Spine Flashcards
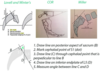
Safe zone for occipital screw placement
Triangular region created by connecting 2 dots 2cm lateral to the external occipital protuberance, and a point 2 cm inferior to it
Point B on the pictures

Slip angle greater than what degree is associated with greater risk of progression?
>50 degrees
6 things to do if a neuro alert during scoliosis surgery
- check equipment
- check blood pressure >90mmHg
- check Hgb
- reverse or lessen correction
- wake up test
- remove implants if spine stable

Risks of postoperative spinal infection
Longer OR time
Immunocompromised state
Increased blood loss (decreases circulating Abx)
Poor nutritional status
Obesity (BMI >35kg/m^2)
Use of instrumentation or OR microscope
Prior spinal surgery or local radiation
Longer constructs or more extensive procedures
Tobacco or alcohol use
Multiple trauma
Anklylosing spondylitis trauma
What must you do?
CT scan of spine
Often skip fractures
Fieldig Classification of AARD
Type I:
Unilateral facet subluxation with intact transverse ligament
Type II:
Unilateral facet subluxation with 3-5mm of anterior displacement (injured TL)
Type III:
Bilateral anterior facet displacement of >5mm
High risk of neuro compromise
Type IV:
Posterior displacement of Atlas (C1)
Safe zone for halo application (anterior pins)?
Lateral 1/3 of eyebrow, below the equator (site D in figure)
Avoids supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves

In facet dislocation, what must you do after successful reduction and why?
MRI - to look for disc herniation
What age does the secondary ossification center of the dens fuse with the rest of C2?
~12 years
Normal range of kyphosis in mid-thorcic spine (T5-12)
20-50 degrees
Power’s Ratio
Basion to posterior arch/Opisthion to anterior arch
Normal is 1
Abnormal: occipito-atlantal instability
Three types of Diastematomyelia?
- boney
- fibrous
- cartilaginous
Why do you have to use a paediatric spinal board for paediatrics? What age do you have to use it until?
To compensate for large head
Paediatric boards have an occipital cutout to compensate for this
Use until 8 years
Name 6 surgical options for degenerative spondy:
Laminoplasty
Laminectomy no fusion
Laminectomy UNinstrumented fusion
Laminectomy + instrumented fusion
(all of the above ± PLIF/ALIF/TLIF)
Dynamic stabilization (see pic)
Lumbar interspinous spacers (prevents extension)

Treatment algorithm for AARD
Acute
- Soft collar, anti-inflammatories, exercise program
Acute >1 week
- Head halter traction and bracing
Subluxation > 1month
- halo traction and bracing
Subluation > 3 months, late diagnosis or neuro deficits
- Posterior C1-2 fusion
If a patient presents with a cervical rotational deformity what injury should you think of?
Unilateral facet dislocation
Disc herniations at the following levels with affect which nerve root?
- C2-C3
- C7-T1
- T4-T5
- L2-L3
- L5-S1
1 - C3
2 - C8
3 - T4
4 - L3
5 - S1
Interpret:
a) ADI < 3 mm
b) ADI between 3 and 5 mm
c) ADI > 5 mm
a) Normal
b) Transverse Ligament Rupture
c) Transverse Ligament and Alar Ligaments Ruptured
Most common locations for pseudoarthrosis in adult spinal deformity?
L5-S1
Thoracolumbar junction
(so any junctional area)
Why is discography not so good?
It causes accelerated disc degeneration and loss of height.
What are the components of TLICS and what score means surgery?
- Morphology
- Neurologic injury
- Status of PLC
5 or more get OR
What type of vertebral malformation is most likely to cause a progressive congenital scoliosis?
Unsegmented bar with a contralateral hemivertebrae
Tx. is PSIF with resection of vertebrea
Components of PLC?
Supraspinous ligament
Interspinous ligament
Facet capsule
Ligamentum flavum
Complications of vertebroplasty/kyphoplasty
Cement extravasation
Cement Embolism
new fracture
neurologic compromise

How to improve outcomes (arthrodesis) in fusion for spondy?
Pedicle screws
Interbody fusion
Non-smokers (major risk for pseudoarthrosis)
Rate of tandem stenosis for patients with lumbar or cervical stenosis?
20%, so image other area if symptoms aren’t clear
5 conditions resulting in Atlanto Axial Instability?
- Downs
- RA
- Dens Fracture
- Atlas Fracture
- Transverse Ligament Rupture
Outcomes of SPORT trial with respect to degenerative scoli
Surgical intervention > non surgical at 2 years and 4 years
No difference in surgical method used
Patients with predominantly leg pain did the best
Pelvic incidence
Pelvic tilt
Sacral slope
Which are position dependent?
Pelvic tilt and sacral slope are position dependent
pelvic incidence does not change after skeletal maturity

What is abnormal structure in congenital muscular torticullis?
Tight SCM
Most common nerve injury with myelopathy decompression?
C5 palst
Treatment is observation
With OPLL and myelopathy, what guides your choice of appraoch?
1) If kyphotic = Have to go ANTERIOR and do corpectomy/OPLL resection
**** Risk of dural tear
2) If lordotic = Can go posterior and do laminoplasty or laminectomy/fusion without OPLL resection
Risk factors for pseudoarthrosis of anterior single rod technique
Smoking
Weight >70kg
Thoracic hyperkyphosis >40 degrees
Risks of Low back pain
Obesity
Smoker
Male
Lifting
Vibration
Prolonged Sitting
Job dissatisfaction
Two surgical options for a curve > 50 in a Juvenile patient?
- Growing rods, VEPTR
- Anterior and Posterior fusion (have to do both sides to avoid crankshaft phenomenon)
Physical exam findings of diastematomyelia:
a) 4 local findings
b) 5 associated conditions
- hairy patch
- skin dimple
- Subcutaneous mass
- teratoma
- scoliosis
- tethered cord
- cavus foot
- claw toes
- clubfoot
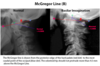
Describe Chamberlains line
Line from dorsal margin of hard palate->posterior edge of the foramen magnum
abnormal if tip of dens > 5 mm proximal Chamberlain’s line
normal distance from tip of dens to basion of occiput is 4-5 mm
this line is often hard to visualize on standard radiographs

What is the success rate of nerve root injections for lumbar herniations?
50%
Describe peltic tilt:
Angle formed between
- Line parallel to side of radiograph
- Line from center of femoral head to the center of the S1 endplate

Isthmic spondy (and spondy in general) is associated with what change in pelvic incidence?
Increased
THINK: higher incidence allows it to slip easier
indications for hemivertebrectomy
- Hemivertebrae (failure of formation) with progressive curve causing truncal imbalance and oblique takeoff
- Patients less than 4-5 years
- Curve less than 40 degrees
Main finding of:
Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of a thoracolumbar burst fracture without neurological deficit. A prospective, randomized study. - Wood 2003
Operative treatment of patients with a stable thoracolumbar burst fracture and normal findings on the neurological examination provided no major long-term advantage compared with nonoperative treatment.
Which of the following shows increased production when adisc herniates?
- osteoprotegrin (OPG)
- interleukin-1 beta
- receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB ligand (RANKL)
- parathyroid hormone (PTH)
All of them.
5 spinal conditions that can result in Juvenile Scoliosis?
- syringomyelia
- arnold-chiari
- tethered cord
- spinal dysraphism
- tumor
What percentage of Juvenile Scoliosis patients have an abnormal MRI?
18-25%
Define Sacral slope
Angle formed between:
- horizontal line parallel to the bottom of radiograph
- Line parallel to the S1 endplate

