Vertebral column Flashcards
Label this diagram using:
- Vertebral body
- Vertebral (Neural) Arch
- Processes:
- Spinous
- Transverse
- Articular
- Mammillary
- Accessory


How many of the following vertebrae types are there in dogs and horses?
- Cervical
- Thoracic
- Lumbar
- Sacral
- Cauda
Cervical
- 7 common to all mammals (ex manatee, sloths)
Thoracic
- 13 in dogs; 18 horses
Lumbar
- 7 in dogs; 6 in horses
Sacral
- 3 fused vertebrae in dogs; 5 in horses
Caudal
- About 20 in dogs and horses
Complete the following:
Vertebral Body
- Overall shape: [flat/cylindrical/conical/spherical]
- [Convex/concave] cranially
- [Convex/concave] caudally
- Dorsally [flattened/convex/conical]
Vertebral Body
- Overall shape: Cylindrical
- Convex cranially
- Concave caudally
- Dorsally flattened
The vertebral arch forms circle of bone around the ____ _____ through which the _____ cord passes. The vertebral foramen is composed of the vertebral ____ at its base, and the arch comprises the ______ that form walls, and a ‘roof’ dorsally where two _____ join.
The vertebral arch forms circle of bone around the vertebral foramen through which the spinal cord passes. The vertebral foramen is composed of the vertebral body at its base, and the arch comprises the pedicles that form walls, and a roof dorsally where two laminae join.
When vertebrae are linked together, the vertebral foramina form the ______ _____ through which the spinal cord runs. Also when vertebrae are linked, a shallow ____ notch and a deeper ______ notch on each vertebra together form _________ foramina, through which spinal nerves exit.
When vertebrae are linked together, the vertebral foramina form the vertebral canal through which the spinal cord runs. Also when vertebrae are linked, a shallow cranial notch and a deeper caudal notch on each vertebra together form intervertebral foramina, through which spinal nerves exit (see diagram).

Spinous processes are situated _______ between the two ______.
Transverse processes are each situated between the _____ and the ______.
The the articular processes are located somewhat _____ on the arch, at the junction of pedicle and lamina. There are two of these on each side of the vertebra: a ______ pair whose articulating surfaces point dorsally or medially and a _______ pair whose surfaces are directed ventrally or laterally.
Spinous processes are situated dorsally between the two laminae.
Transverse processes are each situated between the pedicle and the lamina.
The the articular processes are located somewhat dorsally on the arch, at the junction of pedicle and lamina. There are two of these on each side of the vertebra: a cranial pair whose articulating surfaces point dorsally or medially and a caudal pair whose surfaces are directed ventrally or laterally (see diagram).

The _______ process projects caudally from the pedicle ventral to the caudal articular process and over the dorsal aspect of the intervertebral foramen. It is present from the mid_____ region to the fifth or sixth _______ vertebra.
The _______ process is a knoblike dorsal
projection of the transverse processes of the second through tenth _______ vertebrae and cranial articular processes of the eleventh _____ through the _____ vertebrae. ______ muscles of the transversospinalis system attach to these processes.
Label the following diagram:

The accessory process projects caudally from the pedicle ventral to the caudal articular process and over the dorsal aspect of the intervertebral foramen. It is present from the midthoracic region to the fifth or sixth lumbar vertebra.
The mamillary process is a knoblike dorsal
projection of the transverse processes of the second through tenth thoracic vertebrae and cranial articular processes of the eleventh thoracic through the caudal vertebrae. Epaxial muscles of the transversospinalis system attach to these processes.

What are intervertebral discs made of?
Fibrocartilage
The joint between cranial and caudal articular facets on the vertebrae is a [fibrous/cartilaginous/synovial] joint.
The joint between cranial and caudal articular facets on the vertebrae is a synovial joint.
Intervertebral discs form (fibro)cartilaginous joints between vertebrae, a joint type known as a [symphysis/synchrondrosis] ([synarthrosis/amphiarthrosis/diarthrosis]).
Intervertebral discs form (fibro)cartilaginous joints between vertebrae, a joint type known as a symphysis (amphiarthrosis).
In an intervertebral disc, the tough outer fibrous connective tissue forms the _____ _____, while the core of gelatinous material is known as the ______ ________.
In an intervertebral disc, the tough outer fibrous connective tissue forms the annulus fibrosus, while the core of gelatinous material is known as the nucleus pulposus.
The defining feature of cervical vertebrae is the _______ foramen, though this is absent in __. C1 and C2 are specialised to form the ____ (C1) and ____ (C2).
The defining feature of cervical vertebrae is the transverse foramen, though this is absent in C7. C1 and C2 are specialised to form the atlas (C1) and axis (C2).
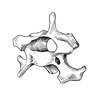
The atlas has an articular surface for the ____ _____ of the skull. This forms the _______ joint, and its movements are _____ and _______.
Note these on diagram (craniolateral view).

The atlas has an articular surface for the occipital condyles of the skull. This forms the atlantooccipital joint, and its movements are flexion and extension.

