Varicose veins Flashcards
Varicose veins?
Veins that become prominently elongated, dilated and tortuous, most commonly superficial veins of the lower limbs.

Varicose veins primary aetiology?
genetic or developmental weakness in the vein wall, resulting in increased elasticity, dilation and valvular incompetence

Varicose veins secondary aetiology?
venous outflow obstruction (pregnancy, pelvic malignancy, ovarian cysts, ascites, lymphadenopathy, retroperitoneal fibrosis)
due to valve damage or due to high flow.
Varicose veins risk factors (5)?
age,
female,
family history,
Caucasian,
obesity.
Varicose veins epidemiology?
Common, 10% of men, 20% of women.
Varicose veins symptoms?
complain of cosmetic appearance, aching in legs, worse at the end of the day, swelling, itching, bleeding, infection, ulceration.

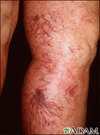
Varicose veins signs (4)?
cough impulse may be felt over the saphenofemoral junction.
Tap test (tapping over the saphenofemoral junction will lead to an impulse felt distally),
Trendelenburg test,
signs of venous insufficiency

Varicose veins Trendelenburg test?
leg is elevated and hand is placed over saphenofemoral junction, the leg is placed back down and filling of the veins is observed before and after hand is released.

Varicose veins investigations?
Duplex ultrasound (locates site of incompetence or reflux)
Varicose veins conservative management (3)?
exercise, elevation of legs at rest, support stockings.
Varicose veins management for telangiectasia and reticular veins?
laser sclerotherapy or micro-injection sclerotherapy.
Varicose veins surgical management (3)?
saphenofemoral ligation,
stripping of the long saphenous vein,
avulsion of varicosities.
Varicose veins complications (4)?
venous pigmentation,
eczema,
lipodermatosclerosis,
venous ulceration


