Sweatman - BBB Flashcards
Where in the body is P-gp?
- Liver
- Intestines
- Placenta
- BBB
Sagittal MRI located at midline. Which space/structure most accurately indicates the image is taken precisely at midline?
- Cerebral aqueduct
- Corpus callosum is also midline, but it is much wider
26-y/o woman brought to ED with 24 hrs of headache, neck pain, neck stiffness, photo-/phonophobia. On exam, she is found to have a temp of 39o C, but o/vitals normal. General med exam normal, with exception that flexion of neck caused her local neck pain. Her neuro exam revealed mild lethargy, but was otherwise non-focal.
What neuroanatomic structure might be responsible for her headache?
- Meninges
- Large blood vessels at brain base
- Or several cranial (i.e., trigeminal), peripheral nerves
26-y/o woman brought to ED with 24 hrs of headache, neck pain, neck stiffness, photo-/phonophobia. On exam, she is found to have a temp of 39o C, but o/vitals normal. General med exam normal, with exception that flexion of neck caused her local neck pain. Her neuro exam revealed mild lethargy, but was otherwise non-focal.
Why is her neck stiff?
- Inflammation of meninges triggers nerve root irritation that causes muscle spasm
26-y/o woman brought to ED with 24 hrs of headache, neck pain, neck stiffness, photo-/phonophobia. On exam, she is found to have a temp of 39o C, but o/vitals normal. General med exam normal, with exception that flexion of neck caused her local neck pain. Her neuro exam revealed mild lethargy, but was otherwise non-focal.
What tests/tx options would you request in ED?
- AB’s: the sooner you tx, the better the outcome, so tx first, and dx later
- Head CT: to make sure nothing else is going on
- LP: after CT bc sometimes dangerous. Even if LP is not conclusive, you can do blood culture bc meningitis usually with bacteremia, and even sepsis
26-y/o woman brought to ED with 24 hrs of headache, neck pain, neck stiffness, photo-/phonophobia. On exam, she is found to have a temp of 39o C, but o/vitals normal. General med exam normal, with exception that flexion of neck caused her local neck pain. Her neuro exam revealed mild lethargy, but was otherwise non-focal.
What results would you expect from CT and LP?
- Inflamed meninges on CT and cloudy CSF from LP
- May also see normal CT and cloudy CSF from LP
26-y/o woman brought to ED with 24 hrs of headache, neck pain, neck stiffness, photo-/phonophobia. On exam, she is found to have a temp of 39o C, but o/vitals normal. General med exam normal, with exception that flexion of neck caused her local neck pain. Her neuro exam revealed mild lethargy, but was otherwise non-focal.
What is important in regards to pharma choice?
- BBB and CSF-brain barriers may block brain entry of drug of choice
26-y/o woman brought to ED with 24 hrs of headache, neck pain, neck stiffness, photo-/phonophobia. On exam, she is found to have a temp of 39o C, but o/vitals normal. General med exam normal, with exception that flexion of neck caused her local neck pain. Her neuro exam revealed mild lethargy, but was otherwise non-focal.
Her headache persists, and she develops papilledema. What does the papilledema mean?
INC intracranial pressure
26-y/o woman brought to ED with 24 hrs of headache, neck pain, neck stiffness, photo-/phonophobia. On exam, she is found to have a temp of 39o C, but o/vitals normal. General med exam normal, with exception that flexion of neck caused her local neck pain. Her neuro exam revealed mild lethargy, but was otherwise non-focal.
Mechanism of INC intracranial pressure?
Blockage of CSF outflow via arachnoid villi
Cerebral endothelial cells are unique in that they form…?
Complex tight junctions
- Attributes of a drug that can pass easily across BBB include?
High lipophilicity
What is the purpose of the BBB?
- To maintain homeostasis for the envo surrounding neurons
- Prevent NT’s from escaping brain, and having peripheral pharmacologic actions
- To prevent free passage of molecules from periphery to CNS, and vice versa
Why is the BBB important for a practicing physician?
- Knowledge of extent to which a drug can penetrate the BBB critical to effective tx of diseases in the CNS
1. Physician needs a working knowledge of drugs that are capable of accessing the CNS - Physician should appreciate that many conditions encountered during pt’s life can compromise BBB integrity, either in progressive manner, or temporarily
1. Progressively: disease or aging
2. Temporarily: post-MI (ischemia, reperfusion) leading to cerebral edema, following marked rise in BP, after injection of hypertonic solutions
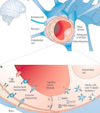
What are some of the features of the BBB that make it unique?
- Formed by endothelial cells at the level of cerebral capillaries -> endo cells interact with basal lamina, astrocytic end-feet processes, perivascular neruons, and pericytes to form a functional BBB
- Cerebral endo cells unique in that they form complex tight junctions produced by interaction of trans-membrane proteins that seal paracellular pathway -> make brain inaccessible for polar molecules, unless transferred by transport pathways of BBB that regulate microenvo of brain
- There are also adherens junctions that stabilize cell-cell interactions in the junctional zone
- IC, EC enzymes like monoamine oxidase (MAO), γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ=GT), alkaline phosphatase, peptidases, nucleotidases, several CYP450 enzymes endow this dynamic interface with metabolic activity
- Large molecules like Ab’s, lipoproteins, proteins, and peptides can be transferred to central compartment by receptor-mediated transcytosis, or non-specific absorptive-mediated transcytosis
1. Receptors for insulin, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), iron transferrin (Tf) and leptin
What are some things that can easily penetrate the BBB?
Water, CO2, O2, lipid-soluble free forms of steroid hormones
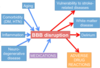
What are some characteristics of a disrupted BBB?
- Permits greater para-cellular permeability due to tight junction disruption
- Greater trans-cellular permeability via upregulated transcytosis
- Drug and toxin accumulation due to DEC efflux by PGP
- Basement membrane disruption and DEC nutrient transport

