Muscles and tendons thoracic limb Flashcards
The Synsarcotic Suspensory Apparatus is also known as the pectoral girdle or ______ _______. This unites of parts of skeleton by muscles.
Muscular sling

What five muscles are involved in the muscular sling?
strop
- serratus ventralis
- trapezius
- rhomboideus
- omotransversarius
- pectoralis profundis
What muscle is this?

Trapezius (cervical part)
What muscle is this?

Trapezius (thoracic part)
Describe the origin and insertion of the trapezius (cervical part).

Origin
- Cervical vertebra 3 to thoracic vertebra 2, median tendinous raphe and supraspinous ligament
Insertion
- Spine of scapula including acromion
Describe the origin and insertion of the trapezius (thoracic part)

Origin
- Supraspinous ligament and transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae 3 to 9
Insertion
- Proximal third of the spine of the scapula into an Aponeurosis
What is the main action of the trapezius muscle?
Elevates and protracts (advances) the limb. Stabilises the shoulder joint. Assists in abduction of the limb.
What is this muscle (2 parts)?

Rhomboideus (cervicis and capitis)
What is the origin and insertion of the rhomboideus (cervicus)?

Rhomboideus cervicus
Origin
- tendinous raphe and spinous processes of cervical vertebra 2 to thoracic vertebra 3
Insertion
- medial aspect of dorsal margin of scapula near cranial angle
What is the origin and insertion of the rhomboideus capitis?

Origin
- cranial to cervical vertebrae 4
Insertion
- occiput of skull
Describe the origin and insertion of Rhomboideus thoracis

Origin
- spinous process of thoracic vertebrae 4 to 7
Insertion
- medial aspect of dorsal margin of the scapula
What is the action of the rhomboideus muscle?
- Elevates the thoracic limb.
- Pulls the limb and cranially (advance) and caudally (retract).
- Adducts the scapula.
- When the shoulder is fixed (i.e. weight-bearing) it can raise the neck.
- Transmits movement from forelimb to neck participating in walking and nodding movements of the head.
What are the two parts of the serratus ventralis muscle?
Cervical and thoracic parts
What is the name of this muscle?

Serratus ventralis
Describe the origin and insertion of the cervical part of the serratus ventralis.

Origin
- Transverse processes of cervical vertebrae 3 to 7
Insertion
- Facies serrata of scapula
describe the origin and insertion of the thoracic part of the serratus ventralis.

Origin
- ribs 1-8
Insertion
- Facies serrata of scapula
What is the action of the serratus ventralis?

- Forms the most important component of the muscular sling of the trunk. At a fast gait and when jumping, acts like a trampoline, cushioning the trunk as it is launched forwards.
- When the limbs are fixed the cervical part (working bilaterally) raises the neck while the thoracic part elevates and protracts (advances) the trunk cranially.
- Protracts and retracts the scapula when working independently
What is the name of this muscle?

Omotransversarius
What are the origin and insertion of the omotransversarius muscle?

Origin
- Acromion of the scapula
Insertion
- Wing of the atlas (cervical vertebra 1)
What is the action of the omotransversarius?
To pull the free limb cranially (advancement of
the limb)
In the trapezius muscle of the pig
- The origin is the _______ bone of the skull to thoracic vertebra 10
- ______ and _______ parts are not distinguishable from each other

In the trapezius muscle of the pig
- The origin is the occipital bone of the skull to thoracic vertebra 10
- Cervical and thoracic parts are not distinguishable from each other
In the the rhomboideus of the horse and ruminant:
- the ______ part is very powerful
- ______ part is absent

In the the rhomboideus of the large ruminant (horse and cattle):
- the cervical part is very powerful
- Capitis part is absent
The serratus ventralis of the horse and ruminant:
- Inserts into _____ distinct areas on the scapula
- Is an important muscle in _____ ____ acting as a trampoline to cushion the trunk.
- When limbs are fixed to ground the thoracic part is powerful (especially in horses) and enables the elevation of the trunk and therefore _______ using hind limbs

The serratus ventralis of the horse and ruminant:
- Inserts into two distinct areas on the scapula
- Is an important muscle in muscular sling acting as a trampoline to cushion the trunk.
- When limbs are fixed to ground the thoracic part is powerful (especially in horses) and enables the elevation of the trunk and therefore kicking using hind limbs
What is the name of this muscle?