Name 6 syndromes/diseases assocated with basilar invagination
Klippel-Feil
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Morquio syndrome
achondroplasia
spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
occipitocervical synostosis
Describe cervicomedullary angle
Angle formed between:
line along ventral surface of medulla
line along upper cervical cord
less than 135 suggests impending neurologic compromise

What is the relationship between:
- sacral slope
- pelvic incidence
- pelvic tilt
pelvic incidence = pelvic tilt + sacral slope
Outcomes of SPORT trial regarding herniated nucleus pulposus?
Surgical intervnetion > nonoperative,
although both groups did well
Define instability on flexion-extension x-rays as it pertains to lumbar spine spondy
4mm of translation or 10 degrees of angulation of motion compared with adjacent motion segment
When do the basilar synchondrosis and secondary ossification centers fuse?
Basilar synchondrosis: age 6
Secondary ossification center: appears at 3, fuses at age 12
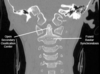
2 deformities associated with Klippel Feil?
- Scoliosis
- Sprengels
6 presenting symptoms in patients with DISH
Dysphagis and stridor
Hoarseness
Sleep apnea
Difficulty with intubation
Cervical myelopathy
Spinal Fracture
What is defined as instability on flex-ex radiographs?
Instability: >3.5mm of motion between flexion and extension views
Two common complications following Postero Decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis?
- Pseudoarthrosis (5-30%)
- Adjacent level disease (2.5% per year)
4 clinical findings associated wiht Scheuermann’s
Hyperlordosis
Spondylolsis
Scoliosis
Pulmonary compromise in curves >100 degrees
For revision anterior cervical approach with previon RLN injury what do you do?
Go from the same side to avoid bilateral injury
Technique for posterior reduction of facet dislocations?
- Can only do after disc is dealt with if present
- Can burr tops of superior facets
- Put lateral mass screws in and then use these to reduce
- Fuse one level above and below
Scheuermann’s kyphosis.
What’s the outcome of non-op curves (by size)
>75 degrees: severe pain that affects ADLs
What percentage of RA patients have atlantoaxial instability?
50-80%
SO CHECK FOR IT - especially in oral exam
Indications & Contraindications for vertebroplasty/kyphoplasty
See pic
New studies show that it may be beneficial, at least in the short term, for vertebral compression fractures

Injury to what nerve structure causes retrograde ejaculation?
Superior hypogastric plexus
(retroperitoneal approach to spine)
What disorder causes a passively correctable chin-on-chest deformity?
Dropped head syndrome
vs. AS (non-correctable chin on chest)
Caused by cervical paraspinal weakness
What is more likely to present with dysphagia: OPLL, DISH or Ank Spon?
DISH
4 dangers of Smith-Robinson Anterior approach to C-spine
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Sympathetic chain
Carotid sheath
Post-operative hematoma
Best phase on MRI to look for foraminal stenosis and what to look for?
T2
Look for loss of perineural fat
What is the treatment for low grade isthmic spondylolistheis that is painful and fails 6 months of physio?
12 weeks of TLSO
Hypoglossal (CN 12) injury during ACDF - tongues deviates which way?
towards side of injury
Indications for MRI in scoliosis workup (7)
Atypical curve pattern (left thoracic curve, short angular curve, apical kyphosis)
Signs of syndromic or neural axis pathology
- Cavus feet
- Signs of dysraphism
- Asymmetric abdominal reflexes
- neurologic symptoms or pain
- Signs of Marfan’s/Down’s/Lysosomal storage disease
Rapid progression
Excessive kyphosis
Structural abnormalities
Child 20 degrees
All patients with congenital scoliosis
Collagen type in nucleus pulposus
Type II
It’s like articular cartilage
What is a Hangman’s fracture?
Traumatic anterior spondylolisthesis due to bilateral fracture of pars interarticularis
Halo application principles in adults (location, pins, tightness)
4 pins
- 2 anterior pins over lateral 1/3 of eyebrow below equator
- 2 posterior pins opposite of anterior ones
8 inch pounds of torque
Best treatment of this fracture?
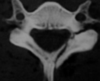
Fracture separation of lateral mass
2 level posterior spinal instrumented fusion (PSIF)
If a patient has a hypoglossal nerve injury after anterior approach, what side will their tongue deviate towards?
Towards the affected side
4 complications with lumbar disc herniation surgery
Dural tear
Recurrent HNP
Discitis
Vascular catastrophy
What is the most common neurologic finding after cervical laminoplasty?
C5 palsy
NOT recurrent laryngel nerve palsy: you’re not going anterior for a laminoplasty
What is the treatment for syringomyelia?
- Cevical dempression without fusion initially once it becomes symptomatic
- Instrumented fusion 3-6 months later
In adults, what is the first line of treatment in spondylolysis with no neuro symptoms?
Observe
Difference between Type 2 and Type 2A Levine/Edwards?
Levine/Edwards is Hangman’s fractures
2 = > 3mm displacement, disc is compromised
Treat with traction then Halo vest.
2 A –> Horizontal fracture
NO TRACTION
Reduce with extension then Halo vest.
C-spine myelopathy. Indications for anterior only, posterior only and anterior + posterior decompression ± fusion
Name 1 absolute contraindication to posterior only decompression
Anterior only (ACDF): gold standard for 1-2 level disease
Posterior only: <13 degrees kyphosis
- Some say <10 degrees but definitely <13 degrees
Anterior + Posterior: rigid kyphosis >10 degrees and multilevel disease (>2 levels)
Kyphosis >13 degrees is an absolute contraindication to any posteriorly only decompression

Changes during normal aging of IV discs
Changes are like that of articular cartilage
Decrease in:
- Collagen II (changes to fibrocartilage)
- nutritional support
- water content
- Absolute number of cells
- Proteoglycans
- pH
Increase in:
- Collagen I
- Keratin sulfate : chondroitin sulfate ratio
- Lactate
- Degradative enzyme activity
No change in:
absolute quantity of collagen
Subaxial insatbility is present in what percent of RA patients?
20%
How long do you have to culture acid fast bacili?
Up to 10 weeks
Do osteoblastoma respond to NSAIDs?
No
When do you brace in scoliosis for:
Congenital
Infantile
Juvenile
AIS
Congenital:
May brace supple compensatory curves
Infantile:
Cobb >20 (consider, but many resolve spontaneously)
Cobb >30 for sure
Juvenile:
Cobb >20
Adoelscent:
Cobb >25
Findings associated with Scheuermann’s kyphosis
Anterior wedging across 3 consecutive vertebra
Disc narrowing
Endplate irregularities
Schmorl’s nodes
- Herniation of disc into vertebral endplate
Scoliosis
Compensatory hyperlordosis
Important to look for spondylylysis
What level does the aorta bifurcate?
L4
4 differences between DISH & AS spine
DISH:
right thoracic often in isolation (protective pulsatile aorta)
nonmarginal osteophytes
preservation of disc space
Flowing candle wax (vs. squared off bamboo spine of AS)
Non HLA-B27 association

What shoulde you rule out with muscualr torticullis with no palpable SCM mass?
Klippel feil
AARD (atlanto-axial rotatory deformity)
3 Indications for PLIF in spondylolisthesis
Severe slip
Neurologic compromise
Saggital imbalance
Name 5 mimickers of lumbar radiculopathy

