STIs Flashcards
What is the definition of sexually transmitted infection?
The main mode of transmission of the organism is through sexual contact
What is the definition of sexually transmitted disease?
A disease caused by a sexually transmitted infection e.g. pelvic inflammatory disease
What is a sexually transmissible infection?
Disease can be transmitted by sexual contact, but it is not its main mode of transmission
What are different forms of sexual contact?

High risk groups for STIs
Age <25
Children of teenage mothers
Sex workers
MDM
Travellers from areas of high IV prevelance and their sexual partners
What are infective causes of vaginal discharge?
- Candida albicans
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- BActerial vaginosis
- Neisseria gonorrhoae
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- HSV
What are non-infective causes of vaginal discharge?
- Cervical polyps
- Neoplasms
- Retained products - tampons
- Chemical irritation
What are infectious causes of urethral discharge?
- Nesseiria gonorrhoae
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Mycoplasma genetalium
- Ureaplasma urealyticum
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- HSV
- HPV
- UTI
- Reponema Pallidum - meatal chancre
What are non-infective causes of urethral discharge?
- Physical/chemical trauma
- Urethral stricture
- Nonspecific
What are infective causes of genital ulceration?
- Sypillis - primary chancre, secondary mucous patches, tertiary gumma
- Chanroid
- Lymphogranuloma venereum
- Donovanosis
- HSV - Primary, recurrent
- HZV
What are non-infective causes of genital ulceration?
- Behcet’s syndrome
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- SJS
- CArcinoma
- Trauma
What are the main symptoms that can occur in STIs?
- Dyspareunia
- Vaginal/urethral discharge
- Ulceration
- Pain
- Itch
- Malodour
- Genital swelling
- Eye symptoms
- Dysuria
- Haematuria
- Abdominal pain
- Systemic symptoms - Skin rash, joint pain, malaise, lymphadenopathy,fever
What things would you want to ask about in a full sexual history?
- PC/HPC
- Past sexual history
- Menstrual history
- Gynae history
- Obstetric history
- PMH
- Medications + Allergies
- Social history
What would you want to ask about in a menstrual history?
MR FLOPPI DIC
- Menopause
- Regularity
- Flow
- Odd bleeding - Post-coital, Post-menopausal, Intermenstrual
- Dysmenorrhoea
- Initiation - menarche
- Cycle - days on/days off
What would you want to ask about in the gynae history section of a sexual history?
- Previous gynaecological disease +/- treatment
- Last smear - date and result
What would you want to ask about in past sexual history?
- Last sexual contact?
- Casual/regular partner - how long for?
- Consensual?
- Male or female?
- Types of sex involved - anal, vaginal, oral, multiple partners
- Contraception used - condoms and/or other
- Nationality of contact
- Any other partners
What would you want to ask about in the obstetric section of the history when taking a full sexual history?
- Contraception being used?
- Current pregnancy/unsure?
What specific questions could you ask about HIV to identify positive risk factors for infection?
- Have you ever had a partner whom is known to be HIV positive?
- Have you ever had sex with a bisexual man/engaged in male homosexual activity?
- Have you ever had sex with someone abroad, or who was born in a different country?
- Have you ever injected drugs?
- Are you aware of any of your previous partners having ever injected drugs?
- Have you ever paid someone for sex, or been paid for sex?
What is the following?

Balanitis - specifically candida balanitis
What is the following?

Genital ulcer - think of infectinve and non-infective causes

What is the following?

