Thyroid gland Flashcards
2 types of thyroid hormone

Thyroxine - T4
Triiodothyronine - T3
- Regulate metabolic rate
- Normal growth and development
- Cretinism associated with abnormal growth of thyroid gland

Function of calcitonin
Control of plasma Ca2+
Structure of thyroid gland
weighs 20g
Goiter => enlarged gland
- Bilobed with thin isthmus
- Highly vascular - 4-6 ml/min/g
Microscopic structure of thyroid gland
Closely packed acini or follicles
WALL
- Single layer of cells
- Columnar - active
- Cuboidal/low columnar - inactive
INTERIOR
- Clear proteinaceous colloid
- Basement membrane
- Mucopolysaccharides
Activity of individual lobules can vary
(photo below - INACTIVE - colloid is large for storage)

I Owe Our Cousin Reimbursement
5 steps in synthesis of thyroid hormones
- Iodide trapping
- Oxidation
- Organification
- Coupling
- Release
Iodide trapping
- Na+ dependent active process
- DIET - Iodide (I-): eggs, seafood, salt - 1mg/week
- Plasma I- = 1-1.5 ug/L
TRAPPING
- Secondary active transport mechanism - Na=/K= ATPase
- Tissue:Plasma [I-]: 20-30:1 // MAX TSH stimulation 200:1

Oxidation
- Iodide to iodine I- + I- => I2
- Catalysed by peroxidase enzymes at cell-colloid interface
- Iodine incorporated into colloid

Thyroglobulin of organification
- Glycoprotein (10% CHO)
- MW 660,000
- 2 identical subunits
- 132 tyrosine residues - 25-30 iodinated
- 6-8 go to form iodo-thyronine
- 3-4 molecules T4 per molecule thyroglobulin
- 1 in 5 thyroglobulin molecules have T3
Organification
- I2 coupled to tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin

Coupling
- Iodinated tyrosine residues
- Coupling of 2 DITs = T4
- Coupling of DIT with MIT = T3

Release
- Pinocytosis
- Exocytosis of colloid via pseudopodia - most recently synthesised first used
- Fuse with lysosomes
- Acid proteases break down thyroglobulin
- Iodide conserved by deiodination of MIT & DIT
- 80 ug of T4 & 4ug T3 (10x more potent) released per day
- Release stimulated // TSH
Total T4 in blood
1 x 10-7 mol/L
Total T3 in blood
2 x 10-9 mol/L
Free circulating T4
0.03% - 3 x 10-11 M
Free circulating T3
10-12 M
- 3 thyroid hormone binding proteins
- where are they degraded
- When are they cleared
- Thyroxin-binding globulin (TBG), Thyroxin binding pre-albumin (TBPA), Albumin
- Liver
- 6-7 days for T4 and 1 day for T3
Hypothalamic Pituitary Thyroid Axis
TRH = Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone
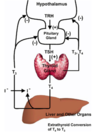
Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone
- Released by
- What does it use as a 2nd messenger
- What does it do
- Where is it degraded
- Tripeptide released by hypothalamus
- Acts using Ca2+ as a 2nd messenger
- Increases secretion of TSH and stimulates prolactin release
- Rapidly degraded in plasma
-ve feedback via T3 & T4
TSH
- Produced by
- Type of protein
- normal plasma conc
- structure
- actions of TSH
- Anterior pituitary
- Glycoprotein - 15% CHO & MW 28000
- 1 x 10-12 M
- 2 peptide chains: alpha = that of LH, FSH, hCG (pregnancy test); specificity lies in beta chain
- Increased iodide uptake
- increased synthesis and secretion of T3 & T4
- increased vascularity & hypertrophy of thyroid gland
Increased basal metabolic rate by thyroid hormone
EUTHYROID
30-40 kCal/m2/hour
HYPERTHYROID
60-65 kCal/m2/hour
HYPOTHYROID
20-25 kCal/m2/hour
Increased O2 consumption/heat production by tissues (as a result of thyroid hormone)
EXCEPT
- Brain
- Spleen
- Testes
- Ovary
Thermogenic effect moderated by:
- Increased blood flow to skin
- Increased sweating
- Increased ventilation
CAUSE
- Increased Na+/K+ dependent ATPase
- Futile metabolic cycles
What are the 3 metabolic effects of thyroid hormones
- Increase muscle protein and fat breakdown
- Increase all aspects of CHO metabolism
- Increase GI motility
Other metabolic effects of thyroid hormones
- Increased HR and contractility
- Increased myosin Ca2+ ATPase gene transcription
- Increased numbers of beta-adrenergic receptors
- Heart
- Skeletal muscle
- Adipose tissue
- Increased sensitivity to catecholamines
- Necessary for normal menstrual cycles
Growth and development - pre-natal effects of thyroid hormones
- Not essential for growth
- Required for reproductive, skeletal and CNS system
- Must be of foetal origin