Major technical factor in improving fusion rates in posterior spinal fusion?
pedicle screws
Differential for myelopathy? (5)
- Stroke
- B12 deficiency
- Movement disorder
- ALS
- MS
What type of sub-cervical spinal trauma almost always gets posterior instrumented fusion 2 levels in each direction?
Thoracolumbar Fracture Dislocation
Commonly occurs at junction (T10-L2)
What cobb angles will puts the patient at risk of cardiopulmonary decline and mortality?
Cardiopulmonary decline:
Thoracic curves >60 degrees affect pulmonary function tests
Thoracic curves >90 degrees affect mortality
What are three signs of segemental spinal instability (specifically lumbar)?
- Degenerative scoliosis
- Spondylolisthesis (degenerative or isthmic)
-
Surgical over resection
- > 50% of either facter
- Complete laminectomy
4 risk factors for myelopathy in OPLL
>60% spinal canal stenosis
≤6 mm of space available for the cord
increased cervical range of motion
OPLL that is laterally deviated within the spinal canal
(JAAOS 2014)
Is bullet removal from spinal canal more likely to improve motor outcomes in incomplete injuries in T12-L4 or from T1-T11?
T12-L4
Most common type of spondylolysis/listhesis in adult?
Degenerative
Symptomatic acute osteoporotic spinal compression fracture (within 5 days). name the medical treatment?
Calcitonin x 4 weeks
AAOS 2010 - moderate evidence for
Who gets OPLL?
ASIANS, Men
Radiographic definition of central stenosis:
Cross sectional area less than 100cm2
or
less than 10mm AP diameter on axial CT
Where is the most common site for isthmic spondy and where is the most common location that predisposes to progression?
L5-S1 most common
L4-5 will progress
In Brown-Seqard syndrome what deficit is there in the contralateral limb?
Spinothalamic - pain and temperature
Findings in anterior cord syndrome
lower extremity affected more than upper extremity
loss:
LCT (motor)
LST (pain, temperature)
preserved:
DC (proprioception, vibratory sense)
Worst prognosis
May mimic complete cord
Where does pseudosubluxation happen and how do you verify diagnosis?
1) C2 on C3
2) Swischuks line should be wihting 1.5 mm of C2 sp and the deformity should reduce on extension xray
What is important to look for on physical exam if considering deformity correction or THA on a patient with Ank Spon?
Hip flexion contractures
In C-spine immobilization of a paediatric patient, where do you want to keep the external auditory meatus?
Keep external auditory meatus inline with the shoulders
This puts them in a slight position of extension
True or false: All congential scoliosis from vertebral malformations is progressive
False.
Depends on etiology. Things like a single unsegmented hemi vertebrae is unlikley to progress.
Unsegmented bars almost always progress.
What other organs do you need to image before surgery on congenital scoliosis?
Heart and kidneys
In doing a laminectomy and fusion, what is the biggest risk of adjacent level change?
Laminectomy (no fusion) at the adjacent level
In AARD, which side will the patient’s head be tilted and rotated to?
Ipsilateral rotation and contralateral tilt of the head in relation to the lateral mass of C1
Opposite of Torticollis
Best candidate for radiosurgery for spinal tumours?
Life expectancy > 1 months, b/c effects don’t come on for 3-4 weeks
How does a well repaired dural tear affect outcomes after lumbar decompression?
No effect
What is rate of overall complications with adult spine deformity correction?
10-20%
Most common surgical technique resulting in pseudoarthrosis in adult spinal defomrity correction?
Posterior fusion only
I think they mean no instrumentation??
Cord syndrome prognosis from best to worst
Brown-sequare (best)
Central cord
Posterior cord
Anterior cord (Worst)
What condition is the Wiltse appraoch best used for?
Far lateral lumbar disc herniation
What do you call a bar that crosses the spinal cord and causes a cleft in the spinal cord?
Diastematomyelia
T/F: helmets increase risk of c-spine injury
False
They do not increase risk of c-spine injury
4 conditions that pre-dispose to traumatic cervical spine trauma
- DISH
- Ank Spon
- Previous Fusion
- Connective Tissue Disorders
What is the most imporant radiographic finding that may predict complete neural recovery post decomrpessive surgery for atlantoaxial instability?
PADI/SAC > 13mm
Anterior reduction technique of facet dislocation?
- Can only do for a unilateral facet dislocation
- Caspar pins in proximal and distal bodies
- Rotate upper pin towards the dislocation
2 Treatment options for synovial facet cyst
Laminectomy & decompression
- classically 1st line treatment but high recurrence rates
Facetectomy & instrmented fusion
- Some now consider this first line
Most important factor when deciding treatment of Axis fracture?
Stability of Transverse Ligament
If it is ruptured then do either C1-C2 or Occ - C2 fusion
Harris Rule of 12: Describe
If either of:
Basion-Dens interval (BDI)
or
Basion posterior axia line interval (BAI)
>12mm, its a sign of occipito-atlanto instability/dislocation
What is radiologic definition of Scheurmans?
Anterior wedging of > 5 degrees accross 3 continuous vertebreas
Are results for revision lumbar discectomies worse, better or the same?
Equivalent
How do vertebral compression fractures affect mortality?
Increase it x2 to matched controls
Higher in men
higher with earlier age of fracture
However, improved with cement augmentation (kyphoplasty) by 2-7 years
(JAAOS 2014)
Functional level of the following spinal level injuries
C4
C5
C6
C7
C4 —> Electric wheelchair with head/chin controls
C5 —> electric wheelchair with hand control
C6 —> Manual wheelchair with sliding board
C7 —> Manual Wheelchair with independent transfers
What is the radiographic sign of an unstable degenerative spondylolisthesis?
> 4mm translation on flex/ex
Where do you find free nerve endings in the spinal unit?
PLL, annulus fibrosis, facet joint
NOT in the nucleus pulposus
Risks of pseudoarthrosis in adult spinal deformity correction (7)
Age >55
kyphosis >20 degrees
positive sagittal balance >5cm
hip arthritis
smoking
thoracoabdominal approach
incomplete lumbopelvic fixation
What reflex differentiates between intracranial and intraspinal lesions?
Jaw Jerk
If positive, then it’s an intracranial cause of myelopathic symptoms
Name 2 radiographic indices that indicate poor outcomes in Spondylolisthesis
Increased lymbosacral kyphosis
Positive sagittal balance
(not really the same)
HOw do you avoid junctional kyphosis post-op Scheuermann’s kyphosis?
Make proper selection of levels
Avoid overcorrection
limit to 50% of original curve
General indications for surgery in adult spinal deformity (6)
Curve > 50 degrees
Sagittal imbalance
Curve progression
Intractable back pain or radicular pain that has failed nonop
Cardiopulmonary decline:
Cosmesis (controversial)
What spinal lesion causes an occipital headache worse with valsalva?
Syringomyelia
What part of the spinal cord is least sensitive to radiation (ie for stereotactic radiosurgery)
Thoracic spine
(JAAOS 2014)
Describe TLICS
Max score: 10
>4 operate
4 = dealer’s choice