Genital warts - specifically HPV warts
What is the causative organism of gonorrhoea?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
What is the general incubation period of neisseria gonorrhoea?
Usually 5-6 days - can be 2 days - 2 weeks
What sex does gonorrhoea occur in most commonly?
Men - often in MSM
(Least common, most serious)
What are symtpoms of gonorrhoea in men?
10% asymptomatic
- Thick profuse yellow discharge
- Dysuria
- Pharyngeal/rectal infection

What are symptoms of gonorrhoea in women?
>50% asymptomatic:
- Vaginal discharge
- Dysuria
- Intermenstrual/post-coital bleeding
What investigations would you consider doing if you suspected gonorrhoea?
-
NAAT testing on samples obtained as follows:
- Women - a vulvovaginal swab (which may be self-taken)
- Men - first pass urine
Sites sampled for swabs should be mucosal sites associated with symptoms, and sites related to the type of sexual activity reported.
- Urethral/endo-cerival swab for gram stain
- Blood culture
- Join aspiration and microscopy if dissmentinated infection suspected
What is NAAT?
Nucleic acid amplification test
A technique utilized to detect a particular nucleic acid, virus, or bacteria which acts as a pathogen in blood, tissue, urine. Amplification is done using PCR or ligase chain reaction

What might you see on urinalysis in someone with gonorrhoea?
Positive leukocyte esterase
What gram-type is gonorrhoea?
Intracellular gram-negative diplococci

Why might you do imaging in someone with gonorrhoea?
Look for features of PID - inflammatory changes of fallopian tubes and ovaries, abnormal fluid collection
How would you treat confirmed gonorrhoea?
- Ceftriaxone 500mg IM once plus Azithromycin 1g Oral
- Add doxycycline +/- metranidazole if complicated
When is metranidazole added to treatment of gonorrhoea?
If there is a history of sexual assault/abuse
What complications can occur in men with gonorrhoea?
- Epididymitis, prostatitis
- Acute mononeuritis
- Disseminated gonococcal infection
- Acute monoarthritis
- Reiter’s syndrome
What complications can occur in women with gonorrohoea?
- PID
- Bartholin’s Abscess
- Peri-heptitis
- Disseminated gonoccocal disease
- Acute Mononeuritis
- Reiter’s syndrome
What is disseminated gonococcal disease?
Bacteremic spread of the sexually transmitted pathogen, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which can lead to a variety of clinical symptoms and signs, such as arthritis or arthralgias, tenosynovitis, and multiple skin lesions

How should you follow-up someone with gonococcal infection?
Test of cure at 2 weeks and test of reinfection at 3 months
What organism causes chlamydia infection?
Chlamydia trachomatis serovars D to K
How does chlamydia present in women?
Asymptomatic - 80%
- Vaginal discharge
- Dysuria
- Intermenstrual/post-coital bleeding
- Dyspareunia
What proportion of women are asymptomatic with chlamydia infection?
80%
(Most common, least serious - although leading cause of infertility in UK)
How can chlamydia present in men?
Asymptomatic > 70%
- Slight watery discharge
- Dysuria
What is the consistency of urethral discharge produced in chlamydial infection?
Watery discharge
What is the consistency of urethral discharge produced in gonococcal infection?
Thick yellow discharge

How would you test for chlamydia infection?
NAAT for diagnosis of smaples collected as follows:
-
Women
- Swabs - urethra, vagina, cervix, rectum
- First void urine
-
Men
- First void urine
- Urethral swab
-
Both
- Rectal swabs if symptomatic
How would you manage someone with chlamydia?
Azithromycin 1g PO
Doxyxycine if rectal infection (CI pregnancy)
What are complications of chlamydia in women?
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease and hence:
- ectopic preganncy
- infertility
- Reactive arthritis/reier’s syndrome
- Cervical cancer
- Perihepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome)
What are complications of chlamydia in men?
- Epididymitis
- Reactive arthritis
What complications can occur in neonates with chlamydia?
- Chlamydia pneumonia
- Opthalmia neonatorum - conjunctivis
What are features of reiter’s syndrome
Can’t see, can’t pee, pain in the knee
- Urethritis/cervicitis
- Conjunctivitis
- Arthritis
What age group does chlamydia usually affect?
<25 years + sexually active
What is the average incubation period of chlamydia trachomatis?
7-21 days
What gram-type is chalmydia trachomatis?
Gram-negative
What herpes viruses cause genital herpes?
HSV 1 + 2
Typical follow up chlamydia
Test for reinfection at 3-21 months. Earlier test not needed unless symptoms persist.
How does HSV infection present?
80% - no symptoms
-
Monthly/annual buring/itching then blistering rash then tender ulceration
- Genital
- Oral
- Tender inguinal nodes
- Flu-like symptoms
- Urethral discharge
- Proctitis
- Dysuria
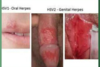
Why is HIV ragarded as a risk factor for clinical presentation of HSV disease?
Increases risk of reactivation and infection
What is the pathogenesis of herpes infection?
Virus initially breaks mucosal barrier/skin. It then replicates in the epidermis, and infects sensory/autonomic nerve endings and travels by retrograde axonal transport to sensory ganglia. It then enters a latent state, which allows the virus to evade the immune system
Reactivation of the virus occurs when it travels by anterograde transport to mucosal/cutaneous surface

