Fibroids Flashcards
What are fibroids?
Benign smooth muscle tumours of the uterus (leiomyomas). They are often multiple, and vary in size from seedlings to tumours. They grow in response to oestrogens and progesterones so don’t tend to progress following menopause.

Risk factors for fibroids
Family history
Afro-caribbean ethnicity
Nulliparity/uniparity
How would you describe the location of the following fibroid?

Submucosal fibroid - protrude into uterine activity
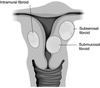
How would you describe the location of the following fibroid?

Subserosal fibroid - project out of uterus into peritoneal cavity

How would you describe the location of the following fibroid?

Intramural fibroid - within uterine wall

How do fibroids form?
Arise from the myometrial layer of the uterine corpus or, less commonly, the uterine cervix, and may occur singly or multiply. Fibroids may remain within the muscular layer (intramural) or protrude outwardly to become subserosal in location or inwardly towards the endometrial cavity, where they become known as submucous fibroids. Subserosal and submucosal fibroids may become pedunculate
When do firboids enlarge?
- Pregnancy - may cause pain, lampresent, obstruct.
- When on OCP
Grow in response to oestrogen and progesterones. Growth is cyclical.
What are symptoms of fibroids?
60% asymptomatic
- Menorrhagia - if enlarge uterine cavity surface area
- Dysmenorrhoea
- Intermenstrual Bleeding - submucous/polyp
- Pelvic pain (pain, pressure or dymenorrhoea)
- Pelvic mass
- Infertility
- Bloating
- Urinary complaints - if pressure on bladder
- Constipation
- Dyspanuri
Why might fibroids be painful?
- Pedunculated fibroids become twisted
- Red degeneration following thrombosis
Why can patients with fibroids experience problems with infertility?
- Submucosal fibroids may interfere with implantation
- Large/multiple tumours distort uterine cavity - may cause miscarriage
What mass effect problems can fibroids cause?
- Bladder compression - frequency, urinary retention
- Venous drainage - leg swelling, varicose veins
- GI - constipation
What investigations would you consider doing if you suspected fibroids?
- TVUS+ Biopsy
- Imaging - Pelvic USS +/- doppler
- Other - Hysteroscopy +/- Endometrial biopy
What might you find on Pelvic USS in someone with fibroids?
Fibroids shape - varies depending on location

Why might you perform endometrial biopsy in someone with suspected fibroids?
Exclude endometrial cancer - if post-menopausal
What might you find on pelvic examination of someone with fibroids?
Firm, enlarged and irregularly shaped uterus
What options are available for medical management of fibroids?
-
Menorrhagia management
- IUS
- Incetions eg depo-provera
- OCP
- Transexamic acid
-
GnRH analogues - goserelin, leuprorelin
- NOT LONG TERM DUE TO DEMINIERALISATION OF BONE
- Ullapristal acetate
How do GnRH analogues help when treating fibroids?
Shrink the fibroids
How does Ullapristal acetate help with fibroids?
Selective progesterone receptor modulator - shrinks fibroids and induces amenorrhoea
What surgical options are available for the management of fibroids?
- Transcervical resection submucous fibroids
- Myomectomy for intramura and subserosal- risk haemorrhage & hysterectomy need caesarean if pregnancy after
- Uterine artery embolisation recommended for women wishing to keep family
- Hysterectomy if family complete
What is the only cure for fibroids?
Hysterectomy
What are complications of fibroids?
- Recurrent fibroids
- Labour/elivery complications
- Acute torsion
- Mechanical incarceration
- Significant haemorrhage
- Severe infection
- Infertility
- Miscarriage
What is UAE?
Uterine artery embolisation
What investigation would you need to do before performing UAE?
MRI pelvis
What is a major side effect of ullapristal acetate?
Deranged LFTs