Radiographic findings of Scheuermann’s kyphosis
anterior wedging across three consecutive vertebrae
disc narrowing
endplate irregularities
Schmorl’s nodes (herniation of disc into vertebral endplate)
scoliosis
compensatory hyperlordosis
important to look for spondylolysis on lumbar films
What are the parameters for a structural minor curve according to lenke?
> 25 degrees and do not bend out to less than 25 degrees with lateral bend
Patient placed in garder wells tongs and reduced with traction for jumped facets. Patient develop nystagmus and other stroke like symptoms.
What is the most likely cause?
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Rate of pseudo arthrosis in single elvel ACDF?
5-10%
45-year-old manual laborer presents to the office with acute onset back pain that radiates to his right leg after carrying a heavy object. He also has mild non-progressive weakness with ankle dorsiflexion on that side. What should be his initial treatment
PT and NSAIDs should be first line
Most common cause of sudden death in RA spine?
Basilar invagination
Patient presents with pain and neuro symptoms.
Plan?
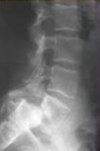
L4-S1 posterior instrumented fusion with anterior column support
What is an absolute contraindication to C1-2 transarticular screws?
Aberrent vertebral artery
Indications for surgery in Atlantoaxial instability: (3)
ADI >10mm (even if no neuro deficits)
SAC/PADI less than 14 (in RA)
Progressive myelopathy
Describe pedicle screw start points in T/L spine
T-spine
- midpoint of Transverse process and lateral pars
- (note: midpoint in height, but you can also follow the superior aspect down to get to the same point - see image)
Mid T spine
- Junction of midpoint of transverse process and lateral 1/3 of superior articular process
Distal T
- Junction of transverse process and lateral pars
Lumbar
- Junction of midpoint of transverse process and 2mm lateral to pars (lateral aspect of facet joint / mamillary process / lateral pars)

Treatment for recurrant lyrangeal nerve injury with anterior approach?
Observe for 6 weeks, if no better consult ENT.
What is the best type of MRI to look for spondylodiskitis?
T1 with gad and fat suppression
How do you measure kyphosis at the C-spine level?
C2-7 kyphotic level
Local kyphotic level
Describe Meyerdeng classification
I: <25%
II: 25-50%
III: 50-75%
IV: 75-100%
V: spondyloptosis
Adult spondylolishtesis at L5-S1. What is the nerve root that is involved?
L5
It affects the exiting nerve root as it causes foraminal stenosis
What is a hangman’s fracture?
Bilateral fracture of pars of Axis allowing for anterolisthesis of C2 on C3
What are 5 indications for MRI in scoliosis?
- Abnormal curve (think Lenke)
- Neurologic deficit
- Infantile or Juvenile onset
- Male patient with large curve
- Thoracic kyphosis > 30 degrees
3 techniques for C1-2 fusion
C1 Lateral mass + C2 pedicle/pars/translaminar (Harms)
C1-2 Transarticular (Magerl)
Sublaminar wiring (Brooks, Gallie)
Describe McRae’s line
defines the opening of the foramen magnum
the tip of the dens may protrude slightly above this line, but if the dens is below this line then impaction is not present

