The nervous system Flashcards
Flatworms have a brain consisting of a cluster of nerve cell bodies which is concentrated where?
In their head or cephalic region
In worms, the cell bodies are no restricted to the head. where do they also occur?
In fused pairs known as glanglia, along a nerve cord
Whats a spinal reflex?
A simple, involunatary movement that can be integrated within the spinal cord without input from the brain
Whats is included in the CNS
The brain and spinal cord
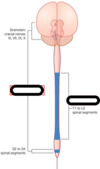
Name the 5 main sections of the spinal cord, which is each divided into smaller sections ?
- cervical
- thoracic
- lumbar
- sacral
- coccygeal
What are the nerves coming off each section of the spinal cord known as?
the spinal nerves/ peripheral nerves
Tell me what the following are
- cranial nerves
- spinal nerves
- ganglia
cranial nerves: nerves coming off the brain stem
Spinal nerves: nerves coming off the spinal cord
ganglia: a structure in the PNS. it houses the cell bodies of afferent and efferent nerves
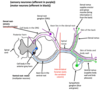
What are afferent nerves?
sensory neurons that carry nerve impulses from the sensory stimuli towards the CNS and brain
What are efferent nerves?
These are motor neurons that carry neural impulses away from the CNS and towards muscle and cause movement
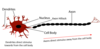
What are neurones and what does this include ?
Neurones are the powerhouse of the nervous system. this includes; axons, dendrites and cell bodies
Whats are dendrites?
The branch off of the cell body and they recieve information and deliver it to the cell body.
There are many denrites in a neurone
Whats an axon?
This takes information away from the cell body
Theres only one axon in a neurone
Whats an axon hillock?
This is the very first part of an axon as it leaves the cell body, it has lots of Na+ channels and is the start of the action potential (trigger zone)
Whats myelin sheath?
this helps to insulate the axon and help speed up electrical conduction
label this neurone

Whats the name of the type of cells that provide support and insulation for neurones?
glial cells
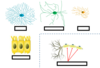
Name the glial cells found in the CNS/PNS and the glial cells found in only the PNS
CNS/PNS
- Astrocyte
- oligodendrocyte
- microglia
- ependymal cells
PNS only
- Schwann cells
What are astrocytes role?
They help to regulate the transmission of electrical impulses
What’s the oligodendrocytes role?
responsible for making myelin
Whats the role of the microglia cells?
Immuce cells, they provide some immune surveillance but not as much as a macrophage
Whats the role of ependymal cells?
cells that provide cerebral spinal fluid that line the open spaces in the brain and spinal cord
Whats the role of the schwann cells in the PNS?
They take up the role of the astrocyte (transmission of electrical impulses) and oligodendrocytes (responsible for making myelin). they’re the powerhouse of the PNS
Identify the glial cells
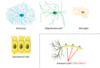
What is grey matter and what resides in it?
Grey matter is greyish nerve tissue of the CNS which is mainly composed of nerve cell bodies and dendrites
Whats white matter?
white matter is whiteish nerve tissue of the CNS that is mainly composed of myelinated nerve fibres (or axons)
What parts of neurones are found in the white matter and whats found in the grey matter?
White matter
- Myelinated axon
- axon hillock
Grey matter
- cell bodies
- unmyelinated axons
- dendrites
What glial cells are found in the white matter and/or in the grey matter
white matter
- astrocytes
- oligodendrocytes
- microglia
- ependyma cells
- schwann cells
Grey matter
- astrocytes
- oligodendrocytes
- microglia
Whats the nucleus/ nuclei and its role?
a group of nerve cell bodies within the CNS, consisting of neurones with relating functions and having defines input and output tracts (bundles of axons connected to different regions of the CNS)
Whats the ganglion?
nerve cell bodies outside the CNS, often visible as a swelling in a nerve or at the junction of a group of nerves e.g. dorsal root ganglia
Whats an interneurone?
this is a neurone completely contained within the CNS
Name the 4 lobes of the brain?
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
- temporal lobe
- occipital lobe
whats meant by sulci?
infoldings of the cerebral hemispheres that form ‘valleys’ between the gyri
(singlular= sulcus)
Whats gyri?
ridges of the infolded cerebral cortex
singular= gyrus
Name the 4 functional areas in the cerebrum and what lobes they are located in?
1. motor
Primary motor and premotor in frontal lobe
2. sensory
Primary somatosensory and somatosensory association areas in paritetal lobe
3. visual
primary visual and visual association areas in occipital lobe
4. auditory
primary auditory and auditory association areas in temporal lobe
What are 2 areas on the left side of the brain and what are they responsible for?
- Broca’s area: responsible for producing language. it controls motor functions with speech
- Wernicke’s area: important for language development and important for the comprehension of speech
what does the diencephalon overarch?
- thalamus
- hypothalamus
whats the thalamus’ role?
a relay station for information coming into the cortex from either sensory impulses (travelling to sensory cortex) or inputs for subcortical motor nuclei and cerebellum (travelling to the cerebral motor cortex)
Whats the hypothalamus important for?
its an important autonomic control centre e.g. homeostasis
Whats does the brain stem overarch?
- midbrain
- pons
- medualla oblongata
what are the 3 centres in the midbrain and what are these centres involved in?
1. superior and inferior colliculi: visual and auditory reflex centres
2. red nucleus: subcortical motor centre
3. substantia nigra: involved in reward-seeking, motor learning and others
Whats does the pons contain and what does this connect?
What do the nuclei in the pons do?
The pons cintains a conduction area which connects the forebrain and cerebellum
the nuclei contribute to the regulation of respiration as well as hearing and balance
What 2 centre does the medulla oblongata contain and what are they involved in?
1. Vital centres: regulating respiratory rhythm, heart rate, blood pressure
2. non-vital centres: regulating coughing, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting
the 2 helispheres in the cerebellum contains what? and are surrounded by what?
the cerebellum has 2 hemispheres which contains internal grey matter nuclei surrounded by white matter and an outer cortex of grey matter
Whats the cerebellum important for?
balance and coordinating motor activity
Whats the spinal cord and what is it protected by?
The spinal cord is a two-way impulse conduction pathway and reflex centre. it is protected by the meninges and CSF
Where are the meninges located and what’s their role?
The meninges lies between the bones and tissues of the CNS.
These membranes help stabilise the neural tissue and protect it from bruising against bones
What are the 3 protective layers in the meninges from the outside in?
outside
Dura mater
arachnoid membrane
pia mater
inside
Tell me about the dura mater?
- thickest of the 3 membranes
- associated with veins that drain blood from the brain through vessels or cavities known as sinuses