Brachiocephalicus
What are the names of the three muscles/parts that make up the brachiocephalicus?

- cleidocervicalus (or the cervical part of the cleidocephalicus in the dog)
- cleidomastoideus (or the mastoid part of the cleidocephalicus in the dog)
- Cleidobrachialis
What is the common origin of all parts of the brachiocephalicus?
Clavicular tendon
What is the origin and insertion of the cleidocervicalis part of the brachiocephalicus muscle? What is this known as in the dog?
Cleidocervicalis
- Origin
- clavicular tendon
- Insertion
- dorsal fibrous raphe of the cranial half of the neck
= Cleidocephalicus (Dog)
- Cervical part
What is the origin and insertion of the cleidomastoideus part of the brachiocephalicus? What is it known as in the dog?

Cleidomastoideus
Origin
- clavicular tendon
Insertion
- mastoid process of temporal bone
= Cleidocephalicus (Dog)
- Mastoid part
What is the origin and insertion of the cleidobrachialis part of the brachiocephalicus muscle?

Cleidobrachialis
Origin
- clavicular tendon
Insertion
- Distally on the cranial aspect of the humerus between biceps brachii and brachialis
What is the action of the brachiocephalicus muscle?

Action:
- Advances (protracts) the limb
- Fixes the neck (bilateral action)

What are the two parts of the pectoralis superficialis? What are their origins and insertions?

Pectoralis superficialis:
Pectoralis descendens
- Origin
- Manubrium of Sternum
- Insertion
- Greater tubercle crest of humerus
Pectoralis transversus
- Origin
- Sternum (first 2 or 3 elements)
- Insertion
- Greater tubercle crest of humerus

What is the action of the pectoralis superficialis muscle?

Adduction of the limb; supports the limb; depending on position can move limb cranially or caudally; it can also move trunk laterally during weight bearing
What is the name of this muscle?

Pectoralis profundis
What is the origin and insertion of the pectoralis profundis?

Origin
- Sternum incl. xiphoid process
Insertion
- Lesser tubercle of humerus, mid shaft humerus, via aponeurosis to greater tubercle
What is the action of the pectoralis profundis?
- Supports the trunk as part of the muscular sling
- When running can move the trunk cranially over the advanced (protracted) fixed limb and extend the shoulder joint
- Retraction of the limb and flexion at the shoulder joint when running
What muscle is this? What are its origin and insertions?

Latissimus dorsi
Origin
- thoracolumbar fascia, spinous processes of lumbar vertebrae 7 to 1 and thoracic vertebrae 13 to 5
Insertion
- Via an aponeurosis onto teres major tuberosity along with the teres major muscle; crest of the greater tubercle via deep branch to pectoral muscles
What is the action of latissimus dorsi?
Flexion of the shoulder joint; draws the free limb caudally, especially when digging
Pectoralis profundis: comparative
Pig
- Fan-shaped. Origin is from 3rd to 9th costal cartilages and _____, narrow and thicker from 3rd rib onwards. Inserts via tendon to _____ tubercle of humerus.
Ox and Horse
- Broad and powerful. Origin is from _____ and most costal cartilages (less in horse 5-9). Partly originates from tunica flava of abdomen. Inserts onto _____ and _____ tubercles of humerus.

Pectoralis profundis: comparative
Pig
- Fan-shaped. Origin is from 3rd to 9th costal cartilages and sternum, narrow and thicker from 3rd rib onwards. Inserts via tendon to lesser tubercle of humerus.
Ox and Horse
- Broad and powerful. Origin is from sternum and most costal cartilages (less in horse 5-9). Partly originates from tunica flava of abdomen. Inserts onto lesser and greater tubercles of humerus.
What is this muscle? What animals is it found in?

