly) and breast and lung (less commonly) can sequester in these venous channels resulting in vertebral column bone cancer…or travel into the cranial cavity resulting in metastatic brain cancer
Spinal tap is performed to obtain a sample of _____; explain the process with ligaments
CSF
Lower lumbar region (L3, L4 or L5) is ideal access site to the subarachnoid space (CSF) because the spinal cord terminates at about L2
nPatients lie with vertebral column flexed which spreads the lamina and spinous process apart
nNeedle is inserted through the:
- Supraspinous ligament
- Interspinous ligament
- Ligamentum flavum and finally the dura/arachnoid membranes into the subarachnoid space where CSF can be aspirated
____ unites the anterior surfaces of the bodies of the vertebrae
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)
____ unites the posterior surface of the bodies of vertebrae- thus located inside the vertebral canal
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)
The posterior and anterior longitudinal ligaments are closely associated with the intervertebral (IV) discs…and provide ____
support/strength for the discs

Posterolateral Herniation

Posterior Herniation
A posterolateral disc herniation between L4 & L5 vertebral level usually affects _____
L5 spinal nerve roots…
termination of the spinal cord ~ L1/L2 vertebral column level
Conus Medullaris
dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar & sacral spinal nerves
Cauda Equina (horse’s tail)
Spinal cord is vascularized by longitudinal arteries that arise mainly from the _____ and _____ that enter the vertebral column via the IV foramen
vertebral arteries; segmental medullary arteries
____ may account for the spread of cancer cells (prostate, breast) within the vertebral column/brain
Vertebral venous plexus (Batson’s)
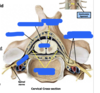














Needle is inserted through what layers for spinal tap?
- Skin
- Supraspinous ligament
- Interspinous ligament
- Ligamentum flavum
- Epidural Space
- Finally through the dura & arachnoid membranes into the subarachnoid space where CSF can be aspirated
Lets return to Walter…now a 48 year-old man that suffered a previous whiplash injury. He visits his physician assistant 3 year after his whiplash injury and complains of recent onset pain/discomfort in his neck and tingling/ numbness in his right shoulder and arm. His physician assistant suspects he might have developed a herniated disc due to the auto accident. MRI scan reveals a posterolateral prolapsed disc between C5 and C6.
Which nerve roots are likely to be affected?
C6
Protrusion of nucleus pulposus generally occurs ____ … where the anulus is thin and poorly supported by the posterior longitudinal ligament
posterolaterally