On x-ray, criteria for absolute and relative cervical stenosis:
Lateral xray:
Absolute: canal diameter less than 10mm
Relative: canal diameter 10-13mm
Normal canal diameter is 17mm
Torg-Pavlov ratio (canal:vertebral body width)
Normal is 1
Doesn’t work for athletes
Halo application principles in paeds (location, pins, tightness, vest)
Generally: more pins, less torque
Pins
- 6-8 pins
- Anterior pins: must be lateral enough to avoid frontal sinuses, supratrochlear & supraorbital nerves
- Posterior pins: anterior enough to avoid temporalis muscle
Torque
- 2-4 inch pounds of torque, or “finger tight”
Brace
- Less than 2 years: Minerva
- >2 years: custom
±CT scan to:
- avoid cranial sutures
- avoid thin skull regions
- limit complications
6 dangers in retroperitoneal approach to lumbar spine?
Sympathetic chain: lateral aspect of vertebral body
Genitofemoral nerve: anterior surface of psoas muscle attached to fascia
Segmental lumbar arteries & veins: Branches from aorta
Aorta: Bifurcates at L4
Ureter: lies between psoas fascia and peritoneum
Superior hypogastric plexus: Injury leads to retrograde ejaculation
Name as many syndromes/causes of dural ectasia (there are 9 on this list)
Dural ectasia: ballooning or widening of the dural sac which can result in posterior vertebral scalloping and is associated with herniation of nerve root sleeves
- Marfan syndrome: dural ectasia has been observed in 60-90% of patients; in these patients, the dilatation of the dural sac is almost always in the lumbar region
- neurofibromatosis type 1
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- ankylosing spondylitis
- osteogenesis imperfecta
- trauma
- post surgery
- tumours
- scoliosis
What is the natural history of OPLL
What percentage of patients get myelopathy
Most will get radiological progression of OPLL
Only half experience worsening clinical symptoms
Contraindications for RTS with cervical stenosis (3)
1) Loss of CSF around Cord or any cord deformity
2) Multiple episodes of transient quadraparesis
3) Bilateral symptoms
Most powerful LOCATION for an osteotomy in AS
Lumbar spine
What are the three ligaments of the C1-C2 ligamentous complaex?
Alar Ligaments
Apical Ligaments
Transverse Ligament
Three findings associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis?
- sacroiliitis
- uveitis
- HLA-B27 +
(Bamboo spine)
What do you need to look for on physical exam of a CP kid for consideration of scoliosis surgery?
hip or knee contractures
What is the most important thing to look for in physical exam for AAI?
Myelopathy
What is the name of the classification system of Spondylolysis? Describe it
Wiltse-Newman
I: dysplastic
II: Isthmic
- a: pars fatigue
- b: pars elongation due to multiple healed stress fracture
- c: acute
III: degenerative: pars instability without a pars fracture
IV: traumatic
V: Neoplastic
Which side do you approach from when using retroperitoneal approach to spine? Why?
Left: Aorta is more resistant to injury
What finding on radiology suggests an occipital condyle is unstable?
Avulsion fractures of alar ligaments.
This is a type 3 injury.
Other types are stable and only need c-collar.
Three characteristics of a pathologic scoliosis curve?
- painful
- rigid
- less severe than other types of scoliosis
Who gets Charcot spine and how do you treat it?
Patients with a spinal cord injury (i.e. with neurologic damage)
It causes instability so the primary treatment is posterolateral instrumented fusion +/- TLIF at level of Charcot disk
Mortality rate of halo in patients aged >79?
21%
Avoid it in this population
What level of the Thoracic or Lumbar spine has smalles pedicle length and diameter?
T4
Name 7 reasons for obtaining an MRI with a patient who presents with scoliosis (older)?
- atypical curve
- rapid progression
- increased kyphosis
- structural abnormality
- neurologic symptoms or pain
- deformity of foot
- assymetric abdominal reflexes
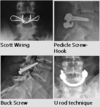
4 techniques for pars repair
Screw
tension wiring
Screw + hooks
U rod
Risks of type II odontoid fracture nonunion: (8)
>6mm displacement
Posterior displacement >5mm
Further posterior displacement after application of a Halo vest >2mm
Angulation > 10 degrees
comminuted fracture
Fracture gap >1mm
Age >50
Delay in treatment >4 days
*Highest rate of nonunion comes from posteriorly displaced an angulated Type II fractures
IN stereotactic radiosurgery, why is the planning treatment volume (PTV) less than the clinical target volume?
To account fro any errors in targeting
(area to be treated with radiation is 2-3mm less than the CTV)
What tract is the mainly affected in central cord syndrome?
Lateral Corticospinal
UE is more medial so more affected.
Three differences between osteoblastoma and osteoid osteoma of the spine?
- OO more likely to respond to NSAIDs
- OB usually bigger (> 1.5 cm)
- OB more likely to have neural involvement
Two surgical options for a symptomatic thoracic disc?
1) Anterior/ Transthoracic (can use VATs)
2) Costotransverectomy (Lateral)
Name 1 poor and 5 good prognostic indicators for surgery to treat lumbar disc herniation
Positive predictors of good outcome with surgery
- Leg pain is chief complaint
- Positive SLR
- Weakness that correlates with nerve root impingement on MRI
- Married
- Age >41
Negative predictors of outcome
- Worker’s compensation
Contraindications to Smith-Peterson Osteotomy?
Anterior fusion at level of osteotomy
b/c the osteotomy hinges through the disc space
Anterolateral approach to lumbar spine
what crosses your field at L4-5
Iliolumbar vein
Crosses left to right as it drains into vena cava
Post-op degenerative spony outcomes
Better pain relief
better functional outcomes
Two indications for open debridement of pediatric diskitis?
- Failure of non-op
- Abcess pressing of thecal sac or paraspinal abscess
Three xray findings of pediatric diskitis?
Loff of lordosis
Disc space narrowing
Late finding of end plate erosions ( 3 weeks)
Burst fracture with retropulsion and > 50% collapse, TLICS score of 3, neuro intact, how do you treat?
- Fit for TLSO
- Dynamic views in TLSO
Removal if C-collar is allowed if patient is:
- Alert
- Awake
- Not intoxicated
- Has no neck pain, tenderness or neurologic deficits
- Has no distracting injuries
Must fulfill ALL above criteria
What is the least useful exam for lumbar stenosis?
A. Physical exam
B. MRI
C. Treadmill test
D. SF-36
Physical exam
Often people present asyptomatic and will have a + treadmill test
Describe a smith peterson osteotomy. How much correction can it give?
Posterior element osteotomy and hinging through disc
Gives 10 degrees of correction per level osteotomized
What cervical approach has the higher infection rate?
Posterior
What are the 6 primary manifestations of VACTERL?
1 ) Vertebral malformation
2) Anal atresia
3) Cardiac malformations
4) T-E fistula
5) Radial anomolies
6) Renal malformations
What Spinal Cord Tumor am I?
Often found on filum terminale
Histology: Rosettes
Intramedullary
Ependymoma
List 5 things to consider in an ank spond patient with a spine injury
More likely to have spine fractures than normal population
Low energy mechanism
High bleeding risk
High risk of epidural hematoma
More likely to be Osteoporotic
More likely to present with neuro deficit
More likely to have progressive (delayed) neuro deficit (b/c of epidural hematoma)
Always unstable (long lever arms and involved anterior and posterior columns)
Higher rate of loss of reduction
30% mortality
50% morbidity
Difficult to brace b/c of severe kyphosis
Lots of reported complications with non-op treatment such as traction and bracing
Profound medical co-morbidities (lungs especially)
3 indications for emergent MRI with Facet injury?
- Altered mental status
- Neuro decline during reduction
- Failed closed reduction
Otherwise get after reduction before OR
Negative prognostic indicators in spinal stenosis surgery
CV comorbid conditions (most important)
Increased comorbid conditions
disorder affecting gait
depression
back pain
scoliosis
Damage to what nerve with anterior approach to lumbar spine causes retrograde ejaculation?
superior hypogastric plexus on L5 body
What non-fracture spinal sequelae can be fatal in AS patients?
Epidural hematoma
Get MRI if suspected
(3) Absolute contraindications to Halo application. Name as many relative ones as possible (5)
Absolute:
- Cranial fracture
- Infection
- Severe soft tissue injury (especially near pin sites)
Relative
- Polytrauma
- Severe chest trauma (b/c of vest)
- Barrel-shaped chest
- Obesity
- Advanced age (this is becoming more absolute)
>12mm on BDI or BAI indicates what?
Anterio rC0-1 displacement
(the classification states that it’s C0 anterior on C1)
Two requirements for treating Chance fracture with TLSO?
1) Neuro intact
2) PLC Intact
** follow over time for progressive kyphosis
Factors contributing to development of sagittal imbalance in adult spinal deformity (4)
Osteoporosis
Preexisting scoliosis
Iatrogenic instability
Degenerative disc disease
Post-traumatic spinal pain in AS patient, what MUSt you do?
CT it
x-rays are not enough
+/- MRI
How do the columns fail in a Chance fracture?
Anterior in compression.
Middle, posterior in tension.
What sense is preserved in anterior cord syndrome?
Dorsal columns - prorioception and vibration
Large/Anterior spinal abscesses are hallmarks of what infection?
TB
3 x-ray findings for lumbar disc herniation
Loss of lordosis
Loss of disc height
Lumbar spondylosis (degenerative changes)
In congenital vertebra, name which have the most risk of scoliosis progression from highest risk to lowest risk
Unilateral bar + contralateral hemi (5-10 deg)
double hemi (4-10 deg - double of a single hemi)
Unilateral bar (5-6 deg)
Unilateral hemi (2-5 deg)
Wedge vertebra (less than 2 deg)
Block vertebra (less than 2 deg)

4 conditions associated with dural ectasia?
Marfan syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
neurofibromatosis type I
ankylosing spondylitis
After pseudoarthrosis of ACDF, what is the preferred treatment?
It is associated with higher rates of what?
Posterior fusion
Higher rates of fusion & overall complications
Even though it has higher overall complications, it is still preferred treatment b/c of higher fusion rates
What is the main prognostic difference between flexion and extension teardrop fractures?
- Flexion are unstable whereas extension are usually stable
- Extension is usually smaller fleck and common at inferior C2 endplate
- Flexion is larger piece and has posterior subluxation into canal of remaining body
Congenital scoli with in kid younger than 5 years old. How do you treat if failure of formation vs. failure of segmentation (describe with curve magnitude)
Failure of formation:
Age less than 5 AND
Curve less than 40: hemiepiphysiodesis
Curve > 40: excision
Failure of segmentation
In-situ fusion
10 Complications of OR for spinal stenosis
Major complication
- wound infection (10%)
- deep surgical infections are to be treated with surgical debridement and irrigation
- pneumonia (5%)
- renal failure (5%)
- neurologic deficits (2%)
Minor complication
- UTI (34%)
- anemia requiring transfusion (27%)
- confusion (27%)
- dural tear
- failure for symptoms to improve
Combined lateral mass overhang should be:
less than 7 mm (8.1mm with radiographic magnification)
Incidence of L5 nerve root injury with spondy reduction
30%
NOT proportional in any way to amount/degree of reduction
Most common nerve injured with halo application and resultant deficit?
CN 6 (Abducens)
Lack of lateral eye movement
Usually treat with observation.
Operating on which side anteriorly in the cervical spine has a higher rate of recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy?
Equivalent
Classically right sided was worse but new studies show injury rates are equivalent
Risks of prolonged immobilization in rigid C-collar
increased risk of aspiration
Inhibitions of respiratory function
Increased risk of decubitus ulcers
Possible increase in intracranial pressure
Three indications for OR with lumbar disc herniations?
1) Failed conservative treatment (6 weeks)
2) Progressive or significant weakness
3) Cauda Equina
Powers ratio. Interpret
>1
less than 1
>1: anterior dislcoation C0-1 (head goes anterior)
Less than 1:
Posterior atlanto-occipital dislocation (head goes posterior)
Odontoid fracture
Ring or atlas fracture