Subclavius; pig, bovine, horse
Pig: Origin from Manubrium, 1st rib and associated costal cartilage. Insertso onto cranial border of scapula and sends a slip to brachiocephalic
muscle.
Ox: Poorly developed. Slim and extends from 1st costal cartilage to the clavicular tendon.
Horse: Well developed. Origin is lateral aspect of sternum from 1st to 4th costal cartilage. Inserts onto the cranial border of supraspinatus muscle. Also runs over tendon of Biceps brachii to insert onto the greater tubercle of the humerus. Muscle is visible under skin.
What is this joint called? What sort of joint is it

Glenohumeral Joint
Spheroidal ball and socket (but functions as a hinge joint)
What muscles stabilise the shoulder joint?

- Infraspinatus
- Supraspinatus
- Subscapularis
The tendon of the bicept brachii is __________ in the shoulder joint of the ruminant and horse, and cushioned by intertubercular ____. The shape of their ________ ________ further restricts medial and lateral movement.

The tendon of the bicept brachii is extracapsular in the shoulder joint of the ruminant and horse, and cushioned by intertubercular bursae. The shape of their humeral head further restricts medial and lateral movement.
What is the name, origin, and insertion of this muscle.

Supraspinatus.
Origin
- Supraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion
- Proximomedial aspect of greater tubercle of humerus
What is the action of supraspinatus?

- Extension of Shoulder Joint
- Fixes and stabilises joint during weight bearing
What is the name, origin, and insertion of this muscle?

Infraspinatus.
Origin
- Infraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion
- Distal aspect of greater tubercle of humerus; joint capsule of shoulder
What is athe action of the infraspinatus muscle?

- Flexion of the shoulder joint
- Extension of the shoulder joint (under certain positions)
- Abduction of the Humerus (non weight-bearing)
- Lateral rotation of Humerus (non weight-bearing)
- Stabilises and fixes the Joint by acting as a lateral collateral ligament
What is the name (both parts), origin, and insertion of this muscle? What is it’s action at the shoulder joint?

deltoideus: scapular part, acromial part
Scapular part
Origin
- Spine of scapula via the aponeurosis
Acromial part
Origin
- Acromion
Insertion
- Deltoid tuberosity
Action:
- Flexion and Abduction of the humerus at the shoulder joint
What is the name, origin, and insertion of this muscle?
What is its action at the shoulder joint?

Teres minor
Origin
- Infraglenoid tubercle, distal third of caudal margin of scapula
Insertion
- Crest of greater tubercle of humerus/tricipital line
Action
- Flexion of the humerus at the shoulder joint
What is the name of this muscle (medial)? What are its origin, insertion, and action?

Subscapularis
Origin
- Subscapular fossa
Insertion
- Lesser tubercle of the humerus, joint capsule of the shoulder joint
Action
- Extension and Adduction at the shoulder joint
- Stabilises the joint by acting as the medial collateral ligament

What is the name of this muscle?
What are its origin, insertion, and action?

Teres major
Origin
- Caudal angle and caudal margin of scapula
Insertion
- Teres tuberosity
Action
- Flexion at the shoulder joint

What is the name of this muscle?
What are its origin, insertion, and action?

Coracobrachialis
Origin
- Coracoid process of scapula
Insertion
- Craniomedial surface of humerus ending on the crest of the lesser tubercle
Action
- Extension and Adduction at the shoulder joint
The supraspinatus of the cow inserts via a _______ tendon onto the _____ and lesser _____ of the humerus. _____ _____ tendon passes between these two tendons of insertion

The supraspinatus of the cow inserts via a branched tendon onto the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus. Biceps brachii tendon passes between these two tendons of insertion
The supraspinatus of the horse:
- very powerful,
- covered with _________,
- bulges considerably beyond ________ margin of scapula and spine of scapula
- Flat at origin becoming _________ distally dividing into two above the supraglenoid tubercle. Insert onto _____ and _____ tubercles with tendon of Biceps brachii running through between them.

