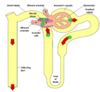
The renal system Flashcards
Tell me the main functions of the kidney and how it effects those parts of the body?
Water: ensures that there is a balance in water levels (not too much but not too little)
Blood pressure: Makes sure that the pressure isn’t too high or too low
Wastes: Gets rid of urea, uric acid, toxins and other wastes
Bones: Activates vitamin D which helps the body to absorb Ca2+
Heart: Maintains a balance of electrolytes (potassium, sodium, calcium) which is critical for heart rhythm
Acid- Base balance: Makes sure that the body isn’t too acidic or too alkaline
Blood: releases Erythropoietic, which induces RBC production from the bone marrow
What does urine analysis tell us?
How the kidneys are functioning by looking at colour, smell, taste, froth, clarity
What are the key functions of a healthy kidney?
- sodium and water removal
- waste removal
- hormone production
What are the key problems with an unhealthy kidney?
- fluid overload
- elevated wastes such as; urea, creatine, potassium
- changes in hormone levels controlling; blood pressure, production of RBC, uptake of calcium
Tell me the main things that the kidney regulates in respect to homeostasis regulation of water and ion content of the blood?
- Regulation of extra-cellular fluid volume
- Regulation of osmolarity
- Maintenance of Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Cl- within normal range
- Homeostatic regulation of pH: H+/ HCO3-
Tell me the main things that the kidney does in respect to the excretions of wastes and forgeign substances?
- By-products of metabolism e.g. creatinine
- Drugs and environmental toxins
Whats Creatine used for and what is it?
- produced in liver
- metabolised by muscle
- kidneys actively secrete it as it’s not wanted in the body
- A toxin
- increases muscle mass so used as a body building supplement
How does the kidney play a role in hormone production?
it plays an important role in endocrine pathways
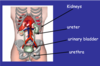
Label the urinary system…

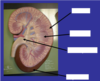
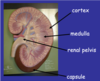
Label this cross section of the kidney…
The kidney is highly vascularised. Fill in the labels of the vasculature and all the blood vessels of the kidney/ nephron…


Label the nephron structures…


In the nephron what does the blood flow through and what does the urine filter through?
Blood in arterioles
Urine in tubules
Label this cartoon of the nephron…
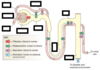

Place the following structures in the order in which the most reabsorption has happened to this point?
How how many L/day filter through each section?
Proximal tubule
Loop of Henle
Bowman’s capsule
Distal loop/ Collecting duct
Bowman’s capsule: 180 L/day
Proximal tubule (70%): 54 L/day
Loop of Henle (90%): 18 L/day
Distal loop/ Collecting duct (99%) 1.5L/day
What are the 4 main functions that the kidney carries out?
- Filtration
- Absorption
- Secretion
- Excretion
What 3 barriers does the filtrate have to pass through during filtration in the kidney?
- glomerular capillary endothelium
- Basal lamina (seperates capillary endothelium from epithelium)
- Epithelium of the bowman’s capsule
Does the glomerulus have a high pressure or low pressure filtration system?
High-pressure filtration system
Whats are the specialised cells found in the Bowman’s capulse and what’s their function?
Podocytes, they are in the Bowman’s capsule and their function is to allow for filtration
Tell me what the capillaries and permeable and impermeable to?
Permeable:
- Glucose
- Small cations; Na, K, H
- Small anions; Cl, HCO3
Impermeable
- Red blood cells
- proteins
What are the forces which influence glomerular filtration?
- Osmotic pressure (30 mmHg)
- Fluid pressure (15 mmHg)
- Capillary blood pressure (55 mmHg)
Whats the formula for the Net filtration pressure?
Net filtration pressure = CBP - OP - FP
Tell me what factors like aging and pregancy do to the GFR?
Aging decreases GFR
Pregnancy increases GFR
Whats the average GFR filtration efficiency?
125 ml/min, 180 L/day
Tell me how the following functions effect the BP?
- constriction of afferent arteriole, and dilation of efferent arteriole
- Dilation of afferent arteriole and constriction of efferent arteriole
- Increased BP –> constrict afferent arteriole, dilate efferent
- Decreased BP –> dilate afferent, constrict efferent
How does the following effect the GFR?
- Constricting efferent arteriole
- Constricting afferent arteriole
- constricting efferent: increases GFR
- constricting afferent: decreases GFR
What is the renal blood flow determined by?
Renal artery pressure and resistance in arterioles