What clinical presentation of herpes does HSV 1 cause?
Mainly oral herpes
What clinical presentation of herpes does HSV2 cause?
Mainly genital herpes
How would you diagnose herpes?
Clinical impression (grouped vesilces/papules = burst forming shallow ulcers)
Swab - viral culture, HSV PCR, IgG assay
How would you manage someone with HSV infection?
- Pain relief - Topical lidocaine, paracetamol/ibuprofen
-
Antivirals - Aciclovir/Valaciclovir/Famciclovir
- Primary outbreak - aciclovir 400mg 5 dats
- Infrequent recurrences - aciclovire 1.2g daily until symptoms gone
- Frequent recurrences - aciclovir 400bd as supression
- Counselling - recurrence, implications for sexual partners (avoid sex if symptomatic)
How does HSV affect pregnancy?
Delivery by caesarean section if priary HSV is contraindicated after 34 weeks within last 6 weeks of pregnancy.
SLight increase in risk of miscarriage in first trimester.
What are complications of HSV infection?
- Autonomic neuropathy (urinary retention)
- Neonatal HSV
- Secondary infection
- Encephalitis/Meningitis
- Keratitis/Keratoconjunctivitis
Incubation period HSV
About 5 days to months. Some people never report symptpms.
What is the causative organism of trichomoniasis?
Trichomonas Vaginalis
COmmon
What are the symptoms of trichomoniasis in men?
Asymptomatic
What are symptoms of trichomoniasis in women?
30% asymptomatic:
- Profuse thin vaginal discharge - greenish, foul-smelling, frothy
- Vulvitis - itching
“strawberry cervic” on speculum
What investigations would you do if you suspected tichomoniasis?
High vaginal swab
- Microscopy of wet preparation
- NAAT testing
- Note that no urine test yet so no test for men
How would you manage someone with trichomoniasis?
-
Metronidazole
- 400mg po bd for 5 days, or
- 2g single dose.
What are complications of trichomoniasis?
- Miscarriage
- Pre-term labour
What is the main organism implicated in anogenital warts?
Human papilloma virus - 6 and 11
How does HPV present?
Anogenital warts - occassionally itchy or painful. Texture of a small cauliflower.
How would you manage anogenital warts?
- Topical podophyllotoxin CI in pregnancy
- Imiquimod CI pregnancy
- Cryotherapy
- Diathermy/Ablation
- Scissor removal
What organism causes syphillis?
Treponema pallidum
What is the incubation period of treponema pallidum?
9-90 days until first chancre. But can be asymptomatic
Describe the natural history of syphillis
Primary = local painless ulcer on trunk/face/palms/soles that results within 2-3 weeks
Secondary = 4-10 weeks post infection with general malaise, fever, generalised ymphadeonpathy etc
Tertiray = the neurovasculr, cardiovasular, gummatous complications. Occurs after a latent period of 2 or more years (when patient is non infectious). Gumma are characteristic lesions.
What are features of primary syphillis?
Chancre
Begins as macule -> papule -> painless ulcer (chancre) with central slough and defined rolled edges

What are features of secondary syphillis?
Dissemination 4-10 weeks after initial chancre:
- Maculopapular rash - can be on palms and soles
- Mucous patches
- Condyloma lata
- Fever
- Headache
- Myalgia
- Lymphadenoapthy
- Hepatitis
- Patchy alopecia
What could cause the following?