The supraspinatus of the horse:
- very powerful,
- covered with aponeurosis,
- bulges considerably beyond cranial margin of scapula and spine of scapula
- Flat at origin becoming thicker distally dividing into two above the supraglenoid tubercle. Insert onto greater and lesser tubercles with tendon of Biceps brachii running through between them.
The deltoideus:
CAT
- ______ part ill-defined; _____ part powerful
PIG and HORESE
- Fused into a _____ muscle
The deltoideus:
CAT
- Scapular part ill-defined; acromial part powerful
PIG
- Fused into a single muscle
What is the name of this muscle?

Biceps brachii
Diagram: left medial thoracic limb muscles

What is the origin and insertion of biceps brachii?
What is its action?

Origin
- Supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
Insertion
- –Ulnar tuberosity
- Radial tuberosity
- Antebrachial fascia
Action
- Flexion of the Elbow Joint
- Extension of the Shoulder Joint

What is the name, origin, insertion, and action of this muscle at the elbow joint?

Brachialis
Origin
- Proximocaudal aspect of the humerus
Insertion
- Ulnar tuberosity
- Tendon of Biceps brachii
Action
- Flexion of the Elbow Joint

What are the names and origins of the four heads of the triceps brachii?
What is their common insertion?

Triceps brachii
Long head
Origin
- Distal 2/3rd of caudal border of scapula
- Infraglenoid tubercle (tendinous)
Lateral head
Origin
- Greater tubercle crest and Tricipital line
Medial head
Origin
- Lesser tubercle crest
Accessory head
Origin
- Caudal aspect of humerus distal to head
Common insertion
• Common tendon of insertion at olecranon of ulna

What is this muscle? What is its origin and insertion? What is its action at the elbow joint?

Anconeus.
Origin
- Lateral supracondylar crest, lateral epicondyle, medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion
- Proximolateral aspect of the olecranon of the ulna
Action
- extends the elbow

What is this muscle? What is its origin and insertion? What is its action at the elbow joint?

Tensor Fasciae Antebrachii
Origin
- Lateral surface of Latissimus dorsi
Insertion
- Common insertion with Triceps brachii (oleacranon), antebrachial fascia
Action
- Extends the elbow

What are the names, origins and insertions of the two pronators that cross the proximoradioulnar joint?

Pronator teres
Origin
- Medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion
- Proximomedial surface of radius
Pronator quadratus
Origin
- Medial surface of ulna
Insertion
- Caudal surface of radius
- Covers interosseous membrane (& ligament)

What is the origin, insertion, and action of the supinator that crosses the proximal radioulnar joint?
In the cat the supinator is _____ developed and ____ than in the dog.

Origin
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus and lateral collateral ligament
- Sesamoid bone in tendon of origin
Insertion
- Proximal 1/4th of radius, cranial aspect ending on the medial border
Action
- Supinate the forearm
In the cat the supinator is better developed and stronger than in the dog.

What is this muscle? What is its origin and insertion? What is its action?

Brachioradialis
Origin
- Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
Insertion
- Distal 1/3rd of radius
Action
- Supinate forearm
What is the name, origin, and insertion of this muscle? What is its action?

Flexor carpi radialis
Origin
- Medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion
- Base of Metacarpals II and III (palmar aspect); enclosed in tendon sheath
Flex the carpus
What is the name, origin (x2), and insertion of this muscle? What is its action?

**Flexor carpi ulnaris** Ulnar head (superficial)
- Origin: caudomedial aspect of olecranon
- Insertion: Accessory carpal bone
Humeral head (deep)
- Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
- Insertion: Accessory carpal bone
What is the name, origin, and insertion of this muscle? What is its action?