The atlas (C1) has an articular surface for C2 (the ____). This articulation forms the _______ joint and its movement is _________.
See diagram (caudal view).

The atlas (C1) has an articular surface for C2 (the axis). This articulation forms the atlantoaxial joint and its movement is rotation.

The transverse processes of the atlas (_____) are explanded to form ______. The spinous process is _______. The vertebral foramen is _______ to accommodate the axis and the brain stem. The _______ foramina run through the wing in an oblique direction, and _______ foramina are present in the craniodorsal aspect.
See diagram of atlas (caudal aspect)

The transverse processes of the atlas (C1) are explanded to form wings. The spinous process is absent. The vertebral foramen is large to accommodate the axis and the brain stem. The transverse foramina run through the wing in an oblique direction, and lateral foramina are present in the craniodorsal aspect.
Name the process on the axis (C2) highlighted in the diagram. What joint does it form part of? What are its differences between the carnivores (top = horse) and herbivores (bottom = lion)?

Odontoid process
- Atlantoaxial joint with atlas (C1)
- Peg‐like in carnivores, humans
- Broad platform in herbivores

The atlantoaxial joint is a synovial [pivot/hinge/gliding] joint and its action is _______.

The atlantoaxial joint is a synovial pivot joint and its action is rotation.
One defining feature of thoracic vertebrae is that they have ____ _____ (surfaces for attachment of the ribs). Label these on the following diagram.

One defining feature of thoracic vertebrae is that they have costal foveae (surfaces for attachment of the ribs; singular = costal fovea).
The first through the tenth thoracic vertebrae have a cranial and a caudal costal fovea on each side for rib articulation. The body of the tenth vertebra frequently lacks caudal foveae, whereas the eleventh through the thirteenth have only one complete cranial costal fovea on each side. The head of the first rib articulates between the last cervical and first thoracic vertebrae. The tubercles of the ribs articulate with the transverse processes of the thoracic vertebrae of the same number in all instances.

The spinous processes on thoracic vertebrate __ - ____ are large, and become shorter from ____ - ____. They are inclined caudally up to this point, but the spinous process of ___ is vertical, and ___ - ___ are inclined cranially.
The spinous processes on thoracic vertebrate T1 - T8 are large, and become shorter from T9 - T10. They are inclined caudally up to this point, but the spinous process of T11 is vertical, and T12 - T13 are inclined cranially.
The bodies of the lumbar vertebrae are ____ than those of the thoracic, and the vertebral canal is ______. The spinous processes are well developed, rectangular, narrowing somewhat dorsally, and slope ______. The transverse processes are large and directed ____ in carnivores but more _____ in herbivores. The mamillary and accessory processes are well developed.

The bodies of the lumbar vertebrae are longer than those of the thorassic, and the vertebral canal is flattened. The spinous processes are well developed, rectangular, narrowing somewhat dorsally, and slope cranially. The transverse processes are large and directed cranially in carnivores but more laterally in herbivores. The mamillary and accessory processes are well developed.

How many bones form the fused complex called the sactum?
Three: S1 - S3
The ___ _____ ____on the dorsal surface of the sacrum represents the fusion of the three spinous processes.
The median sacral crest on the dorsal surface of the sacrum represents the fusion of the three spinous processes.
The dorsal surface of the sacrum also bears two pairs of____ _____ ____, which transmit the dorsal branches of the first two sacral spinal nerves.
The pelvic (ventral) surface has two pairs of ____ ____ _____. They transmit the ventral branches of the first two sacral spinal nerves.

The dorsal surface of the sacrum also bears two pairs of dorsal sacral foramina, which transmit the dorsal branches of the first two sacral spinal nerves.
The pelvic (ventral) surface has two pairs of pelvic sacral foramina. They transmit the ventral branches of the first two sacral spinal nerves.

In the sacrum, the ___ ____ is continuous with the vertebral canal. It is large [cranially/caudally] and narrows [cranially/caudally].
In the sacrum, the sacral canal is continuous with the vertebral canal. It is large cranially and narrows caudally.
What is the name of the large rough surface on the enlarged lateral part of the wing od the sacrum that articulates with the ilium?
The auricular face
Caudal (Coccygeal) Vertebra are varied in size and shape, becoming rod-like distally. The ____ _____ (top left diagram on Ca4 Ca5 Ca6) provide protection for median coccygeal vein.

Caudal (Coccygeal) Vertebra are varied in size and shape, becoming rod-like distally. The haemal arches (top left diagram on Ca4 Ca5 Ca6) provide protection for median coccygeal vein.

In the vertebral column:
____ ligaments
- Connect adjacent vertebrae
_____ ligaments
- Pass over several vertebrae
Label the ligaments in the following diagram.
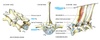
Short ligaments
- Connect adjacent vertebrae
Long ligaments
- Pass over several vertebrae

Label the following diagram with the ligaments found at C1 and C1 (atlas and axis)




