The cardiovascular system Flashcards
What’s the role of the plasma membrane?
To seperate the intracellular and extracellular components
What in the memrbane provides homeostatic control of the intracellular properties?
The transmembrane proteins
Tell me some advantages of being multicellular?
- calls can be specialised
- organisms can create their own internal environment
- Homeostatic control
- complexity
Tell me some disadvantages of being multicellular?
- Necrosis
- diffusion is slow (high energy use to substances in)
- cannot individual sense external environment
- many cells need to be coordinated in order to effect a change
- communication, intercellular signalling is needed
Why do we need a heart?
- diffusion is too slow over great distances to survive on that alone
- to supply O2 and substrates and remove CO2 and waste products
- heart helps transport these substances by allowing bulk flow movement of blood
What can the process of oxidative phosphorylation produce a lot of? what does it depend on though?
ATP from energy and substrates
Provided that oxygen is available as an electron acceptor for mitochondria
What has a higher affinity for oxygen, adult or fetal haemoglobin?
fetal
When does the human heart first start beating?
day 20 from conception until death. It beats continuously whilst being formed
Tell me the ciruclation of blood through the heart starting at the right atria
- left atrium
- left AV valve
- Left ventricle
- Aortic SL valve
- arteries of each organ
- arterioles of each organ
- capillaries of each organ
- venules of each organ
- veins of each organ
- vena cava
- right atrium
- right AV valve
- right ventricle
- pulmonary SL valve
- pulmonary artery
- lungs arteries
- lungs arterioles
- lungs capillaries
- lungs venules
- lungs veins
- pulmonary veins
- left atrium
What are the three major types of cardiac muscle that the heart is composed of?
- atrial muscles
- ventricular muscles
- excitatory and conductive muscle fibres
What is the tricuspid valve also known as?
The atria-ventricular valve
Label the heart and its internal structures


Tell me some key features of the cardiac muscle?
- myogenic
- inherent pacemaker activity
- coordinated pattern of contraction
- striated and has branching
- syncytial- intercalated discs (gap junctions)
What drives the heart rhythm?
The sino-artial node in the right atrium
What do the gap junctions between cells allow>
the spread of excitation
What are the steps to the depolarisation of the sarcolemma and then how this leads to muscular contraction?
What stages are known as the E-C coupling stage (excitation-contraction coupling)
- An impulse travels to the neuromuscular junction on a muscle cell
- ACh is released from the axon to receptors located on the sarcolemma
- The binding ACh causes depolarisation of the sacolemma by opening ion channnels and allowing Na+ ions into the muscle cells
- Na+ ions diffuse into the muscle fibre and depolarisation occurs
- depolarisation creates a wave of AP across the sacolemma
- AP travels across the sarcolemma and down the T-tubules which triggers the sarcoplasmic reticulium to release Ca2+ through ryanodine receptor channels (RyR)
- Ca2+ binds to troponin which removes the blocking action of the tropomyosin from the actin binding sites
- myosin is now ready to bind with the actin and from cross-bridges which begins the contraction process
- in order to contract, ATP binds to the myosin
- ATP is hydrolysed to ADP + Pi, which gives the myosin the energy to move its head to the high-energy position
- actin and myosin bind together to form a cross-bridge
- the myosin heads then pull the actin filaments inward and release the SDP and Pi and return to a low energy position
The myosin is now ready for more ATP to bind and repeat the cycle (it will continue as long as theres CA2+ ions and ATP available)
The steps in italic are the E-C coupling stages
All muscles have an intrinsic rhythm, but why is rhythm said to be controlled by the SA node?
the SA node has a faster rhythm so ends up gouverning the entire rhythm of the heart and masks the other cells intronsic rhythm
What can modify the rate at the SA node?
The nervous system
Label this conductive fibre containing the AV node ?
What do the number represent?

The numbers represent the interval of time (secs) from the origin of the impulse in the sinus node?
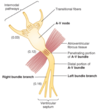
Name and conductive fibre and it’s role within the heart?
The bundle of His spreads the excitation rapidly through the heart, producing a co-ordinated, bio-mechanically efficient beating of the heart
Whats positive charge movement called?
An inward current
Whats the name of the current that makes the heart beat reguarly>
the pacemaker current