Motor Disorders Flashcards
(28 cards)
Where is the cerebellum located within the cranial cavity?
posterior cranial fossa
What separates the occipital and parietal lobes from the cerebellum?
tentorium cerebelli
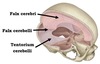
How is the cerebellum attached to the brainstem?
Superior Cerebella Peduncle (midbrain)
Middle Cerebellar Peduncle (pons)
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle (medulla)

Does pathology originating in the cerebellum present with ipsilateral or contra-lateral signs?
Ipsilateral
How do the areas of the body innervated by the cerebellum differ between the vermis and latral hemispheres?
Lateral Hemispheres
distal structures (e.g. limbs)
Vermis
trunk musculature

Why can cerebellar pathology potentially lead to hydrocephalus?
cerebellum located posterior to the 4th ventricle, compression by a mass may occlude CSF flow
What symptoms may a patient with cerebellar disease present with?
“DANISH”
- D - dysdiadocokinesis
- A - ataxia
- N - nystagmus
- I - intention tremor
- S - slurred speech
- H - hypotonia

What is the basal ganglia?
an areas of the basal forebrain and midbrain known to be involved in the control of movement
Which structures from the lentiform nucleus?
Putamen
Globus Pallidus Interna
Globus Pallidus Externa

When considering the basal ganglia, which structures form the striatum?
Putamen
Caudate Nucleus

Identify these important structures in the basal ganglia

Caudate Nucleus
Putamen
Globus Pallius (int/ext)
Substantia Nigra (pc/pr)
Subthalamic Nucleus

Within which area of the substantia nigra are the dopaminergic neurones located?
in the substantia nigra pars compacta
(dorsally)
Is dopamine and inhibitory or excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain?
can be either depending upon the receptor it is acting
Using the diagram as a point of reference, outline what happens when the cortex is stimulated to initiate movement via the direct pathway

- cortex stimulates basal ganglia and putamen
- substandia nigra (pars, com.) release dopamine
- putamen is stimulated to inhibit the globus pallidus (int.)
- globus pallidus (int.) no longer able to inhibit thalamus (brakes removed)
- thalamus then releases excitatory glutamate to stimulate cortex

What is the overall effect of the direct pathway in the basal ganglia on the thalamus and cortex (excluding the substantia nigra)?
&
How is that affected by the addition of dopamine from the SNc?
excitatory
dopamine encourages stimulation of the cortex

Using the diagram as a point of reference, outline what happens when the cortex is stimulated to initiate movement via the indirect pathway

- cortex stimulates basal ganglia and putamen
- substandia nigra (pars, com.) release dopamine
- putamen does not release inhibitory GABA onto the globus pallidus (ext.)
- globus pallidus (ext.) is able to release inhibitory GABA onto subthalamic nucleus
- subthalamic nucleus does not release excitatory glutamate onto globus pallidus (int.)
- globus pallidu (int.) does not release inhibitory GABA onto the thalamus
- thalamus is free to release excitatory glutamate onto the cortex (brakes removed from thalamus)

What is the overall effect of the indirect pathway in the basal ganglia on the thalamus and cortex (excluding the substantia nigra)?
&
How is that affected by the addition of dopamine from the SNc?
inhibitory
dopamine promotes stimulation of cortex
(opposite to without dopamine)

What overall net effect does dopamine have on the direct and indirect pathways of motor cortex stimulation via the thalamus?
stimulation
(excitation of motor cortex)
Does the motor cortex communiate with the basal ganglia on the ipsilateral or contra-lateral side and how is this relevant clinially?
ipsilateral side
decussation does not occur until the UMN reaches the distal meduallary pyramids
clinically relevant as patients with a right sided basal ganglia disorder, will manifest with left sided symptoms
What triad of symptoms is characteristic for Parkinson’s disease?
Bradykinesia
Resting Tremor
Rigidity
(hypertonia/cogwheel)
What is the underlying pathology in Parkinson’s disease?
degeneration of the substantia nigra pars compacta > resulting in a dopamine deficiency
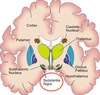
How can the symptom of bradykinesia in parkinson’s disease be attributed to the loss of dopamine?
dopamine is no longer stimulating the putamen to inhibit the globus pallidus interna
dopamine is also no longer inhibiting the GABA produced by the putamen that acts to inhuit the subthalamic nucleus
there is therefore more inhibition of the thalamus via the direct and indirect pathways, which reduces the secretion of glutamate onto the cortex
resulting in slower movement (bradykinesia)

Give two other symptoms assiociated with Parkinson’s disease except the cardinal features of resting tremor, bradykinesia and rigidity (hypertonia)
- hypophonia
- rediced facial expression (mask-like facies)
- micrographia
- dementia
Outline how the indirect pathway is affected in Huntington’s disease

substantia nigra is functioning normally therefore dopamine inputs work as expected
- loss of neurones in putamen causes loss of inhibitory GABA signals to the globus pallidus (ext.)
- increased GABA output from globus pallidus (ext.) to subthalamic nucleus
- subthalamic nucleus therefore has reudced output of excitatory glutamate to globus pallidus (int.)
- reduced inhibition of thalamus due to reduced output from globus pallidus (int.)
- reduced inhibition of thalamus allows increased output of excitatory glutamate to the motor cortex





