The Pituitary Gland Clinical Case & Discussion Flashcards
State some pituitary diseases that involve hyperfunction/hypersecretion
- Acromegaly (gigantism)
- Cushing’s disease
- Hyperprolactinaemia
State some pituitary diseases that involve hypofunction/hyposecretion
- Hypopituitarism (lower secretion of anterior pituitary hormones)
- Cranial diabetes insipidus (lower secretion of vasopressin from the posterior pituitary gland)
What does space occupation in the pituitary region cause?
- Optic chiasmal compression
(IN THE NEURO LECTURES: bilateral hemianopia)

In terms of the clinical features of acromegaly, what symptoms/features are associated with soft tissue overgrowth?
- Spade like hands
- Wide feet (shoes)
- Coarse facial features
- Thick lips and tongue
- Carpal tissue syndrome (compression of the median nerve causes numbness, weakness and tingling in the hand and arm)
- Sweating

What are the complications of acromegaly?
Complications:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
- Hypertension
- Headache
- Chiasmal compression
- Cardiomyopathy
How do we diagnose acromegaly?
Diagnosis of acromegaly :
- Oral glucose tolerance test: Growth hormone (GH) fails to suppress in the presence of glucose
AND
- ↑IGF-1
- MRI (look for pituitary tumour)
- Is vision normal?

What is Cushing’s syndrome?
- Excess glucocorticoids/corticosteroids (i.e cortisol)
What type of hormone is cortisol and how do we know this?
- CATABOLIC hormone
This is becuase it:
- Breaks down tissue (causing weakness of skin, muscle and bone)
- Causes sodium retention (may cause hypertension and heart failure)
- Insulin antagonism (causing diabetes mellitus)
What are the symptoms and signs of Cushing’s syndome that are of high diagnostic value?
High value:
- Proximal myopathy
- Osteoporosis
- Growth arrest in children
- Skin atrophy
- Spontaneous purpura
What are the symptoms and signs of Cushing’s syndome that are of intermediete diagnostic value?
Intermediate value:
- Pink striae
- Oedema
- Facial mooning and hirsutism (body hair in areas where there shouldn’t be)
What are the symptoms and signs of Cushing’s syndome that are of non-specific value?
- Central obesity
- Hypertension
What are the ACTH dependent causes of cushing’s syndrome
ACTH-dependent causes (↑ACTH):
- Pituitary tumour (which secretes ACTH)
- Ectopic ACTH secretion (i.e small cell lung cancers and carcinoid tumours)
What are the ACTH independent causes of cushing’s syndrome
ACTH-independent causes (↓ACTH due to negative feedback):
- Corticosteroid therapy (e.g for asthma, IBD)
- Adrenal tumour (adenoma or carcinoma)
State the causes of hyperprolactinaemia under the following headings:
(a) Physiological
(b) Pharamacological
(c) Pathological
(a) Physiological:
- Lactation
- Pregnancy
- Stress
(b) Pharmacological
- Dopamine antagonist drugs (neuroleptic e.g. chlorpromazine and anti-emetics e.g. metoclopramide) (dopamine inhibits prolactin production)
- DA-depleting agents
- Oestrogens
- Some antidepressents
(c) Pathological
- Pituitary lesions (i.e prolactinoma = excess production of prolactin from the anterior pituitary or increase in pituitary stalk pressure due to compression)
In hyperprolactinaemia, what should we not forget to ask about?
Don’t forget to ask about homeopathic or herbal remedies
Whar are the clinical features of hypopituitarism in adults?
Clinical features in adults:
- Tiredness (due to ↓TSH secretion)
- Weight gain (due to ↓TSH secretion)
- Depression (due to ↓TSH secretion)
- Reduced libido (due to gonadotrophin deficiency)
- Impotence (a man cannot get an erection or orgasm: due to gonadotrophin deficiency)
- Menstrual problems (due to gonadotrophin deficiency)
- Skin pallor (due to ↓ACTH secretion)
- Reduced body hair (due to ↓TSH secretion and gonadotrophin deficiency)
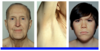
Whar are the clinical features of hypopituitarism in children?
Clinical features in children:
- Reduced linear growth (due to ↓growth hormone secretion and TSH deficiency)
- Delayed puberty (due to ↓ACTH secretion and gonadotrophin deficiency)

How is cranial diabetes insipidus diagnosed?
- Water deprivation test
(Explanation not in lecture: Empty the bladder then no drinks/fluids for up to 8 hours or until 3% of their body weight has been lost. Body weight, urine output, serum osmolality, urine volume, and urine osmolality are measured hourly. Normal response equates to a rise in urine osmolality to >700 mOsm/kg.)

How is cranial diabetes insipidus treated?
- DDAVP (desmopressin: This hormone which acts on the kidneys to ↓flow of urine)
What is the differential diagnosis for cranial diabetes insipidus?
Differential diagnosis:
- Post-trauma
- Idiopathic
- Metastatic carcinoma
- Rare causes e.g. sarcoidosis
- Other brain tumours e.g. germinoma
- Craniopharyngioma
Label the following diagram and state what it shows

- Large pituitary adenoma
(REMEMBER: This causes optic chiasmal compression

Discuss the management of pituitary tumours under the following headings:
(a) Hypersecretion
(b) Hyposecretion
(c) Tumour
(a) For hypersecretion:
- Dopamine (for prolactinoma)
- Somatostatin (for acromegaly)
- GH receptor antagonist (for acromegaly)
(b) For hyposecretion:
- Cortisol
- T4 (thyroxine)
- Sex steroids
- Growth hormone
- Desmopressin (hormone which acts on the kidneys to ↓flow of urine)
(c) Tumour:
- Surgery (mostly transsphenoidal: surgery done through the sphenoid sinus)
- Radiotherapy
How is Cushing’s disease treated?
- Pituitary surgery

How is acromegaly treated?
- Transsphenoidal surgery (surgery done through the sphenoid sinus to remove the pituitary tumour)
- Somatostatin analogues (e.g. lanreotide)
- Pegvisomant (GH antagonist)


