Orthopedic Radiology COPY Flashcards
Reasons for radiographic testing in orthopedics
6
- History of blunt trauma
- Deformity of bone or joint following injury
- History of pain, swelling, or loss of motion of a joint, sense of instability
- Infection
- Foreign body
- Night pain
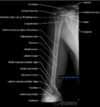
MRI provides good contrast between the different soft tissues of the body, which make it especially useful in imaging the what? 4
- brain,
- muscles,
- the heart
- cancers compared with other medical imaging techniques
Uses of MRI in orthopedics
6
- Evaluate soft tissue injury as apposed to bony injury. Example is ligament injury, tendon injury, muscle
- Better evaluate soft tissue mass
- R/O fluid collection in the body
- Define abnormalities within bone seen on x-ray
- R/O stress fracture or infection
- Evaluate spinal injury
Ligament, tendon, soft tissue evaluation with MRI
- Knee? 6
- Shoulder? 3
- Elbow? 4
- Wrist? 2
- Ankle and foot? 4
- Hip? 1
- Knee:
- ACL,
- MCL,
- PCL,
- LCL,
- meniscus,
- loose body - Shoulder:
- Rotator cuff,
- biceps tendon,
- labrum - Elbow:
- Ulnar and radial collateral ligaments,
- Extensor and flexor tendon insertion for epicondylitis,
- biceps tendon rupture,
- loose body - Wrist:
- Extensor Carpi Ulnaris injury,
- TFCC tear - Ankle and foot:
- Anterior tibial tendon injury,
- peroneal,
- tibial tendon,
- achilles tendon partial tear - Hip: Labral tear
Soft tissue mass with MRI
4
- Lipoma
- Hematoma
- Osteosarcoma
- Ganglion cyst
Use MRI to rule out fluid collection?
4
- Effusion of a joint, shoulder, hip
- No need to MRI, olecrenon bursitis, patellar bursitis
- Infection fluid collection within soft tissue compartments
- Baker’s cyst in the knee
Bone abnormalities
seen on MRI
6
- Stress fracture
- Lytic or blastic lesions seen on x-ray
- Bone contusion (you may find it but dont order one for it)
- R/O occult fracture, scaphoid
- Avascular necrosis
- Osteomylitis
Where are the common stress fracture locations?
4
- tibia,
- metatarsals,
- tibial plateau,
- femoral neck
Spine pathology on MRI? 6
- Herniated disc
- Bulged disc
- Spinal stenosis
- Compression fracture, acute vs chronic
- Neoplasm
- Pars defect
What is this an MRI of?
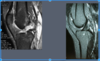
ACL
What is this an MRI of?

Lipoma
What is this an MRI of?

Bone edema
What is this an MRI of?

HNP
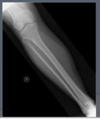
Reasons for ordering CT-scan
4
- Cervical injury, due to multiple overlaping shadows and images on x-ray, CT-scan better r/o cervical fracture after trauma
- Reconstructing and better defining comminuted fractures such as; acetabular fracture, calcaneous fracture, articular fractures
- Evaluating joints for preoperative evaluation for surgery
- CT myelogram of spine for individuals that cannot undergo MRI due to pacemaker or other metal objects. Myelogram is a CT with radiographic dye injected into the dura.
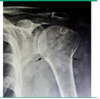
What is this a CT of?

CT Calcaneous Fx
What is this a CT of?

Pelvic fx
What is this a CT of?

Tibial Plateau fx
What are these CTs of?

CT Cervical Fx
Reasons for ordering CT-scan
Reconstructing and better defining comminuted fractures such as?
3
- acetabular fracture,
- calcaneous fracture,
- articular fractures
What is a myelogram?
Myelogram is a CT with radiographic dye injected into the dura.
Bone Scans
- What is it?
- Over what areas can this scan?
- What will the scans show? 2
- What will it not show?
- Bone scans are used best for what?
- Nuclear medicine study in which the patient is injected into a vein with a small amount of radioactive material such as 600 MBq of technetium-99m-MDP and then scanned with a gamma camera, which is sensative to the radioactive material.
- The scan may be a full body study or localized to a body part called a SPECT which will look at smaller lesions.
- The scan will show
- bone turn over and
- osteblastic activity. - It however will not show osteclastic activity.
- Bone scans are used best for bone metastatic disease
What kind of mets disease usually show up on bone scans? 2
Other reasons for use? 3
1.
- prostate cancer and
- less for lytic such as multiple myeloma.
2. Other reasons for scans include, - stress fracture,
- infection,
- occult fractures
What is this bone scan showing?

Bone scan infection
What is this showing on the scan?

Stress Fx