How do you test for CSF (ie dural tear) on swab/analysis
beta-2-transferrin
Two causes of a pathologic scoliosis?
Osteoid osteoma
Osteoblastoma
In adult spinal deformity, what is the best predictor of pre and post-operative symptoms?
Sagittal balance (ie kyphosis)
What are the 2 approved uses of rhBMP?
rhBMP-2 is FDA approved for:
use together with the lumbar tapered fusion device (LT Cage; Medtronic) in single-level ALIF from L2 to S1 levels in degenerative disc disease.
Open tibial shaft fractures treated with IM nail with 14 days
Radiographic signs of unstable C1 fracture
Combined lateral mass displacement of >7mm (8.1mm with radiographic magnification) on open mouth view
ADI >3mm (normal is <3mm)
- ADI 3-5mm: TL injury, alar & apical ligaments intact
- ADI >5mm: Injury to TL & alar ligaments ± tectorial membrane
Describe ranawat classification for RA C-spine
I: pain only
II: subjective weakness, hyperreflexia, dysaesthsia
IIIa: objective weakness, long tract signs, ambulatory
IIIb: objective weakness, long tract signs, non-ambulatory
What are two types of strut graft that can be used for an anterior decompression for spondylodiskitis?
1) tricortical autograft from Ilium, rig or fibula
2) Titanium mesh cage filled with autograft
In AIS, what curves are least and most likely to progress?
Skeletally mature:
Least: curves <45
Most: Thoracic curves >55 degrees
45-55 - don’t know
Skeletally immature:
>25-30 deg will progress
Difference on x-ray between DISH and AS?
DISH spares the disc spaces
vs.
AS: discs will be ossified, resulting in fusion of vertebrae
See pic of AS
Briefly Describe a pedicle subtracting osteotomy. How much correction can you get from a PSO?
Posterior osteotomy including vertebral body
Can give 30-35 degrees of correction

How do these lesions affect disc space?
- TB spondylodiskitis
- Pyogenic spondylodiskitis
- Tumor
- TB spondylodiskitis = No early disk involvement
- Pyogenic spondylodiskitis = Involves the disk space
- Tumor = Spares the disk space
Where should sagittal C7 plumb line end?
posterior superior corner of S1
Procedure if neurologic event (as per MEPs, SSEPs) occurs intraop:
Take control of the room
Check for technical errors
Test screws
Make sure there is no anesthetic affecting readings
Check blood pressure and evaluate if low
MAP > 75-90mmHg
Check hemoglobin and transfuse as necessary
Check O2 sats >90%
Lessen/reverse correction
Administer Stagnara wake up testWake the patient up and evaluate voluntary motor function
Ask them to move their feet
Remove instrumentation if spine is stable
Call for second opinion
Give steroids
What is the relationship between pelvic incidence and Spondylolisthesis?
Direct linear relationship between pelvic incidence and the severity of the spondylolisthesis
Three indications for surgery according to Wai?
- unpinch a nerve
- instability
- restore a balanced spine
Two techniques to increase maximal insertional torque for pedicle screws?
1) under tap by 1 mm
2) Straightfroward trajectory parallel to superior endplate
Describe pedicle - nerve root match/mismatch
Pedicle - nerve root:
Mismatch: different level nerve root travels under numbered pedicle
ie: C-spine: C6 nerve root travels under C5 pedicle
Match: same level nerve root exits numbered pedicle
ieL L-spine: L5 nerve root travels under L5 pedicle
C8 nerve root allows transition b/c no C8 pedicle

Most sensitive and specific test for predicting neurologic compromise in subaxial instability?
Cervical height index
=body height/width
<2 is 100% sensitive & specific for predicting neurologic compromise
*So normally should be 2x taller than it is wide - flattened is bad
Contraindications to transarticular (Magerl) technique
Large, medially located vertebral artery
Hypoplastic C2 pars
Inability to obtain an anatomic reduction of C1 over C2
Substantial thoracic kyphosis that precludes the angle necessary for this approach
Causes of AARD (10)
Degenerative:
- Down’s syndrome
- RA/JRA
- Os odontoideum
Traumatic
- Type I odontoid fracture (rare)
- Atlas fracture
- Transverse ligament injuries
Other:
- Grisel’s disease (retropharyngeal irritation)
- Morquio’s
- Tumour
- Congenital
Are uni or bilateral facet dislocations easier to reduce?
Which are easier to maintain reduction once reduced?
Bilateral easier to reduce
Unilateral easier to maintain reduction once reduced
What is the incidence of neural axis abnormalities in infantile scoli?
Same as that of juvenile idiopathic
20-30%
What is Swischuk’s line?
the Spinolaminar line drawn from C1-C3
Tests for pseudosubluxation of C-spine in paeds
normal: C2 should be within 1.5mm of spinolaminar line
Antibiotic treatment for Potts disease?
Isoniazid
Rifampin
Pyrazanimide
*** 9 - 18 months!!!
What is characteristic of a Type IIA Hangman’s fracture? What is indicated and contraindicated in treatment?
IIA: Horizontal fracture line
Absolute contraindications: traction
Classic treatment: ACDF

When is calcitonin useful for compression fractures?
Acute (, 4 days old) osteoporotic compression fractures.
Use for four weeks.
Useful for pain.
Where is diastematomyelia most common?
L1 - L3
What percent of RA patients has basilar invagination?
40%
What is Swischuks line?
Line from Sp of C1 to C3, the SP of C2 should be within 1.5 mm in true pseudosubluxation
In patients with adult scoliosis requiring long thoracolumbar fusions, what is the major advantage of extending the fusion to the sacrum as opposed to ending at L5
Improved correction and maintenance of sagittal balance
Describe retroperitoneal approach to L-spine
- Oblique Incision From posterior half of 12th rib to lateral border of rectus abdominis
- incise subcutaneous fat
- expose aponeurosis of external oblique muscle
- divide external oblique in line with fibers
- divide internal oblique in line with incision and perpendicular to muscle fibers
- divide transverus abdominis in line with skin incision
- bluntly dissect plane between retroperitoneal fat and psoas fascia
- retract peritoneal cavity medially
- bring ureter medially with peritoneal cavity
- follow surface of psoas muscle to vertebral bodies
- tie off segmental lumbar arteries of aorta in the field of dissection
- L4/5 disc space
- mobilize aorta to the contralateral side
- place needle in disc and take lateral xray to identify level
- L5/S1 disc space
- work between the bifurcation of aorta
- place needle in disc and take lateral xray to identify level
Which side of the curve do osteoid osteomas live in?
concave side, usually at the apex
Acute managmement of occipito-cervical instability
NO movement of the head
Must immobilize head/neck with sandbags & tape (C-collar doesn’t do much in these cases)
Mark patient with instructions not to move head
3 radipgrahic lines for basilar invagination:
Ranawat’s line
McGregor’s line
Chamberlain’s line
McRae’s line
Diagnostic criteria Scheuermann’s kyphosis
>3 consecutive wedged vertebrae > 5 degrees
Thoracic kyphosis >45 degrees
or
Thoracolumbar kyphosis > 30 degrees
Positive predictors for spinal stenosis surgery
good self reported health (most important)
higher income (most important)
good self reported ambulatory status
central stenosis
shorter duration of symptoms
younger
male
more expectations for function
T/F: helmets control rotational forces
True
Which myelopathy classification is based on physical exam findings and which is based on functional ability?
a) Nurick is Functional
b) Ranawat is based on exam
4 indications and 1 contraindication to pars repair
spondylolytic defects L1 through L4:
spondylolytic defects of multiple vertebral levels
low-grade but reducible spondylolisthesis at levels
cephalad to L5 with an intact vertebral disk at the level of slippage
Contraindicated in L5 and below
Is DM a risk of pseudoarthrosis of the spine after PSIF?
No
Had 91% fusion rates at 5 months, which is comparable to non-DM
(JAAOS 2014)
What are the different means of getting to a thoracic disc (deep approaches)?
- laminectomy/hemilaminectomy
- transpedicular
- costotransversectomy
- lateral extracavitary
- anterior intracavitary
- thoracotomy
- VATS (video assisted thoracoscopic surgery)
In early onset scoliosis, what are radiologic signs for risk of progression (4)
Rib phase 2 (rib-apical vertebra overlap)
RVAD (Mehta angle) > 20degrees (80% progress)
Cobb angle > 20 degrees
Thoracolumbar curve
Conversely, phase 1 rib (no overlap), RVAD
RVAD
Which nerve roots do central, paracentral and far-lateral discs affect higher than C8 and lower than C8?
Cervical:
central and foraminal disc will affect the same nerve root
Always the exiting one
due to horizontal nerve root anatomy
Lumbar:
paracentral and far lateral affect different roots
paracentral: affects traversing nerve root
Far lateral: affects exiting nerve root

