The Brainstem and Consciousness (Reticular Formation) Flashcards
Define arousal
the emotional state associated with some kind of goal or avoidance of something noxious
Define consciousness
difficult to define but:
something to do with ‘awareness’ of both the external world and internal states
What two areas of the brain are requried for consciousness?
Cerebral Cortex + Reticular Formation

Where is the reticular formation located?
Located in the Brainstem
(diffuse structure/area)

What is the nature of the feedback loop between the cerebral cortex and reticular formation?
Positive Feedback Loop

Damage or lesions to which 3 areas of the brain can cause an altered level of consciousness?
Cerebral Cortex
Brainstem (reticular formation)
- *Conenctions Between Both**
- (e.g. in diffuse axonal injury)*
Which neurotransmitter is used by the excitatory neurones originating from the reticular formation to stimulate the subcortical nuclei?
Acetylcholine
(cirlces left to right:
basal F/B nuclei, hypothalamus, thalamus)
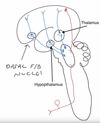
Which neurotransmitter is used from the neurones of the basal nuclei to excite the coertex?
Acetylcholine

Which neurotransmitter is used by the hypothalamic neuronal projections to the cortex, which help maintain consciousiness?
Histamine

What neurotransmitter is used by the thalamic projections to the cerebral cortex to help maintain consciousness?
Glutamate

How can anticholinergic drugs and anti-histamines cause drowsiness?
inhbit the positive/excitatory inputs from the reticular formation to the cerebral cortex
What scale is used to assess a patients level of consciousness?
Glasgow Coma Scale
(GCS)
What is measured by an electroencephalogram (EEG)?
combined activity of thousands of neurones
located to different geographical regions of the brain

What happens to the EEG waveform as you progress into deeper sleep?
decreasing frequency in firing
increasing amplitude as neuronal populations become synchronous
Which types of waves are found on an EEG when a person is awake?
Beta Waves

Irregular - up to 50Hz
When do alpha waves appear on an EEG?
Once eyes are closed and visual stimuli are removed
pattern becomes more synchronous
around 10Hz

How many stages of sleep are there on an EEG?
5 Stages (including REM)

What are sleep spindles seen during stage 2 of sleep cycles on an EEG?
rapid neuronal firing from the thalamus in an effort to maintain consciousness

Which type of waves are predominant during stage 2/3 of the sleep cycle on an EEG?
Theta Waves
around 5Hz

Why does REM sleep appear similar to the beta waves seen when patients are awake?
period when patients are dreaming
visual simulation from brain generated images > stimulated cortex
What changes in the brain occur to allow you to sleep?
deactivation of the reticular activating system (and therefore thalamus), to allow decreased cortical activity
achieved by removal of sensory inputs
e.g. closing eyes
Which area of the brain is responsible for initiating REM sleep?
neurones in the pons
Why are patinets in the REM phase of sleep difficult to rouse?
strong inhibition of the thalamus
Patients in the REM phase of sleep have very little muscle tone, outline the neruonal mechanism of this phenomenon
descending inhibition of LMNs by glycinergic fibres arising in the reticular formation
What autonomic effects are seen during the REM phase of sleep?
Penile Erection
Loss of Thermoregulation
What are 2 functions of sleep?
Energy Conservation & Bodily Repair
Memory Consolidation
Clearance of Extracellular Debris
What are the two most common causes of insomnia?
Depression
Anxiety
What causes narcolepsy?
issues with neurotransmitters
patients are unable to maintain the positive feedback between reticular activating system and cortex
patients are unable to stay awake
How can sleep apnoea cause sleep disturbances?
soft tissues compress the neck during sleep and cause obstruction to airflow
common in obese patients
obstruction results in hypoxia and awakening to change position and remove obstructon
Outline the EEG findings in a patient with brain death?
flat EEG
widespread cortical and brainstem damage
Outline the features of a patient in coma (including EEG findings)
widespread brainstem & cortical damage
unarousable and unresponsible to psychologically meaningful stimuli
EEG - various disorganised patterns
no sleep-wake cycle detectable
How do patients with permenant vegetative state differ from those in a coma?
some sponteanous eye opening is possible
some patients can localise to stimuli via brainstem reflexes
sleep-wake cycle detectable
What is a cause of locked in syndrome and how do patients present?
caused by basilar/pontine artery occlusion
eye movements can be preserved but loss of ALL somatic motor functions from pons down


