The Endocrine Pancreas 1 Flashcards
Energy (food) intake is the determined by the balance of activity in what 2 hypothalamic centres?
- Feeding centre: Promotes feeling of hunger and drive to eat
- Satiety centre: Promotes feeling of fullness by suppressing the Feeding centre
State the “glucostatic theory”
- Food intake is determined by blood glucose: as [BG] increases, the drive to eat decreases (-Feeding Centre; +Satiety centre)
State “lipostatic theory”
- Food intake is determined by fat stores: as fat stores increase, the drive to eat decreases (-feeding centre; + Satiety Centre)
(Leptin is a peptide hormone released by fat stores which depresses feeding activity.)
What are the 3 categories of energy output?
- Mechanical work: Movement, we can regulate this voluntarily using skeletal muscle
- Cellular work: Transporting molecules across membranes, growth and repair, storage of energy
- Heat loss: (half our energy output)
What are the 3 elements of metabolism?
- Extracting energy from nutrients in food
- Storing that energy
- Utilising that energy for work
Compare anabolic and catabolic pathways.
Anabolic pathways = Build up, synthesis of large molecules from smaller ones, usually for storage purposes
Catabolic pathways = Break down, degredation of large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy for work
What is meant by:
(a) Absorptive state
(b) Post-absorptive state
(a) Right after a meal ingested nutrients supply the energy needs of the body and excess is stored - this is an ANABOLIC phase
(b) Between meals where the pool of nutrients from the plasma decreases and we rely on body stores to release energy - this is a CATABOLIC phase
The brain is an “obligatory glucose utiliser”. What does this mean?
- The brain can only use GLUCOSE for energy
(execpt in extreme starvation)
How do we maintain blood glucose? (2)
BY SYNTHESISING GLUCOSE:
- Glycogen → Glucose (glycogenolysis)
- Amino acids → Glucose (gluconeogenesis)

Normal ranges of blood glucose (LATER):
LATER
The pancreas is __% exocrine and __% endocrine
- 99 % exocrine (acini)
- 1 % endocrine (islets of Langerhans)
State the 4 islet cells found in the Islets of Langerhans and state what each cells produces
4 types of islet cells: α, β, δ & F (hormone secreting cells)
- α cells produce GLUCAGON
- β cells produce INSULIN
- δ cells produce SOMATOSTATIN
F cells produce pancreatic polypeptide

State the function of the peptide hormone insulin
- Decreases blood glucose levels by stimulating glucose uptake by cells
(major stimulus = increase in blood glucose concentration)

Describe the mechanism by which a high blood glucose leads to the secretion of insulin
- High abundant glucose in the blood enters the β cell through glucose transporter proteins (GLUT)
- Metabolism increases and glucose is metabolised to produce ATP
- ATP levels rise
- ATP binds to K+ ion channels causing it to close
- K+ cannot leave the cell so K+ levels in the cell build up, leading to depolarisation of the cell
- Depolarisation of the cell causes voltage gated dependent Ca2+ ion channels to open
- Ca2+ enters the cell and creates an intracellular signal which which triggers insulin vesicle exocytosis into the circulation

Descibe why, when blood gluose levels are low, why insulin is NOT secreted
- When blood glucose is low, glucose does not diffuse in the β cell
- Metabolism decreases
- ATP production decreases
- Low levels of ATP leave K+ ion channels open
- K+ ions leak out, therefore positive charge is removed from the cell, hyperpolarising it
- Therefore voltage gated Ca2+ channels remain closed and so insulin is NOT secreted

Describe how insulin increases the uptake of glucose by cells
- After insulin is released from β cells thorugh exocytosis and is in the blood, it then leaves the blood and binds to tyrosine kinase receptors on the cell membrane of insulin-sensitive tissues
- In muscle and adipose/fat tissue, this binding of insulin to tyrosine kinase receptors stimulates the migration of GLUT 4 transporters to the cell membrane (which normally resides in the cytoplasm of these cells)
- GLUT 4 allows the transportation of glucose into the cell
(when insulin stimulation stops, the GLUT 4 transporters return to the cytoplasmic pool)
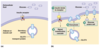
Which cells in the body are insulin dependent?
- Muscle cells
- Fat cells
Descibe the role of insulin in the uptake of glucose by hepatocytes in the fed state
- In the fed state, the liver takes up glucose becuase insulin activates HEXOKINASE
- HEXOKINASE lowers glucose levels in the cell
- This creates a gradient, favouring glucose movement into the cells
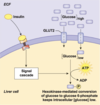
Descibe the role of hepatocytes in the fasted state
- In the fasted state, the liver synthesis glucose via glycogenolysis (from glycogen) and gluconeogenesis (from amino acids)
- This INCREASES glucose levels in the cell
- This creates a gradient favouring the movement of glucose movement out of the cells into the blood

Additional actions of insulin (LATER)
LATER
Insulin has a half life of __ minutes and is principally broken down in the ______ and _______
- 5 minutes
- Liver and Kidneys
Insulin protease (LATER)
LATER
Why effect does increased glucagon have on insulin?
- Stimulates insulin release
- Glucagon causes the synthesis of glucose via gluconeogenesis in the liver
- This glucose is released into the blood
- So blood glucose then rises
- And insulin does its thing to decrease blood glucose
State the stimuli which increase insulin release
- Increased blood glucose
- Increased amino acids in the plasma
- Glucagon
- Other (incretin) hormones controlling GI secretion and motility e.g gastrin, secretin, CCK
- Vagal nerve activity