6 Indications for surgery with spondylodiscitis?
- intractable neck pain
- septicemia
- epidural abscess
- neurological compromise
- gross kyphotic deformity with extensive destruction
- failure of conservative treatment.
Type of pars defect in degenerative spondy
NO PARS DEFECT
This differentiates it from adult/paeds isthmic spondy
When will osteoid osteoma caused scoli resolve?
After resection only if performed 15-18 months of age in a child
Indication for bracing in Scheuermann’s kyphosis
Observation alone:
- Kyphosis less than 60 degrees and asymptomatic
- Most patinets fall into this group
Bracing with extension type orthosis Modified milwaukee brace:
- Kyphosis 60-80 degrees in patients Risser 3 or below & asymptomatic
How does Scheurmans differ from physiologic kyphosis?
> 45 degrees
can be painful
rigid
anterior vertebral wedging
Dangers of retroperitoneal (anterolateral) approach to spine?
Sympathetic chain
Ureter
Genitofemoral nerve
Aorta
Segemental lumbar vertebral arteries
Superior hypogastric plexus
Definidtion of instability on flex-ex views in degenerative spondy?
4mm translation
10 degrees of angulation
When is an isthmic spony most likely to progress?
in adolescence during growth spurt
What is a type 1 Dens fracture and what imaging should be performed in these cases?
Avulsion of tip of Dens.
Should do flex/ex views to check for AAI.
Infantile scoliosis normally is which direction?
Left thoracic
(vs AIS: right thoracic)
What is the only cervical dermatome with an autonomous zone?
C4 - over AC joint
After facet dislocation, what is an absolute indication for an anterior approach?
Herniated disc
Two reasons to add posterior instrumentation after doing an anterior decompression and strut graft for spondylodiskitis?
1) Severe kyphosis
2) If the anterior decompression was multilevel
5 Indications for MRI for lumbar discogenic pain
Pain > 1 month and not responding to nonoperative managmeent
Infection (IVDU, hx of fevers/chills)
Tumour: hx of cancer
Trauma
Cauda equina syndrome
Risk factors for OPLL
idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
Hypoparathyroidism
hypophosphatemic rickets
hyperinsulinemia
obesity
Body mass index
insulinogenic index (serum insulin divided by serum glucose)
Two most common types of extradural spinal cord tumours?
Mets
Lymphoma
What lab test confirms CSF fluid?
beta-2 transferrin
Anterolateral approach to lumbar spine
What crosses your field at the sacral promontory (L5-S1)
Median sacral artery
What finding on radiology do you need to check for if doing an anterior cervical decompression?
OPLL (can result in dural tears)
T/F? Spony is not associated with increased risk of back pain in adulthood compared to age-matched individuals
True
NO risk of back pain in adults
What percentage of asymptomatic patients have cord compression from thoracic disc pathology?
29%!!
What is the typical proximal levels with scoliosis correction in CP?
T1 or T2
Spinal ring enhancing lesion on MR + Gad?
Abscess
Where should incision for thoracotomy be?
2 levels above where you want to go

Classic triad of Klippel Feil?
- short webbed neck
- decreased cervical ROM
- low posterior hairline
Outcomes of SPORT trial regarding lumbar stenosis
surgical > nonsurgical at 2 & 4 years
What is a syrinx?
What is a syringomyelia?
a) Fluid filled cavity in spinal cord
b) Fluid filled cavity that expands and causes deficits
Most common site for adult isthmic spondylolysis/listhesis?
L5-S1
L4-L5 is second most common
Indications for decompression of TB spinal Abscess?
(4)
- Neuro deficit
- Presence of caseation
- Failure of 6 months non-op
- Progressive kyphosis or instability
Collagen type in annulus fibrosis
Type I
3 pathological processes associated with sacroiliitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Reiter’s syndrome (oligoarticualr arthritis, conjunctivitis, uveitis)
Joint arthritis
Burst fracture with retropulsed fragment and neuro injury, TLICS is 6:
1) How do you decompress?
2) If posterior, how many levels to instrument?
1) Either anterior or posterior via transpedicle decompression or indirect decompression with distraction and ligamentotaxis
2) One level above and below (old fashioned is three above and below)
What is favoured treatment for sympotmatic synovial facet cyst?
Facetectomy and instrumented fusion
(Lower recurrance rate than laminectomy)
Main problem with MRI of thoracic disc herniation?
High false + rate
C1-2 instability
How does treatment differ if it is redicible vs. irreducible
Irreducible:
Cannot do Magerl
Must do laminectomy and then fuse
Most likley associated injury in a chance fracture?
GI (50%)
Name 4 approaches to the lumbar spine:
Posterior
Wiltse
Anterior intra-peritoneal
Anterior retroperitoneal approach
2 signs on MRI to suggest significant stenosis
- effacement of CSF
- Myelomalacia (bright on T2)
Two conditions associated with vertebral malformations?
1) VACTERL
2) Klippel Feil
How much torque should be on an adult and pediatric halo pin?
a) Adult is 8 inch lbs
b) Pediatric is 2-4 inch lbs, you use more pins to make up for the decrease in torque
Difference between vertebroplasty & kyphoplasty? Which is recommended/not recommended?
Kyphoplasty: creates a cavity in which cement can be injected into. Recommended by AAOS (although limited evidence)
vs.
Vertebroplasty: straight injection of cement into vertebral body - no cavity (NOT recommended by AAOS)
What kind of spondy is associated with spina bifida?
Isthmic
Most common complication following Anterior/ Transthoracic approach (+/- VATs)?
Intercostal neuralgia
A patient has a compression fracture, what are 4 signs that it may be caused by a Met?
- Higher than T5
- Atypical radiographs
- Constitutional symptoms
- Young patient with no trauma history
How do you immobilize a c-spine in a patient younger than 8?
They have relatively large heads. Use a coard with a cut out for the head or sandbags. The auditory meatus should be in line with the shoulder.
What is an absolute indication for fusing to the pelvis with CP scoliosis?
Pelvic obliquity > 15 degrees
anterior decomrpession of OPLL has higher rates of what complication?
Dural tear
Describe McGregor’s line
For basilar invagination
Timeline for treatment of cauda equina syndrome
decompression within 48 hours
shows better recovery of bladder and bowel function and motor and sensory recovery than delayed surgery >48 hours
What is cephalomedullary angle and what does it predict?
- Angle between cerebrum and branstem on saggital MRI
- Severity of Basilar Invagination
What nerve is most commonly injured with reduction of an isthmic spondylolisthesis?
L5
Where is the most common extrapulmonary site for TB?
Thoracic Spine
Normal BDI/BAI?
less than 12mm
>12mm indicates atlanto-occipital dissociation
In Infantile Scoliosis what degrees of curve are associated with a) pulmonary insufficiency and b) cardio pulmonary insufficiency?
a) 60
b) 90
Nerves at risk with medial Halo pins?
Supraorbital
Supratrochlear
What percentage of vertebral compression fractures come to clinical attention?
Less than 30%
4 positive predictors of success in lumbar discectomy and 1 negative predictor
Positive: Leg pain, + SLR, Weakness that corresponds with MRI, Married
Negative: Workmans Comp.
Pedicles angulate more as you move distal.
medial
What part of ATLS do you change for a patient with AS?
May skip C-collar
Do not “correct” their deformity to fit them into a collar
This will cause more damage
What Spinal Cord Tumor am I?
Common
Associated with NF 2
Histology: meningothelic whorls
Meningioma
Three conditions common for RA involving the c-spine?
- Atlanto-Axial istability
- Basilar Invagination
- Sub-Axial Subluxation
What does a fluid sign on MR suggest with a vertebral body lesion?
Osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
What Spinal Cord Tumor am I?
Very common
Associated with NF 2
Forms at dorsal nerve root
S-100 +
Schwanoma
4 angles or clnical tests for AS
Schober test
Chin-brow angle
Occiput to wall angle
Gaze angle
What are Waddells signs?
- Over-reaction
- Simulation (reaction to simulated test)
- Distraction (neg. SLR when distracted)
- Regional (non-dermotermal)
- Tenderness (to light touch)
How much correction can you get with a vertebral column resection?
45 degrees
What spinal condition shows sparing of the right thoracic area?
DISH
What must you do before operating on a c-spine?
CT scan to look for course of vertebral artery
Name the following vertebral levels and landmarks
C2-3
C3
C4-5
C6
C7
T3
T8
T10
L4
S1
C2-3: Mandible
C3: Hyoid
C4-5: thyroid
C6: Cricoid
C7: vertberal prominence
T3: Spine of scapula
T8: nipples
T10: xiphoid
L4: bifurcation of aorta
S1: Bifurcation of iliacs
3 pediatric causes of AAI?
- Morquios
- JRA
- Rotatory AA subluxation
Spondy incidence in Inuit
high!
Not rare
Describe pelvic incidence:
Pelvic Incidence = pelvic tilt + sacral slope
Angle formed by:
- a line from the center of the femoral head to the middle of the S1 end plate
- a line perpendicular to the S1 endplate

