Urogenital Anatomy Flashcards
How do primary sexual characteristics develop in males and females?
- all of the primary sexual characteristics (internal and external organs of reproduction) develop from the same starting point in males and females
- all of these organs have homologs in both sexes
- renal and reproductive development are intertwined
Describe development of XX genotype
- cortex (pink) of the indifferent gonad develops
- perimesonephric duct stays attached to it and descends into the pelvis to become the ovary
- mesonephric kidney and mesonephric duct system mainly disappears

Describe the development of the XX genotype with the kidney
- the cortex of the indifferent gonad develops and stays attached to the perimesonephric tube, mesonephric kidney and duct mostly disappear
- develop a metanephric kidney; a branch off of the mesonephric duct connects to the developing metanephric kidney which ascends in the body wall while the gonad descends

What are the homologs between males and females?
- ovary and testes
- clitoris and erectile tissue of corpus cavernosum
- glans of penis is homologous to glans of clitoris
- round ligament and remains of the gubernaculum
- scrotum and labium majora
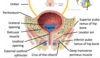
Identify structures

Describe the path of the ureter
- travels along the posterior body wall behind the peritoneum
- ureteropelvic junction is the first narrowing of the ureter
- crosses over the psoas and iliacus muscles and external iliac artery
- ureterovesicular junction is narrowing as the ureter enters the bladder
- kidney can make stones in the pelvis and they get trapped at these points along the path

What occurs if the ureter gets blocked at the ureteropelvic junction?
- hydronephrosis
- build up fluid and pressure back into kidney causing renal pelvis to expand
- influences the ability of the kidney to make urine
What could occur with a blockage of the ureter at the iliacus/psoas muscles and external carotid?
- hydronephrosis and hydroureter
- greatly expanded ureter
- urine is produced so the ureter is expanded

Describe the muscle of the ureter
- longitudinal layer of muscle closest to the lumen of the ureter
- circular layer of smooth muscle on the outside
What function does the mucosal lining of the ureter serve?
- mucus makes it harder for bacteria to adhere to the epithelium
- protects from ascending bacteria/viruses from the bladder infecting the ureter





- sacroiliac is a gliding joint
- sacrococcygeal joint doesn’t move much except in childbirth it moves coccyx out of the way
-

How do the pelvic joints change during gestation?
- in the last 3 months of gestation, the joints relax remarkably
- movement of the SI joint when the woman is in dorsal lithotomy position may increase pelvic diamter 1.5-2cm
- not necessarily the best position to labour in as it compresses blood vessels around pelvis and can compromise venous return

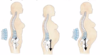
Contrast the gynecoid and android pelvis
- gynecoid is light and thin, android is thick and heavy
- gynecoid has shallow false pelvis (area bound between ischiums and towards pubic symphysis), android has deep cup shaped false pelvis
- gynecoid true pelvis is large and slightly oval pelvic brim, android is small heart shaped pelvic brim
- pubic arch is greater than 90 degrees in gynecoid, android pubic arch is less than 90 degrees
- coccyx angled toward anterior in gynecoid, angled strongly toward anterior in android
- anterior area in male pelvis is much larger which is indicative of its not round shape

What is the antero-posterior and transverse diameter of the gynecoid pelvic inlet?
-10cm

Describe the differences in primate pelvis structure

How do the male and female lumbar spine differ?
-in females, L3,4,5 are all wedge shaped

What benefit does the structure of the lumbar spine provide to females?
- during pregnancy, the curvature of the spine can balance out the centre of mass to what it would be if you were not pregnant
- in non-pregnant state the COM is above the head of the femur
- pregnant abdomen will unbalance the pelvis by moving the COM forward if there is no compensation
- the pregnant abdomen does not alter the COM because of the increase in lumbar lordosis
- “pregnancy walk” can develop later in pregnancy with more mass/inadequate changes in the spine; COM will move forward causing difficult gait

- suspensory ligament of the ovary is really a neurovascular bundle
- uterus is able to move during pregnancy
- cervix has its own attachment and doesn’t need to move during pregnancy


- everything is covered in peritoneum
- comes together where the broad ligament is indicated
- peritoneum provides some support particularly since it folds over the side of the uterus and uterine tubes to make a double thick layer of parietal peritoneum called the broad ligament

What occurs with a prolapsed uterus? How can it be treated?
- uterus descends down the vagina
- puts pressure on the bladder
- females don’t have an internal sphincter so causes urinary incontinence
- if you don’t treat anything, cervix will continue down and come out of vagina
- put in a pessary which will push the uterus back up
- hysterectomy to remove the uterus
- colpopexy: pull uterus up and tie to posterior body wall
- uterine inversion: inverted uterus can happen from pulling on umbilical cord (instead of cervix coming out the uterus will come out inverted)
- uterus is getting a lot of blood but venous return is poor


- labium majora; stratified squamous epithelium
- labium minora; delicate mucous membrane
- inside of vaginal wall have rugae/bumps but these are lost and walls get thinner as you get older
- this uterus is antiverted and retroflexed
- when uterus becomes pregnant, it will become more retroverted and retroflexed


- muscles of the pelvic floor support and maintain the pelvic viscera
- can help with urinary continence and guard to some degree against prolapse