The Thyroid Gland Flashcards
How much does the thyroid gland weigh?
- 15-20g

Which thyroid hormones does the thyroid gland synthesise that are physiologically active
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Thyroxine (T4)

Which 2 cell types are found in the thyroid gland
- C (clear) cells
- Follicular cells

State the funcitons of the 2 cell types found in the thyroid gland
- C (clear) cells: Secretes calcitonin (Ca2+ regulating hormone)
- Follicular cells: Support thyroid hormone synthesis and surround hollow follicles

What are thyroid follicles?
- Spherical structures whose walls are made of follicular cells
- Centre of the follicle is filled with colloid which is a sticky glycoprotein matrix which contains 2-3 months supply of thyroid hormone

How to follicular cells support thyroid hormone synthesis?
Follicular cells manufacture enzymes that make thyroid hormones
(note: also makes thyroglobulin)

Apart from enzymes, what else do follicular cells manufacture?
Thyroglobulin: A large protein rich in tyrosine residues

After follicular cells manufacture enzymes and thyroglobulin, what happens to these products?
- The enzymes and thyroglobulin are packages into vesicles and exported from the follicular cell into the colloid

What substance do the follicular cells actively concentrate from the plasma into the colloid and what does this allow?
- Iodine
This allows the iodine to combine with tyrosine residues to form the thyroid hormones

How does Iodine enter follicular cells?
Iodine enters follicular cells from the plasma via a Na+/I-transporter (symporter)
How does Iodine enter the colloid?
- Pendrin transporter
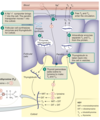
After iodine reaches the colloid, what processes occur to form thyroid hormones?
- Enzymes and thyroglobulin are exocytosed into the colloid
- The enzyme thyroid peroxidase (aka thyroperoxidase) converts I- to I2 by removing an electron
- This catalyses the addition of iodine to tyrosine residues on the thyroglobulin molecule forming thyroid hormones

How is triiodothyronine (T3) formed?
- One iodine + tyrosine ➔ MIT
- Addition of a 2nd iodine ➔ DIT
MIT + DIT ➔ T3

How is thyroxine (T4) formed?
- One iodine + tyrosine ➔ MIT
- Addition of a 2nd iodine ➔ DIT
DIT + DIT ➔ T4

After thyroid hormone synthesis in the colloid, what happens next?
- In response to TSH, the thyroglobulin T3/T4 complex is taken back into the follicular cells by endocytosis
- Within the cells, they form vesicles which contain proteolytic enzymes that cut the thyroglobulin to release thyroid hormones (T3/T4)
Both T3 and T4 are water/lipid soluble
- Lipid soluble
Both T3 and T4 circulate/do not circulate in the plasma
- Circulate
Most T3/T4 circulates freely in the plasma.
True/false
False
More than 99.8% of T3 and T4 circulates in plasma bound to plasma protein.
(REMEMBER: Thyroid hormones are hydrophobic and so bind to plasma proteins due to their low solubility in water)
Why does T4 have a longer half life than T3?
- Thyroxine Binding Globulin (TBG) has a particularly higher affinity for T4 releasing it only slowly into the plasma
(also in the lecture: most TH circulates in the form of protein bound T4)
How can T4 be converted into T3?
And what is this process called?
- Remove an iodine
- Deiodinease enzymes (half deiodinated in plasma, half in target cells)

“However 90% of TH binding to TH receptors inside cells is T3.”
(DON’T GET IT!!)
Descibe the regulation of thyroid hormone release
- A stimulus (i.e cold, exercise, pregnancy) causes the trophic hormone Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH) in the hypothalamus to act on the anterior pituitary to release Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- TSH from the anterior pituitary in turn acts on the thyroid gland to promote hormone synthesis (T3/T4)
- The thyroid hormones normally act as a negative feedback signal to prevent oversecretion

Describe how thyroid hormones function affect thier target cells
- Thyroid hormone (TH) binds to nuclear receptors in target cells
- The complex then binds to specefic sequences of DNA
- This changes transcription and translation to alter protein synthesis
State some functions of thyroid hormones
- Increase metabolic rate (by stimulating the use of cellular O2 to produce ATP)
- Promotes thermogenesis (production of heat)
- Increases hepatic gluconeogenesis although has no effect on BG (providing the pancreas is releasing adequete insulin)
- Net increase in proteolysis
- Net increase in lipolysis
- Critical for growth (lack of TH results in retarded growth)
- Astimulates GH receptor expression
- Essential for brain development in utero (maternal iodine deficiency = congenital hypothyroidism/cretinism)


