The digestive system Flashcards
the digestive system is a tube called what?
the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract)
Where does the GI tract run from and to where?
runs from the mouth to the anus with everything in between
whats helps to aid digestion in the GI tract?
enzymes
A food and enzyme mixture is called what?
chyme
digested food is absorbed across what?
the intestinal epithelium
roughly how long is the GI tract?
8m long
What 3 structures are found in the small intestine?
- duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
What structures are included in the large intestine?
- caecum
- ascending colon
- transverse colon
- descending colon
- sigmoid colon
- rectum
- anus
What are the functions of the Oral cavity and oesophagus?
- digestion of carbohydrates
- NO absorption
- chewing and swallowing
What are the functions of the stomach?
- digestion of proteins and fats
- absoption of lipid soluble substances
- peristaltic mixing and propulsion
what are the functions of the small intestine?
- digestion of polypeptides, carbohydrates, fats and nucleic acids
- wide range of absoption
- mixing and propulsion
What are the functions of the large intestine?
- no digestion
- absorption of ions, mineral, vitamins and water
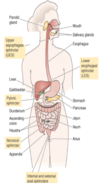
Label the GI tract


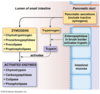
What do sphincters guard and control?
They guard different sections
they control movement through the digestive tract
Label the sphincters

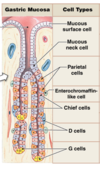
Label the stomach


What are the 3 main areas of the stomach?
- fundus
- body
- antrum
What does the folded area in the stomach help to increase?
the surface area which allows food to be moved around
What do stomach acid aid?
digestion
What does the stomach also produce and what does this provide?
the stomach also produces mucus which coats the inside lining of the stomach and provides protection
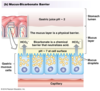
Label the small intestine


How many layers does the lining of the small intestine have?
4 layers
The small intestine has 2 layers of muscle, what does this allow?
allows contraction of the muscle which shortens and lengthen it, also contracts the diameter. This helps with digestion and propulsion
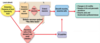
What are the 4 layers of the GI tract and the role/ importance/function of each layer?
Outside
1. Mucosa
includes transporting epithelial cells, connective tissue and nerve fibres and blood vessels
Lamina propria within this layer just under the epithelium
2. Submucosa
contains the submucosal plexus
3. Smooth muscle
important for lumen contraction, myenteric plexus
4. Serosa
outer layer
Inside

Label what region of the GI tract this electromicrograph was taken


why has the duodenum got such large micro villi?
a large surface area is needed
Label this sectional view of the stomach?


Label this sectional view of the small intestine?


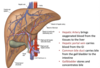
Name the accessory organs of the digestive system? what do these organs provide?
The accessory organs
- salivary glands
- pancreas
- liver and gall bladder
The provide secretions to enable digestive function
Label the salivary glands?


do the salivary glands secrete the same or different enzymes?
different enzymes
Label the pancreas

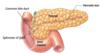
What does the bile duct in the pacreas lead to?
The liver
What is meant by the endocrine functions of the pancreas?
The release of hormones directly into the blood
What do Duct cells run along the edge of?
What do they secrete?
Duct cells run along the edge of the limen of pancreatic duct which secrete sodium bicarbonate that enters the digestive tract
what does sodium bicarbonate help to do?
neutrsalise acids
Label this cross-sectional area of the pancreas?