Environment of the Brain (Neurones & Glia) Flashcards
(37 cards)
What is the general function of neurones?
sense changes and communicate with one another
What is the general function of glial cells?
support, nourish and insulate neurones
remove waste
What are the 3 primary types of glial cells?
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
What is the most abundant type of glial cell in the CNS?
Astrocytes

What are 3 roles of the astrocytes?
Provide Nutrition for Neurones
Remove Neurotransmitters
Maintain Ionic Environment
(K+ buffering)
(glucose-lactate shuttle)
Outline the two sources of energy available for neurons to utilise
- *glucose directly from the blood**
- (taken up into brain ECF, then transported into neurone for conversion to ATP)*
glucose is stored in astrocytes as glycogen that can be released when necessary
(astrocyte glucogen > glucose > pyruvate > lactate > shuttled from astrocyte into neurone > converted back to pyruvate > converted to ATP)

How do astrocytes help to limit the effects of neurotransmitters?
re-uptake neurotransmitter from synapse
astrocytes uptake glutamate from the synapse, convert it to glutamine and deliver it back to the presynaptic terminal to be converted back to glutamate and further released as a neurotransmitter

Neuronal depolarisation causes efflux of K+ to restore the RMP, how is this counteracted in the brain-ECF to prevent elevated K+ levels?
astrocytes uptake excess K+ via:
K+ Channels
Na+/K+/2Cl- Channels
Na+/K+ ATPase

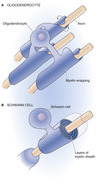
What is the difference between Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells?
Oligodendrocytes
CNS - can myelinate multiple neurones
Schwann Cells
PNS - can only myelinate single neurones
What structure is damaged in multiple sclerosis??
myelin sheaths attacked by auto-antibodies
commonly affects the CNS (optic nerve)
deposition of plaques/scar tissue
What is the function of the microglia of the CNS?
brains main defence system
immunocompetent cells - capable of phagocytosing foerign material

What is the function of the blood brain barrier and how is it formed?
limits diffusion of substance from blood to brain ECF - allows a specific environment around the brain to be maintained
formed by tight junctions between brain capillaries - these are promoted by the astrocyte foot processes

How is the environment around the brain maintained, utilising the tight junctions formed by the capillaries?
specific transporters allow movement of substances across the basement membrane of the brain capillary endothelium

The CNS is isolated from the immune system to prevent injury?
TRUE / FALSE
FALSE
the CNS is not isolated, rather specialised, to allow it to limit the pro-inflammatory T cell response as the rigid skull would not tolerate volume expansion
What are the 4 main sections of a neurone?
Cell Soma
Dendrites
Axon
Terminals

Outline how neurotransmitters are released from the pre-synmaptic vesicles
- Action potential travels down pre-synpatic axon to terminal
- Depolarisation causes Ca2+ entry through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
- Ca2+ binds to synaptotagmin
- Vesicle brought close to membrane
- Snare complex make a fusion pore
- Transmitter released through pore
- Neurotransmitter binds to post-synaptic receptor

What are the 3 major groups of neurotransmitters in the CNS?
- *Amino Acids**
- (e.g. glutamate, GABA)*
- *Biogenic Amines**
- (e.g. acetylcholine, noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin)*
- *Peptides**
- (substance p, somatostatin, NPY)*
What are the main excitatory synapses in the CNS?
Glutaminergic Synapses
What is the difference between the inotropic and metabotropic receptors, which are subtypes of the glutamate receptors?
Inotropic
have an integral ligand-gated ion channel
Metabotropic
linkted to a GPCR
What electrochemical effect is caused when glutamate binds to an inotropic glutamate receptor on a neuronal cell?
activation causes depolarisation of the neurone
AMPA receptors = Na+/K+
NMDA Receptors = Na+/K+ and Ca2+
opening channels causes an influx of Na+ and efflux of K+
What effects does glutamate have on the excitability of neurones?
Increases Excitation
Why does binding of glutamate to AMPA and NMDA receptors cause slightly differing responses?
AMPA Receptor
only ligand gated channels - allowing rapid depolarisation due to Na2+ influx
NMDA Receptor
ligand and voltage gated channels - voltage gated portion is opened by AMPA stimulation, which causes the Mg2+ blocking the pore to be removed and allow Na+ and Ca2+ influx - glutamate is also required to open the ligand gated portion

What is the molecular basis for long term potentiation in neurones and what is thought to be the biological benfit of such effects?
activation of NMDA receptors allows Ca2+ influx which can then activate second messengers
second messengers cause up-regulation of AMPA receptors and cause an increased conductance of ions > generating larger action potentials
believed to be essential for the formation of memories and learning

What risk is posed to neurones if excess glutamate is present around synapses?
excess NMDA stimulation
excess calcium entry into post synaptic terminals
Ca2+ is TOXIC to neurones











