Clinical Aspects of the Adrenal Gland Clinical Case & Discussion Flashcards
What are the 3 categories of adrenal hypofunction disorders?
- Adrenal destruction
- Adrenal dysgenesis (congenital adrenal structural developmental defects)
- Impaired steroidogenesis

What are the causes of primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease)?
- Autoimmune destruction
- Infection (i.e TB)
- Infarction
- Invasion
- Infiltration
- Iatrogenic (long term steroid therapy suppresses the pituitary-adrenal axis but this only becomes apparent on withdrawal of the steroids)
What test is +ve in 70% of cases of autoimmune Addison’s disease?
- 21-Hydroxylase adrenal autoantibodies
What autoimmune diseases are commonly associated with autoimmune Addison’s disease?
Associated autoimmune diseases:
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Thyroid disease
- Premature ovarian failure
In Addison’s disease, state some common symptoms of primary adrenal failure
What are the possible clues to the diagnosis of adrenal failure?
How do we diagnose adrenal insufficiency?
Diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency:
- Routine blood: FBC, U&E, ↓glucose (due to ↓cortisol and therefore ↓gluconeogenesis), ↓Na+ and ↑K+ (due to ↓aldosterone)
Early morning cortisol:
> 450 nmol/L = Not Addison’s
< 350 nmol/L = Adrenal status uncertain
- Synacthen test
(Take 7 ml of blood to measure cortisol and ACTH levels. Then give 250mg of tetracosactrin IM. At 30 mins, take 7 ml of blood to measure cortisol. At 60 mins, take 7 ml of blood to measure cortisol. If impaired cortisol response and ACTH > 200ng/L, then diagnosis is Addison’s disease. If ACTH is <10ng/L, then diagnosis is secondary adrenal failure)
Look at this flow chart!

How is Addison’s disease (adrenal insufficiency) treated?
Glucocorticoid replacement:
- Hydrocortisone 20-30mg in 2-3 doses per day to ‘mimic normal diurnal variation’ (this is the main steroid used for adrenal insufficiency)
- Prednisolone
- Dexamethasone
Mineralocorticoid replacement:
- Fludrocortisone 50-300mg per day (synthetic steroid which binds to aldosterone receptors)
State some adrenal disorders that are to do with hypersecretion
Adrenal cortex:
- Cushing’s syndrome (↑cortisol)
- Conn’s syndrome (↑aldosterone)
Adrenal medula:
- Phaeochromocytoma (↑catecholamines)
What are the side effect of glucocorticoid therapy?

Look at this for Cushing’s Syndrome:

What is the approach to hypercortisolism?
How do screen for suspected Cushing’s syndrome?
- 24 hour urinary free cortisol (normal 14–135 nmol/24h
- 1 mg overnight Dexamethasone suppression test taken at midnight. Measure serum cortisol at 9am. Normal < 50 nmol/L
After screening for Cushing’s syndrome and confirming the diagnosis, what other tests can we do?
- Pituitary MRI (shows pituitary tumour)
- CT scan (for patients with a suspected adrenal tumour)

What is Conn’s syndrome?
- Excess aldosterone
Describe the pathophysiology of primary hyperaldosteronism
Pathophysiology of primary hyperaldosteronism:
- An aldosterone-producing tumour produces ↑aldosterone
- This leads to ↑Na+absorption, ↑blood volume, ↑BP and ↑K+ excreted in the urine
- This then leads to ↓renin release (in attempt to ↓BP)
- Thus ↑aldosterone,↓renin and so the A/R ratio ↑

How do we screen to differentiate between primary and secondary aldosteronism?
Differentiating between primary and secondary aldosteronism:
- Primary: PA/PRA ratio > 20
- Secondary: PA/PRA ratio < 20 (could also mean essential hypertension)
PA = Primary aldosteronism
PRA = Plasma renin activity
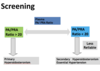
How do we diagnose hyperaldosteronism?
Clinical suspicion of hyperaldosteronism
Screening tests:
- Primary: PA/PRA ratio > 20
- Secondary: PA/PRA ratio < 20 (could also mean essential hypertension)
Confirmatory tests:
- 24 hour urine aldosterone > 12 μg/day and urinary Na+ > 200 mEq/day during 4 days of salt loading
Establishing the aldosterone source:
- CT scan of the adrenal glands
- Upright posture test
- Plasma 18-hydroxycorticosterone
- Adrenal venous sampling if CT scan is inconclusive or discordant eith posture test

In primary hyperaldosteronism, plasma aldosterone will be ____ and plasma renin will be ____
In primary hyperaldosteronism, plasma aldosterone will be HIGH and plasma renin will be LOW
How is Conn’s syndrome treated?
Surgery:
- Laparoscopic adrenalectomy

What is phaeochromocytoma?
Catecholamine producing tumour
(adrenal medulla)

How does phaeochromocytoma present?
- Hypertension
- Tachycardia
Paroxysmal attacks of:
- Headaches
- Sweating
- Palpitation
- Tremor
- Anxiety/fear
- Pallor
Why is phaeochromocytoma known as the 10% tumour?
Phaeochromocytoma roughly follows the 10% rule:
- 10% malignant
- 10% extra-adrenal
- 10% multiple
- 10% hyperglycaemia
- 30% inherited origin




