Normal Growth and Clinical Aspects Flashcards
Growth hormone (GH) is a ______ hormone which is released from where?
- Peptide
- Anterior pituitary
(GH also called somatotropin)

Growth hormone release is controlled via the release of what 2 hypothalmic neurohormones?
- Growth hormone inhibiting hormone (somatostatin)
- Growth hormone releasing hormone
State the direct and indirect actions of growth hormone
Direct action: Regulation of metabolism
Indirect action: Growth and development
Growth hormone requires permissive action of what before it will stimulate growth?
- Insulin
- Thyroid hormones
Thorugh the growth-promoting effects of GH, cells can undergo
- Hypertrophy (increase in cell size)
- Hyperplasia (cell division)
Descibe how GH affects growth
- The effect of GH on growth is INDIRECT
- GH acts as a trophic hormone to stimulate the secretion of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-1) aka somatomedin C from the liver and other cell types
- IGF-1 controls GH release through a negative feedback loop via inhibiting GHRH and stimulating GHIH (somatostatin)

IGF-I mainly binds to receptors on what type of cells?
- Muscle cells
(liver and adipose tissue have insulin receptors like muscle cells but have few IGF receptors unlike muscle cells)
Even though both peptide hormones, how do GH and IGF-1 behave like steroid and thyroid hormones?
- GH and IGF-1 are both transported in the blood bound to carrier proteins
In the blood, GH is always bound to a protein.
True/False
- False
(~50% of GH is in the bound form)
Why is it important for nearly half of GH in the blood to be bound to a growth hormone binding protein?
- Binding protein prevents plasma GH from being excreted in the urine and so by doing this, extends the half life of GH
Describe the effects of GH/IGF-1 on bone growth
- GH stimulates: chondrocyte precursor cells (prechondrocytes) → chondrocytes
- During differentiaiton, the chondrocytes begin to secrete IGF-I and become responsive to IGF-I
- IGF-I then acts as an autocrine or paracrine agent to stimulate the differentiating chondrocytes to undergo cell division and produce cartilage, the foundation for bone growth

What are the specefic direct effects of GH in the regulation of metabolism
- Increased gluconeogenesis
- Reduced abilty of insulin to stimulate glucose uptake by muscle and fat cells (by reducing the number of insulin receptors on muscle and fat cells)
- Maled adipocytes more sensitive to lipolytic stimuli
- Increased amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in almost all cells (anabolic effect)

Bone requires insulin for glucose uptake.
True/False
- False
Only fat and muscle cells require insulin for glucose uptake
In which age group is the highest rate of secretion of GH from the pituitary seen?
- Teenage years
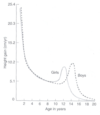
How does the release of GH compare when asleep and awake
- Majority of GH released during the first 2 hours of sleep (deep delta sleep)
- GH release during waking hours is low
(Diagram shows fluctuation in level of growth hormone in a 7 year old child: most prominent during sleeping hours!)

How would plasma levels of IGF-I vary?

- Remains relatively constant
(suggesting that IGF-I buffers the pulsatile variance in GH levels)
How does nutrition control of the release of GH?
- It is mediated via the modulation of control of GHRH/GHIH release from the hypothalamus
Stimuli that increase GHRH secretion:

Stimuli that increase GHIH secretion:

The physiology of growth is a very complex phenomenon affected by what 3 factors?
- Hormones
- Genetics
- Nutrition
Fill in the blanks for by stating the appropriate hormone:


Describe the importance of hormones on growth:
LATER
Descibe the importance of nutrition on growth
Adequate diet in terms of protein content and essential vitamins and minerals is just as important as enough calories. Important in utero and during development.
Describe the importance of genetic factors on growth:
Helps determine maximum growth