Secondary syphillis - maculopapular rash
What could cause the following?

Secondary syphillis - mucous patches
What could cause the following painless ulcer?

Primary syphillis - chancre
What could cause the following?

Secondary syphillis - condyloma lata - pale, raised plaques
What are features of tertiary syphillis?
Occurs 20-40 years after initial infection
- Aseptic meningitis
- Neurosyphillis - Seizures, Psychiatric symptoms, Focal neurological deficit
- Tabes dorsalis
- Gummatous syphillis
- Cardiovascular syphillis
(v rare)
What is tabes doralis?
Also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the neural tracts primarily in the dorsal columns (posterior columns) of the spinal cord (the portion closest to the back of the body) & dorsal roots.
What are argyle robertson pupils?
Characterised by:
- Miosis (small pupils)
- Absence of the pupillary light response
- Brisk accommodation reaction
- Bilateral involvement.

What is the mechanism behind Argyll-Robertson pupils?
Caused by a pretectal lesion in the dorsal midbrain affecting the fibres of light reflex, which spare the fibres of the accommodation pathway that innervate the Edinger–Westphal nuclei

What are features of tabes dorsalis?
- Dorsal column degeneration
- Orthapaedic pain - Charcots joint
- Reflexes - Areflexia and extensor plantars
- Shooting pain
- Argyll-robertson pupil
- Locomotor ataxia
- Impaired proprioception
- Syphillis

What are features of gummatous syphillis?
Destructive granulomata in skin, mucous membranes, bones, viscera

What stage of syphillis is gummatous syphillis?
Tertiary syphillis
What are features of cardiovascular syphillis?
- Aortitis
- Aortic regurgitation +/- aneurysm

What are features of neurosyphillis?
- Asymtpomatic neurosyphillus - postive CSF serology without symptoms ro signs
- Meningovascular syphillus - subacute meningitis with CN palsies, GUMMA, paraperesis
- General paresis of the insane - progressive dementia, brisk reflexes
- Tabes dorsalis - lightening pains in legs, ataxia loss of reflexes, neuropathic (charcot’s) joint
- Argyll robson pupuil
What could cause the following?

