Vander's GIT Flashcards
(96 cards)
Only substance that can cross the epithelium of the gastric wall
Water
Intake vs output in digestive system
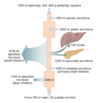
CNS receives info from GIT
Afferent input
CNS has an influence on GIT
Efferent input
Structure of GIT wall
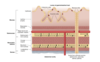
Contraction of circular muscle
Produces a narrowing of the lumen
Contraction of longitudinal muscle
Shortens the tube
Function of Peyer’s Patches and immune cells in SI
Secrete inflammatory mediators (e.g. cytokines) and alter motility
Where do carboxypeptidases come from
The pancreas
Where are aminopeptidases found
On the luminal membranes of epithelial cells
How do free AAs enter the epithelial cells
// Secondary active transport coupled to Na+
How are short chains of 2 or 3 AAs absorbed
By a secondary active transport coupled to H+ gradient
Within the epithelial cell, these di- and tri-peptides are hydrolysed to AAs, which then leave the cell and enter the blood through a facilitated diffusion carrier in the basolateral membranes
Difference between CHO and protein absorption
With CHO absorption, molecules larger than monosaccharides are not absorbed
With protein absorption, short chains of 2/3 AAs are absorbed by a secondary active transport coupled to H+ gradient
How do the SMALL NUMBER of intact proteins cross the intestinal epithelium and gain access to interstitial fluid
Endocytosis & exocytosis
(absorptive capacity for intact proteins is much greater in infants than in adults - antibodies)
Action of lipase
catalyses the splitting of bonds linking FAs to the 1st and 3rd C atoms of glycerol

Action of phospholipids on fat digestion
They are amphipathic molecules consisting of 2 non-polar FA chains attached to glycerol with a charged phosphate grp located on glycerol’s 3rd carbon
EMULSIFYING AGENT
What are bile salts formed from
Cholesterol in the liver - amphipathic
How do we over come the empairment of the accessibility of water-soluble lipase to its substrate
- COLIPASE from pancreas, which is amphipathic, lodges on the lipid droplet surface
- COLIPASE binds the lipase enzyme, holding it on the surface of the lipid droplet
Components of micelles
- Bile salts
- FAs (low solubility in water)
- Monoglycerides (low solubility in water)
- Phospholipids
- During their passage through the epithelial cells, what are FAs and monoglycerides re-synthesised to
- How is a diffusion gradient for these molecules maintained
- What is the function of these packages
- Triglycerides
- This process lowers the conc of cytosolic free FAs and monoglycerides and thus maintains a diffusion gradient for these molecules into the cell
- The re-synthesised fat aggregates into small droplets coated with amphipathic proteins that perform an emulsifying function similar to that of bile salts
How are the fat droplets released into IS fluid
Vesicles containing the droplet pinch off the ER, are processed through the golgi apparatus and eventually fuse with the plasma membrane
These are known as CHYLOMICRONS
Content of chylomicrons
Triglycerides
Other lipids
Where do the chylomicrons pass into
- Chylomicrons released from epithelial cells pass into the lacteal rather than the blood capillaries because the BASEMENT MEMBRANE (an EC glycoprotein layer) at the outer surface of the capillary provides a BARRIER to the diffusion of large chylomicrons
- Lacteals have large, slit like pores between their endothelial cells
- Lymph eventually empties into system veins via thoracic duct
Overview of fat digestion and absorption