5 signs of UMN injury:
- increased reflexes
- inverted radial reflex
- Positive hoffmans
- Positive babinsky
- Sustained CLonus (more than 3 beats)
PADI/SAC: less than what amount is associated with risk of neurologic injury and an indication for surgery?
less than 14mm
>17 is normal
14-17mm is grey zone
Poor prognostic indicators for spinal stenosis
cardiovascular comorbidity
Disordered walking condition
Scoliosis
Depression
Three indications for surgery with spondylodiskitis?
1) Refractory to medical amagement
2) Neurologic deficits
3) Progressive kyphosis or gross instability
If you have an anterior fusion, what kind of spinal osteotomy can you do?
Pedicle subtracting osteotomy
b/c it does not hinge on the disc, but the vertebral body instead

Whar is the most reproducible measure of basilar invagination on xray?
Ranawat Index
(shoulde be > 14 mm)
Measure from center of C2 pedicle to a line connecting the anterior and posterior C1 arches
normal measurement in men is 17 mm, whereas in women it is 15 mm
distance of
most reproducible measurement
Also: cervicomedullary angle on MRI

What are 4 factors supporting pseudosubluxation in paediatric C-spine?
Reduction of subluation with neck extension
Spinolaminar line within 1.5mm of C2
No hx of exam findings of significant trauma
Absence of anterior soft-tissue swelling
What Spinal Cord Tumor am I?
Found at cervicothoracic junction in kids
Histology: Fusiform
Intramedullary
Astrocytoma
Treatment of spine fracture in ank spond?
Long PSIF construct
What abdominal pathology can cause paresthesias along medial aspect of knee that may be confused with L3 sensory symptoms?
PSOAS Abcess
What is Spear Tacklers Spine?
Cervical stenosis due to multiple microtrauma caused by bad tackling technique.
No RTS.
Management of cauda equina syndrome
Decompression
Classic: wide laminectomy + discectomy. “pedicle to pedicle decompression”
However, no comparative studies for wide decompression and discectomy vs. microdiscectomy
What is the organization of the cauda equina?
describe location of Sacral and lumbar roots
Motor and sensory fibers
Sacral roots central to lumbar
Motor fibers anterior, sensory dorsal

What is the indication for pars repair?
Spondylolysis at L4 or above with no listhesis.
Fails bracing.
If at L5 you have to fuse .
Mortality rate of patients over 79 treated with Halo?
21%
Which side do you approach from during an anterior/transthoracic appraoch to the spine? Why?
Left side
Aorta is more resiliant to injury
Avoids liver
How many occipital screws are optimal in an occiput - C2 fusion?
6
First line of treatment for adult spondylolisthesis?
Nonoperative observation
NOT TLSO, although it may be beneficial
This was an orthobullets question
Describe Smith-Robinson Approach
Incision
make transverse skin crease incision at appropriate level
extend obliquely from the midline to the posterior border of the SCN
Superficial Dissection
incise fascia over platysma
spit platysma with finger
identify anterior border of SCM
incise fascia and retract SCM lateral
identify and retract strap muscles medially (sternohyoid and sternothyroid)
identify the carotid pulse and retract carotid sheath lateral
cut through pretrachial fascia
localize superior and inferior thyroid arteries and tie off if necessary
Deep dissection
split longus colli muscles and anterior longitudinal ligament
be aware of sympathetic chain that lies on longus colli lateral to vertebral body
subperiostally disect to expose anterior surface of vertebral body
retract longus colli muscles and ALL laterally
identify level with needle in disc space and lateral xray
How is treatment of Type 2 Dens fractures different in the elderly?
They can’t tolerate Halo so lower threshold to fuse.
In the young can do Halo if no risk factors for non-union. Benefit is preservation of ROM.
What orientation are a) Thoracic and b) Lumbar facets (largest dimension)?
a) coronal
b) saggital
How do you decide betwwen Occiput –> C2 and C1 –< C2 posterior fusion in treatment of AAI?
Either the presence of significant basilar invagination or if C2 is not reducible suggests you should do occ. –> C2 fusion
What percentage of SCI patients have major depressive disorder?
11%
Why do Down’s get occipitalcervical instability and how is it treated?
1) Hypoplastic occipital condyles
2) Occiput –> C2 fusion if symptomatic
What is the finger escape sign suggest?
Myelopathy
(due to intrinsic weakness)
Indication for surgery in Scheuermanns kyphosis
Kyphosis >75 degrees that is rigid in a skeletally mature patient
Neurologic deficit
Spinal cord compression
Severe pain in adults
Name 5 complications with anterior approach to the cervical spine
Postoperative C5 palsy incidence
Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury
Hardware failure and migration
Postlaminectomy kyphosisPostoperative axial neck pain
Vertebral artery injury
Esophageal Injury
Dysphagia & alteration in speech


