Non-malignant breast disease Flashcards
What is acute pyogenic mastitis?
Painful acute inflammatory condition of the lactigerous duct which usually occurs weeks after delivery.
S. aureus is the most common cause (transmitted y infant during lactation).
How do organisms get into the breast tissue to cause acute pygenic mastitis?
A crack in the nipple - infection is usually confined to one segment of the breast
What can occur as a complication of acute pygenic mastitis?
Breast abscess
How do breast abscesses present?
Painful, hot swelling of breast segment. Erythema and tenderness wtih palpable lump.

How would you manage someone with a breast abscess?
- Antibiotics
- Repeated US guided drainage as often as needed
What is ductal ectasia?
Condition in which the lactiferous duct becomes blocked or clogged.
The ducts are dilated and filled with white–green viscid matter, which may be discharged from the nipple.
If bloodstained, this can be mistaken for carcinoma, but there is no relationship to malignancy.
When in a womans life does ductal most commonly occur?
During menopause - normal changes where ducts dilate with age.
How does someone with ductal ectasia present?
- Nipple discharge - green/brown/can be bloody “cheesy”
- Nipple retraction - due to eventual duct fibrosis
- Lump
May also present with microcalcification on routine mamogram.
Non cyclical mastalgia.
How would you manage someone with ductal ectasia?
- Refer for diagnosis
- No treatment normally needed
- Advise to stop smoking
- Exision of duct in persistant/recurrent cases
What would you advise someone with ductal ectasia to stop doing?
Smoking
What is fat necrosis?
Fibrosis and calcification after trauma to the breast eg seatbelt injury/prior surgical intervetnion.
Macroscopically, the tissue is yellow and haemorrhagic, with flecks of calcification.
Fibrous tissue is also present, the amount depending on the duration of the condition.
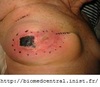
How do those with fat necrosis of the breast present?
- Firm lump (painful/painless)
- History of trauma
(Can mimic carcinoma clinically and mammographically)
More likely to occur in overweight women.

How would you manage someone with fat necrosis of the breast?
- Refer for triple assessment
- No treatment once diagnosis confirmed - usually resolves spontaneously
What is gynaecomastia?
Gynaecomastia is benign enlargement of the male breast tissue. The breast may resemble that of a young adolescent female in appearance and consistency, or there may be a firm, mobile disc beneath the nipple
What is a fibroadenoma?
Commonest type of primary benign tumour which arises from overgrowth of collagenous mesenchyme of one breast lobule.
They involve proliferation of both the connective tissue stroma and the glands.
Peak incidence fibroadeoma
20-24 years
How do fibroadenomas present?
Firm, smooth, painless, well-circumscribed mobile lump in the breast
May be multiple
How would you manage someone with a fibroadenoma?
- Observation and reassurance
- Refer for USS +/- FNA - if unsure
- Consider surgery if large (>3cm)
Does a fibroadenoma progress to malignancy?
No
When do fibroadenomas tend to present?
<30 yrs
Partially hormone regulated so may regress after menopause
What is a duct papilloma?
Commonest cause of discharge
Arise from solitary lesion within a large duct. They consist of branching fibrvascular cores covered by epithelium.
Are a wart like growth that sits just behind areaolar
Presentation of duct papilloma
Nipple discharge
Mass feels elongated 0 along lumen of duct
Management duct papilloma
Microdeochectomy - excision of duct
What is the commonest cause of a mobiile lump?
Fibroadenoma

What is the commonest cause of ill-defined lump or lumpy areas?
Fibrocystic changes

What is the commonest cause of clear nipple discharge?
Duct ectasia

When do breast cysts occur most commonly?
Perimenopause
How do breast cysts present?
- Benign, fluid filled rounded lump
- Can be painful - worse during second half of menstrual cycle
- Not fixed to surrounding tissues so is mobile
- Red, hot, tender swelling
Commonly in those aged 40-45
Management of breast cyst
Aspiration nd cytology if bloody fluid suggestive of malignancy
Aspiration and reassurance
Can commonly recurr, slight increased risk of breast cancer.
What is the most commonly implicated organism in a breast abscess?
Staph aureus
What investigation would you do if you suspected a breast abscess?
Breast USS
What could a breast abscess be linked with in elderly women?
Could be part of mammary duct ectasia
Typical cause of cyclical mastalgia?
Occurs in response to hormonal changes of menstrual changes
Pain from mid-cycle to menstruation
Breast heaviness and lumpiness
Consider fibradenosis
Typical causes of non cyclincal breast pain?
- Mastitis
- Trauma
- Inflammatory breast cancer
- Duct ectasia
- Drugs (HRT, antidepressants, spironolactone, digoxin)
How would you manage mastalgia?
- Analgesia - paracetamol, NSAIDs
- Primrose oil/Starflower oil - GAMELONIC ACID (few SEs)
- Continuous/severe - Low dose Danazol or Bromocriptine
What referred pain could cause mastalgia?
- Arthritis or chest wall
- Lung disease
- Angina
- Gallstones
- Others - HRT
What would be your differential diagnosis for the following?

- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Dermatitis
- Paget’s disease
How would you investigate the following?

- Punch biopsy
- Mammogram
- Consider triple investigation
How would you investigate nipple retraction?
Mammogram and USS
How would you investigate Nipple discharge?
- Clinical exam
- Mammogram
- USS
- Discharge cytology
What would pussy nipple discharge indicate?
Infection
What might milky nipple diuscharge indicate?
- Pregnancy
- Prolactinoma
- Post-pregnancy
What might bloody nipple discharge indicate?
Intraduct papilloma/malignancy
What might toothpaste-like nipple discharge indicate as a cause?
Duct ectasia
What are causes of gynaecomastia?
- Genetic/Gender disorder (Klinefelter)
- Young boy (pubertal)*
- Neonate*
- Estrogen
- Cirrhosis/ Cimetidine/ Ca Channel blockers
- Old age*
- Marijuana
- Alcoholism
- Spironolactone
- Tumors (Testicular & adrenal)
- Isoniazid/ Inhibition of testosterone
- Antineoplastics (Alkylating Agents)/ Antifungal(ketoconazole)
What drugs can cause gynaecomastia?
- S = Spironolactone
- A = Alcohol
- C = Cimetidine
- K = Ketocanazole
- E = Estrogen
- D = Digitalis, digoxin
What is phyllodes tumour
Tumour of fibro-epithelial stroma (majority benign)
Presentation of phyodelles tumour
Firm lump that is fast growing. Large masses.
Commonest in women aged between 40-50 who haven’t yet been through menopause.
What is seen on imaging of phyllodes tumour?
Leaf like appearance
Management of phyllodes tumour
Wide excision - can be benign, borderline, malignant.
Follow up needed due to risk of recurrence.
Mastectomy for large tumours.
Briefly discuss the following:
- Fibroadenoma
- Breast abscess
- Fat necrosis
- Intraduct papilloma
- Duct ectasia
- Fibroadeoma:
- Firm, smooth, well circumscribed mobile limb (non tender)
- Breast abscess
- Pain wrose second half of menstrual cycle
- Fat necrosis
- Firm localised lump (trauma associated)
- Need to exclude carcinoma
- Intraduct papilloma
- Blood stained nipple discharge
- Duct ectasia
- Green, brown, bloody “cheese” secretions