Tertiary syphillis - gummatous syphillis
What are features of early congenital syphillis?
Presentation before 2 years
- Prematurity + IUGR
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Nasal chondritis
- Skin rash
- Osteochondritis
- Neuro symptoms - cranial nerve palsies, hydrocephalus
What are features of late congenital syphillis?
Presentation after 2 years
- Craniofacial abnormalities
- Hutchison’s triad - hutchisons teeth, intersitial keratitis, CNVIII deafness
- Neurosyphillis
- Saber shins
- Frontal bossing
- Paroxysmal cold haemoglobinuria
How would you investigate if you suspected syphillitic infection?
-
Bloods - TP IgG/IgM, TPPA, RPR
- TP IgG/IgM
- EIA = enzyme imune assay (remains life long in the presence of current or past infection) TREPONEMAL SPECIFIC
- TPPA = T pallidum particle agglutination (remains life long in the presence of current or past infection) TREPONEMAL SPECIFIC
- FTA-ABS (fluorescent antibody absorption) (remains life long in the presence of current or past infection) TREPONEMAL SPECIFIC
- RPR = rapid plasma reagin test (correaltes with disease activity) TREPONEMA NON SPECIFIC
- VDRL = venereal disease research lab test (marker of treatment efficaicy) NON TREPONEMAL SPECIFIC
- Imaging - CXR, ECHO, CT/MRI
- Other - swab + dark-field microscopy (FROM LESIONS)
What type of organism is trepnema pallidum?
Coiled Spirochaete
What is TPPA?
Serum T pallidum particle agglutinin
What is RPR testing for syphillis testing?
Serum rapid plasma reagin test
Correlates with disease activity, and can also be used as a marker of treatment efficacy
Why might you consider doing a CXR in someone with syphillis?
Cardiac abnormality
Why might you do an ECHO in someone with syphillis?
Looking for cardiac abnormalityif suspected
How would you manage someone with early syphillis (<2 years)?
- Benzathine penicillin IM 2.4 MU
- Consider Doxycycline 100mg Bd if allergic
How would you manage late syphillis (>2 years)?
- Benzathine penicillin 2.4MU im weekly for 3 doses
- Consider Doxycycline 100mg bd po 28 days if allergic
What is lymphogranuloma venerum?
A STD caused by the invasive serovars L1, L2, L2a or L3 of Chlamydia trachomatis
What are features of lymphogranuloma venerum?
Painless papule/ulcer, which can be followed by:
- Lymphadenopathy
- Fever
- Arthritis
- Pneumonitis
Can also have haemorrhagic prostatitis
What is chancroid?
A bacterial STD caused by infection with Haemophilus ducreyi. It is characterized by painful necrotizing genital ulcers that may be accompanied by inguinal lymphadenopathy
What would you want to look for on examination of someone with an STI in a male?
- Retract foreskin
- Inpect urethral meatus
- Scrotal contents/tenderness/swelling
What might you look for on exmaination in a woman with a suspected STI?
- Vulval examination
- Speculum examination
- Bimanual examination for adnexal tenderness
- Palpate abdomen for masses
- Consider PR exam - if anal symptoms
- Inguinal lymph nodes
- Oral mucosa
What is pelvic inflammatory disease?
Results when infection ascend from the cervix or vagina into the upper genital tract. It includes endometritis, salpingitis, tubo-ovarian abscess and pelvic peritonitis.
Salpingitis is used interchangably with PID
What are the most common causes of pelvic inflammatory disease?
- Chlamydia (most common)
- Gonorrhoea
- Uterine instrumentation
- Post-partum infection
What are symptoms of PID?
- Lower abdominal pain - usually bilateral
- Increased vaginal discharge (cervicitis)
- Heavy mesntrual bleeding (endometriosis)
- Irregular bleeding
- Postcoital bleeding
- Deep dyspareunia
Suspect in any female with lower abdo pain with unusual cervical/vaginal discharge
What are signs of PID?
- Mucopurulent discharge from cervix with contact bleeding - cervicitis
- Adnexal/suprapubic tenderness
- Cervical motion tenderness
- Pyrexia
- Palpable adnexal mass
Cervical excitation
How would you diagnose PID?
Clinical diagnosis mostly, but laparoscopy is the gold standard (only indicated if diagnosis is uncertain)
- Bloods - FBC + CRP + Blood cultures (if unwell)
- Other - swabs
What precautions may a woman who is pregnant with HSV have to take to protect her unborn child form HSV infection?
- Delivery by C-section - if PRIMARY HSV infection contracted after 34 weeks (Risk of infecting baby is very high if delivered vaginally)
- If primary infection > 2 months prior to delivery - vaginal delivery likely to be safe to baby as antibodies will have been passed on.
- If patient has developed HSV in the first trimester - small risk of miscarriage
- Aciclovir - generally is not advocated before 20 weeks.
What are complications fo PID?
- Tubo-ovarian abscess
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome - liver capsule inflammation with perihepatic adhesions
- Recurrent PID
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Subfertility/infertility
- Bilateral hydronephrosis
How would you manage PID?
- Admit if severe
- Antibiotics - IM ceftriaxone/azithromycin + PO doxycycline + metranidazole
- Drain abscess
- Consider anti-emetics - if vomiting
There should be a low threshold for treatment
What are some of the features of chronic PID?
- Pelvic pain
- Menorrhagia
- Secondary dysmenorrhoea
- Discharge
- Deep dyspareunia
Why can bilateral hydronephrosis occur as a complication of PID?
Due to local inflammation of the ureters - causes them to stenose and back up
What STI’s are associated with Ftz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome?
- C. Trochamatis
- Can be in gonorrhoea
What is the following?

Ftiz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome


