Intersex Flashcards
What are types of sex?
Genetic sex:
XX=female
XY=male
Phenotypic sex:
-appearance
Gonadal sex:
- testes=male
- ovaries=female
Behavioural/psychological:
- how the person self-identifies (gender identity), if the “assigned sex” is different than the gender identity they are transexual
- transexual is a medical/historical term that is more binary, transgender is less binary
- the term “trans” is non-medical
Describe the embryo at 5 weeks
- mesonephric kidney which has mesonephric duct (Wolfiann duct)
- paramesonephric duct
- indifferent gonad (potential ovary on outer surface, potential testis in stroma)
- ducts drain into the cloaca (will divide and become rectum in back and bladder up front) the urogenital sinus

What does the Y chromosome do at 6 weeks?
- presence of active Y chromosome leads to differentiation of the genital tract after about 6 weeks
- the uro part of the urogenital development happens concurrently
How does the Y chromosome create male characteristics
- sex determining region of Y (SRY gene) gives testis determining factor (TDF)
- TDF is essential for generating XY phenotype by stimulating Sertoli cells in gonad which make anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) causing the Mullerian ducts to regress
- paramesonephric (Mullerian) ducts typically form female genital tract
- TDF affects Leydig cells in gonad which make testosterone and androgens which stimulates mesonephric ducts to develop in male
- mesonephric ducts give a lot of male repro tract
- testosterone stimulates secondary male characteristics

Describe the XX embryology
- outer part of indifferent gonad develops into ovary
- paramesonephros occurs and end up with more female phenotype
- paramesonephric ducts give fallopian tubes which fuse with uterus/cervix/vagina
- no anti-Wolffian system/hormone

Describe renal and gonadal development in XY phenotype
- lose paramesonephric duct and mesonephric kidney
- convert indifferent gonad to testes which descends and occurs at same time as the development of metanephric kidney
- kidney ascends to position on posterior body wall
- gonad descends with the mesonephric duct which makes the vas deferens
- pass each other and ureter is underneath vas deferens (water under the bridge)

What is persistent Mullerian duct syndrome?
- if the paramesonephric ducts do not degenerate (usually because of a shortage of MIS) then the testicles can be held up in the abdomen or pelvis
- bilateral cryptorchidism

Describe the descent of the testes
- the descent of the testes into the scrotum must occur through the inguinal canal
- the inguinal canal has a deep ring (opens to the abdomen) and a superficial ring which opens to the scrotum
- the testes will move downwards with gubernaculum
- as testicle gets pulled down it pulls some peritoneum
- happens late in 3rd trimester
- peritoneum must seal off so that bowel material does not enter scrotum





What is the obliterated processus vaginalis? Scrotal cavity?
- results from the inguinal canal
- scrotal cavity is a potential space
- visceral and parietal layer of tunica vaginalis which is lost peritoneum
- epididymis which contains the seminiferous tubules

What is the path of the sperm?
- testis
- epididymis
- vas deferens
What is a hematocoele/hydrocoele?
-fluid or blood filling scrotal cavity

When is orchidopexy required?
- if testes do not descend
- about 4% of male newborns have undescended testis
- this is much higher in premature babies since the inguinal part of the testicular descent is a 3rd trimester occurrence
- usually there will be a period of watchful waiting to see if testis descend by itself
- about 75% will descend in the first year
- abdominal incision
- take the testicle out through abdominal incision (cut away gubernaculum)
- testicle has blood supply and nerve coming with it
- attach suture material to the end of the testis and put the suture material down through the scrotum
- pull on the suture material to pull the testicle into place in the scrotum
- seal off the bottom of the inguinal canal

Why do the male gonads end up outside of the body?
- sperm
- spermatozoa will only develop at temperatures 2-3 degrees below body temperature
- to maintain this temperature the testes will move up and down in an attempt to keep at the proper temperature
- movement upwards is accomplished with the cremaster muscle (striated, extension of interal oblique muscle which comes down as part of wall of inguinal canal)
- dartos muscle compresses the scrotum (smooth muscle, reflexes control it)
- to cool down, relax cremaster and dartos and testicles move away from body
- both are activated to keep testes close to abdomen

Describe the testicular thermostat
- gonadal artery is surrounded by a venous plexus
- warm arterial blood
- venous blood in panpiniform plexus has been in testicle and is returning to body
- the blood in panpiniform plexus has cooled from being outside of body and so it will cool the incoming warm blood
- allows us to have cooler blood to testicle to allow for 2-3 degree difference

What is an inguinal hernia?
- males have almost all of the inguinal hernias (about 25 to 1) and there are close to 100 000 hernia repairs a year in Canada
- inguinal canal had to stay open for gonad to descend which makes a weak point in abdominal wall
- this can allow a part of intestine to push out and through the fascia of the abdomen
- comes into the scrotum
- this is a direct hernia because the hernia came directly through the abdominal wall into the inguinal canal
- normally acquired later in life

When can an indirect inguinal hernia develop?
- early in life and development
- hernia goes through the inguinal canal
- inguinal canal hasn’t closed off and processus vaginalis hasn’t disappeared
- relatively rare
How does external genitalia develop (at 5 week stage)?
- start with the indifferent stage
- genital tubercle with labioscrotal swellings on either side
- urethral folds in middle
- genital tubercle becomes clitoris or penis
- labioscrotal swelling becomes labia majora or scrotum
- urethral folds become labia minora and form part of urethra
- urogenital sinus is open to the bladder

How does external genitalia develop (at 10 weeks)?
- under the influence of androgens (regardless of XX or XY) the urethral folds begin to meet and seal up
- in females without androgen influence, the urethral folds will not seal up
- labioscrotal swellings will swell towards each other
- tip of genital tubercle begins to take on appearance of glans penis
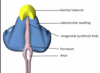
How does external genitalia develop (after 10 weeks)?
- scrotum forms and is divided by midline raphe (where labioscrotal swellings have fused)
- urethra has sealed and now opens at the tip of the penis in the glans and are emptying now at the tip of the glans penis

How does the female external genitalia develop?
- labioscrotal swellings don’t fuse and make the labia majora
- the urogenital folds don’t fuse and stay as labia minora
- urethra opens in the area that the two urogenital folds did not fuse
- genital tubercle becomes clitoris
- with no androgens around, tend to get this pattern

What is intersex (DSD)?
- having both male and female sexual characteristics and organs; at birth an unambiguous assignment of male or female cannot be made
- about 1-2 out of 1000 newborns will end up with some sort of surgery to “correct” ambiguous genitalia
- 4/100 newborns fulfill the broadest definition of intersex (ie. some people may refer to a baby born with bilateral cryptorchidism)
- traditional terms include hermaphroditic or gynandromorphic but are no longer used and may be offensive
- very few gonadal intersex which would mean both male and female gonads (testicles and ovaries)
- greatest number of intersex have undeterminable genitalia at birth




