Spinal Cord Injuries Flashcards
(15 cards)
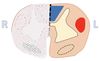
Which tracts of the spinal cord are represented by the red, blue and green colours on the included image?

Blue
dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
Red
corticospinal tract
Green
spinothalamic tract

What type of neck fracture may be associated with an extension injury of the neck?
Hangman’s Fracture
(fracture of both pedicles or pars interarticularis of the axis vertebra (C2), X-ray demonstrates anterior movement of C2 on C3)

What type of cervical spine fracture may occur due to a hyperflexion injury?
anterior wedge fracture

What motor ± sensory deficit would a patient present with following a compelte cord transection?
complete loss of sensation below lesion
compelte paralysis below lesion

What mechanism could lead to a Brown-Sequard syndrome?
Penetrating Traums
Fractured Vertebrae
What motor ± sensory affects would a patient report following a right sided cord hemisection?
Right Sided (ipsilateral)
loss of motor function > damage to corticospinal tract
loss of proprioception, vibration, fine touch > damage to dorsal column
Left Sided (contralateral)
loss of pain & temerature > damage to spinothalamic tract

What type of cord syndrome may be caused by an anterior spinal artery lesion and which tracts may be affected?
Anterior Cord Syndrome
may affect corticospinal and spinothalamaic tracts

What motor ± sensory symptoms may a patient develop with an anterior cord injuy?
Motor Deficit
flaccid paralysis @ level of the lesion (LMN damage)
spasticity below the level of the lesion (loss of UMN innervation)
Sensory Deficit
loss of pain and temperature sensation below the lesion

What pathology can lead to a central cord injury?
Trauma
Syringomyelia
(cyst within spinal cord)

Why does a central cord lesion present with more pronounced motor symptoms than sensory symptoms?
central cord cyst compresses the ventral (anterior) horns most

Why are the upper extremities affected more than the lower extremities in a central cord lesion?
medial portion of the lateral corticospinal tract is affected which provides innervation to upper limbs

Why are distal muscles affected more than proximal muscles in a central cord lesion?
lateral corticospinal tract is affected more than the ventral corticospinal tract

What pathology can cause a posterior cord syndrome?
Spondylosis
Spinal Stenosis
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
What clinical features would a patient with a posterior cord syndrome present with?
RARE Condition!
loss of conscious priprioception, vibration sensation, two point discrimination, light touch

Summary of Spinal Cord Lesions

Summary of Spinal Cord Lesions