What does this image illustrate?

- Diverse distribution of energy-dependent pumps involved in the ADME of nutrients/drugs in the BBB
- ABC family of proteins (squares) inducible in many cancers, where they serve to mediate resistance to substrate therapeutics
- P-gp is a significant barrier in the BBB: anti-cancer agents, anti-depressants, etc. -> drugs that are P-gp substrates will lead to less effective tx in the CNS
What are some things that can disrupt the integrity of the BBB?
- Comorbidities and drugs compound BBB changes that accompany aging
- Compromise of BBB associated w/several age-related disorders
- Evidence that repeated sub-concussive collisions in high school American football players can also lead to disruption of BBB integrity -> surge in astrocytic protein S100B in blood, which may elicit production of immune response via generation of auto-Ab’s
1. Loss of BBB integrity may be partly responsible for neurodegenerative changes that only become evident decades later
How does lipophilicity affect drug access to the BBB?
- Lipophilicity INC drug access to the CNS
- Measured experimentally by octanol (lipid)/water partition coefficient -> graph shows that the more lipid soluble a drug is, the easier it gets access to the CNS
1. This equates to more rapid onset of drug activity and higher, more effective, drug levels in the brain

What are some parameters that INC drug access to the CNS?
- Lipophilic
- Free-drug (not protein bound): protein-bound drugs, and those carrying chemical charge (like quaternary amine) prohibited access to CNS
- Non-ionized
- In general, all proteins and polypeptides prevented from accessing CNS
- NOTE: these factors can be used in drug design to INC or DEC CNS access, i.e., L-dopa (pro-drug) or 2nd-gen anti-histamines
Do lipid-soluble drugs generally have a long or short duration of action? Why?
- Generally have long elimination half-lives, but SHORT duration of clinical action
- Undergo rapid redistribution from their main site of action to non-active sites, making their clinical duration short, but INC length of elim from non-active sites, e.g., adipose
- Passage across BBB a 2-way street -> these drugs can easily get in, and back out
This important concept is illustrated nicely by considering the 0me=course of drug distribu0on following a single IV injec0on of an anesthe0c like pentobarbital. As you will observe, the drug passes easily from the blood, in which it in injected, into the brain, moving passively down the concentra0on gradient. As the concentra0on con0nues to fall, this gradient, from blood to brain, is reversed and now the lipophilic drug redistributes out of the brain into other organs, moving down the concentra0on gradient. Thus 15 minutes aeer the injec0on the pa0ent awakens, not because the drug has been eliminated from the body, but because ease of passage across the BBB has permiqed redistribu0on away from this organ. That is to say, it has been eliminated from its target organ, the brain.