Extensor carpi radialis
Origin
- Lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
Insertion
- Dorsal aspect of the base of Metacarpals II & III
Action
- Extension of the carpus
What is the name, origin, and insertion of this muscle? What is its action?

Ulnaris lateralis (Extensor carpi ulnaris) Origin
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion
- Accessory carpal bone and proximolateral on metacarpal V
Action
- Flexion of the carpus
Comparative Aspects: Flexor carpi radialis (see diagram of medial view horse lower limb)
RUMINANT
- Long tendon enclosed in a tendon sheath, inserting onto palmar aspect of ______ __
HORSE
- Slim, spindle shaped; enclosed in a tendon sheath; inserts onto ______ __ (medial splint bone)

Comparative Aspects: Flexor carpi radialis
RUMINANT
- Long tendon enclosed in a tendon sheath, inserting onto palmar aspect of metacarpal III
HORSE
- Slim, spindle shaped; enclosed in a tendon sheath; inserts onto metacarpal II (medial splint bone)
Comparative Aspects: Flexor carpi ulnaris
RUMINANT
- Weak ____ head (tendinous in smaller ruminants)
- Flat and broad in appearance
HORSE
- _____ head weak and tendinous
- Broad, flattened muscle heavily permeated by tendons
- Short strong terminal tendon that blend with _____ ________ to insert on accessory carpal bone

Comparative Aspects: Flexor carpi ulnaris
RUMINANT
- Weak ulnar head (tendinous in smaller ruminants)
- Flat and broad in appearance
HORSE
- Ulnar head weak and tendinous
- Broad, flattened muscle heavily permeated by tendons
- Short strong terminal tendon that blend with flexor retinaculum to insert on accessory carpal bone
What muscle is this? What are its origins (x3), insertion, and action?

Flexor digitorum profundus (Deep Digital Flexor)
Humeral head
- Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus
Ulnar head
- Origin: Distal 1/4th of caudal border of ulna
Radial head
- Origin: Proximal 3/5th of medial border of radius
Insertion
- Flexor protuberance of the distal phalanx of digits II to V
Action
- Flexion of the carpus, metacarpophalangeal, proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints

What is the tendon highlighted in red? What is happening in this diagram?

Tendon of the deep digital flexor in red. Superficial digital flexor splits to allow deep flexor to pass through
What is this muscle called? What is its origin, insertion, and action?

Extensor digitorum communis (Common digital extensor)
Origin
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion
- Dorsal aspect of distal phalanx of digits II-V
Action
- Extension of the carpus, metacarpophalangeal, proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints

What is this muscle called? What is its origin, insertion, and action?

Extensor digitorum lateralis (Lateral digital extensor)
Origin
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus
- Cranial margin of the lateral collateral ligament
Insertion
- Two tendons share a common synovial sheath
- Large caudal tendon inserts onto the dorsal aspect of the proximal phalanx of digit V and then unites with the tendon of common digital extensor to finally insert onto distal phalanx
- Smaller cranial tendon branches at the carpus to insert on the dorsal aspect of the proximal phalanx of digits III and IV and then unites with the tendon of common digital extensor to finally insert onto distal phalanx

What is this muscle called? What is its origin, insertion, and action?

Abductor digiti I longus (=Abductor pollicus longus in humans)
Origin
- Lateral surface of radius, ulna and interosseous membrane
Insertion
- Proximomedially on metacarpal I
Action
- Abduction and extension of digit 1; medial deviation of the forepaw

What is the extensor tendon highlighted in red? What is the uncoloured tendon on the lateral side? What is the blue arrow pointing to?

Extensor digitorum communis (Common digital
extensor) (red)
Extensor digitorum lateralis (Lateral digital extensor)
Abductor digiti I longus (blue arrow)

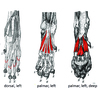
What are these muscles? What are their origins and insertions?

Interosseous Muscles (Palmar) Origin
- Proximal ends of metacarpals II - V
Insertion
- Proximal ends of proximal phalanx after splitting in two