Session 3: Neck and Face Flashcards
What are the three main functions of the neck?
Structural – support and move the head Visceral functions Conduit for blood vessels and nerves
How are the components of these functions divided structurally in the neck?
Structural – inside prevertebral fascia Visceral – inside or associated with pretracheal fascia Blood vessels and nerves – carotid sheaths

What are the two large muscles that are found on the anterior and posterior sides of the neck?
Anterior – sternocleidomastoid Posterior – trapezius
What are the contents of the carotid sheath?
Internal jugular vein Common carotid artery Vagus nerve

What are the contents of the visceral fascia?
Oesophagus Trachea Thyroid Gland
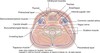
What is the name given to the fascia between the posterior aspect of the oesophagus and the anterior part of the prevertebral fascia?
Buccopharyngeal fascia

Which fascia splits in two around the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius?
Investing layer
What important structures are at C2
Superior cervical ganglion
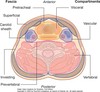
What are the two triangles of the neck?
Anterior triangle Posterior triangle

Which nerves innervate each of the four infrahyoid muscles?
Omohyoid – ansa cervicalis Sternohyoid – ansa cervicalis Sternothyroid – ansa cervicalis THYROHYOID – C1 fibres via the hypoglossal nerve
The posterior triangle consists mainly of blood vessels and nerves. Which blood vessels and nerves are in the posterior triangle?
External jugular vein Subclavian artery Trunks of brachial plexus Phrenic nerve Spinal accessory nerve
Where do the trunks of the brachial plexus emerge?
Posterior to scalenus anterior
Where are the subclavian artery and vein relative to the scalene muscles?
Subclavian artery = posterior to scalenus anterior Subclavian vein = anterior to scalenus anterior
Where is the phrenic nerve relative to the scalene muscles?
Phrenic nerve lies on the anterior surface of scalene anterior
Which spinal nerves contribute to the phrenic nerve and what isits main function?
C3, C4 and C5 Motor supply of the diaphragm Sensory innervation to the diaphragmatic pleura and peritoneum
What is platysma innervated by?
Facial nerve (cervical branch)
What is mylohyoid innervated by?
Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve
What are the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle innervated by?
Anterior – mandibular division of trigeminal nerve Posterior – facial nerve
What are the clinical applications of a carotid pulse?
Measuring pulse rate
List the main sites of access for central venous lines.
Internal jugular (most common) Subclavian vein Femoral vein
What are the uses of central venous lines?
Long-term access e.g. for chemotherapy drugs Parenteral nutrition Monitoring blood pressure
What are the complications of insertion of central venous lines?
Accidental arterial puncture Tracheal injury Arrhythmia Emboli Infection Pneumothorax or haemothorax
Where does the accessory nerve exit the skull?
The accessory nerve begins in the upper spinal cord and ascends to enter the skull through the foramen magnum The accessory nerve then leaves via the jugular foramen

What does the accessory nerve innervate?
Trapezius Sternocleidomastoid
How would you test the function of the accessory nerve?
Ask the patient to shrug their shoulders and hold it there
What important structures are at C3
Body of hyoid
What important structures are at C4
Bifurcation of carotid artery Upper border of thyroid cartilage
What important structures are at C6
Cricoid cartilage Middle cervical ganglion
What important structures are at C7
Inferior cervical ganglion
Borders of anterior triangle in neck
Inferior border of mandible Anterior border of sternocleidomastoid Midline
What are main muscles in anterior triangle of neck
Platysma Mylohyoid Digastric muscles Infrahyoid muscles
4 infrahyoid muscles
Sternohyoid Sternothyroid Thyrohyoid Omohyoid

Attachments of omohyoid muscles
Superior border of scapular by scapular notch to hyoid bone
Attachment of thyrohyoid muscle
Thyroid cartilage to hyoid
Attachment of sternothyroid bone
Sternum to thyroid cartilage
Attachment of sternohyoid bone
Sternum to hyoid bone
What vessels are carried in anterior triangle of neck
Carotid arteries and internal jugular vein

Posterior triangle of neck border
Posterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle Anterior border of trapezius Clavicle
Nervous supply of platysma
Facial nerve
Nervous supply of mylohyoid
mandibular division of trigeminal
Nerve supply of anterior belly of digastric
mandibular division of trigeminal nerve
Nerve supply of posterior belly of digastric muscle
facial nerve
Nerve supply of infrahyoid muscles
Omohyoid- ansa cervicalis Sternothyroid- ansa cervicalis Sternohyoid- ansa cervicalis Thyrohyoid- C1 fibres via hypoglossal nerve
Lymph drainage in neck area
All nodes lead to superior and inferior deep cervical ganglions

Where are superior and inferior deep cervical ganglions found
Along internal jugular vein


