The hand Flashcards
How are the thumb and digits named?
Thumb Index Finger Middle Finger Ring Finger Little Finger
Name the carpal bones.
SLTP + TTCH Scaphoid, Lunate Triquetrum, Pisiform Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
What other bones make up the hand?
Metacarpals Proximal, Middle and Distal Phalanges
What are the four parts of the metacarpals?
Head (distal), tubercle, shaft and base
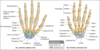
Which two carpal bones have bone protrusions?
Hook of Hamate Tubercle of Trapezium
What type of skin do you get on the palms of your hands?
Palmar-plantar skin
Which muscle forms the palmar aponeurosis?
It is the distal end of palmaris longus
What is the palmar aponeurosis distally and proximally continuous with?
Distal – fibrous digital sheaths Proximal – flexor retinaculum

What is contained within the fibrous digital sheaths?
Flexor tendons and their synovial sheaths
Which small quadrate muscle is found proximal to the hypothenar compartment?
Palmaris brevis

What is another name for the flexor retinaculum?
Transverse carpal ligament
Name the compartments of the hand.
Thenar Hypothenar Adductor Central

What separates the compartments of the hand?
Fibrous septa
What are the two main spaces found within the hand?
Midpalmar Thenar

What structures do the septa form within the hand?
Channels that contain various structures e.g. long flexors passing from the wrist into the digits
Name all the intrinsic muscles of the hand.
Thenar: Abductor pollicis brevis (APB), Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB), Opponens pollicis (OP) Hypothenar:Abductor digiti minimi (ADM), Flexor digiti minimi (FDM), Opponens digiti minimi (ODM) Adductor: Adductor pollicis (AP) Interossei and Lumbricals: Palmar interossei Dorsal interossei Lumbricals
What movements are the lumbricals responsible for?
Flexion of metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP) Extension of the interphalangeal joints (IPJs)
What movements are the palmar and dorsal interossei responsible for?
PAD & DAB Palmar = ADduction of the fingers Dorsal = ABduction of the fingers
Which muscles are responsible for the following thumb movements:
Abduction: Abductor pollicis longus (APL), Abductor pollicis brevis (APB) Adduction: Adductor pollicis (AP), First dorsal interosseus Extension: Extensor pollicis longus (EPL), Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB), Abductor pollicis longus (APL) Flexion: Flexor pollicis longus (FPL), Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB) Opposition: Opponens pollicis
Why is adductor pollicis in a different compartment to the other pollicis muscles?
It is innervated by the ulnar nerve whereas the thenar muscles are all innervated by the median nerve
How many lumbricals, dorsal interossei and palmar interossei are there?
Lumbricals – 4 Dorsal interossei – 4 Palmar interossei - 3
Describe the attachments of the dorsal interossei and explain why they cause abduction of the fingers.
Dorsal interossei are attached proximally to adjacent metacarpals They attach distally to the base of the proximal phalanx and extensor expansion towards the axial line (through the middle finger) of the hand Dorsal interossei 2 and 3 are attached to opposite sides of the middle finger so it fixes the middle finger in the midline while dorsal interossei 1 and 4 cause abduction of the index and little fingers

Describe the attachments of the palmar interossei.
Palmar interossei are attached to the extensor expansion away from the axial line (there is no palmar interossei attached to the middle finger) The cause adduction of the fingers whilst the middle finger remains still

Describe the attachments of the lumbricals.
They are attached proximally to the tendons of flexor digitorum profundus They come around the lateral side of the digits and inserts onto a hood of connective tissue called the extensor expansion over the proximal interphalangeal joint




