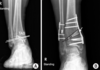
Foot & Ankle Flashcards
Name and describe 2 classifications for charcot foot
Eichenholtz:
Stage 0: joint edema, x-rays negative
Stage 1: fragmentation
- Local edema
- osseous fragmentation with joint dislocation
Stage 2: coalescence:
- decreased local edema
- x-rays show coalescence of fragments and absorption of fine bone debris
Stage 3: Reconstruction
- no local edema
- x-rays show consolidation and remodeling of fracture fragments
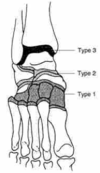
Brodsky
Type 1: (midfoot)
- TMT and naviculocuneiform joints (60%)
Type 2 (Hindfoot):
- subtalar, TN, CC joints
Type 3: Ankle of calcaneus
- A: tibiotalar joint
- B: Follows fracture of calcaneal tuberosity
Type 4: Combination of areas
Type 5: solely in forefoot
How many people get subtalar arthritis 10 years post tibiotalar arthrodesis?
50%
Syndesmosis screw technique
Be specific
2 x 3.5 or 4.5mm syndesmotic screws
Through 3-4 cortices
2-5cm above plafond
Screw material:
No difference between types of metal or bioabsorbable
Cortices:
No difference between 3-4
Number of screws:
2 is better
Position of foot
Recent studies challenge the principle of holding the ankle in maximal dorsiflexion to avoid over tightening
Post-operative care:
Typically non-weight bearing 6-12 weeks
May prolong if screw breakage is a concern
Name 3 gait advantages of total ankle replacement vs. arthrodesis
Increased stride length
Improved cadence
Increased stride velocity
4 common technical errors in Total ankle arthroplasty
Prosthesis is too lateral
Prosthesis is too small - will subside
Failing to solve preoperative varus/valgus malalignment
Attempting to replace an ankle that is too anteriorly subluxed
os trigonum syndrome is associated with pathology in what structure?
FHL
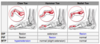
What are Scarf and Ludloff osteotomies used for? Differentiate them in one sentence.
Promixal metatarsal osteotomies for the treatment of moderate hallux valgus, usually in combination with a modified McBride distally.
See picture for differences.

Recalcitrant forefoot plantar ulcers
What is an important aspect of treatment
TAL vs. gastrocs lengthening
Decreaes plantarflexion and decreases pressure on forefoot
Neuropathic joint
Technetium bone scan will be
Indium WBC scan will be
Tc: ± positive in charcot (positive for OM)
indium WBC scan: negative in charcot (+OM)
Sectioning of which collateral ligament leads to more instability?
Accessory
B/c it attaches directly to the plantar plate
(vs. proper collateral, attaches to the proximal aspect of the phalanx)

Three differentials for posterior ankle pain not involving the Achilles.
- Os Trigonum Syndrome
- Posterior impingement
- FHL Tendonitis
Describe ankle arthroscopy portals
Anteromedial
- Primary viewing portal
- Established 1st
- medial to tib ant & lateral to medial malleolus
- Danger: saphenous nerve & vein
Anterolateral:
- Primary viewing portal
- Lateral to peroneus tertius & superficial peroneal nerve & medial to lateral malleolus
- Danger: Dorsal cutaneous branch of SPN
Anterocentral
- Anterior viewing portal
- Medial to EDC and lateral to EHL
- Not commonly used due to risk to DP artery
Posterolateral
- Posterior viewing portal
- 2cm proximal to tip of lateral malleolus
- Between peroneal tendons and achilles tendon
- Danger: sural nerve and small saphenous vein
Posteromedial
- posterior viewing portal
- just medial to achilles
- Risks: posterior tibial artery

Diagnosis & Treatment (chronic)

Ankle synovitis
Arthroscopy and synovectomy
What are 2 associated conditions of anterior ankle impingement?
Ankle instability (up to 35% will continue to have pain after stabilization procedure)
OCD
(Technically NOT OA, b/c this is pre-OA)
Best predictor of post-op ROM with TAA
Pre-op ROM
Differenes of Juvenile HV vs. Adult:
Juvenile is:
- Often bilateral
- Often familial
- Pain is not the primary complaint
- varus 1st MT with widened IMA usually present
- DMAA usually increased
- often associated with flexible flatfoot
In os trigonum syndome, in the absence of an obvious os trigonum, what may be another cause?
scar tissue behind posterior talus (where the os should be)
Found on MRI
4 pathologic conditions secondary to cavus foot
(what does cavus foot cause, NOT what causes cavus foot)
Lateral column stress fractures
Lateral ligament injury
peroneal tendon injury
Lateral column overload
1st step in lisfranc ORIF?
Intercuneiform reduction and fixation
Name & Describe classic tendon transfer for foot drop
Bridle Procedure
- Classically PTT, TA & PL transfer & tritendon anastomosis
Tib post:
- transferred to middle/lateral cuneiform
- THROUGH split in tib ant
Tib Ant
- Anastomosed to Tib post
Peroneus Longus
- PL: cut 5cm above fibula
- Proximal end sewn to PB
- distal end is anastomosed to newly transferred PTT
Effect
- As tib post pulls, it will also pull on PL and TA, causing dorsiflexion & eversion (motion lost with peroneal nerve injury)
Classification of Hallux Rigidus:
Coughlin & Shurnas Classification
Grade 0:
- Stiffness with normal x-ray
Grade 1:
- mild pain at extreme range of motion
- X-rays show mild dorsal osteophyte and normal joint space
Grade 2:
- Moderate pain with range of motion
- Moderate dorsal osteotomy
- <50% joint space narrowing
Grade 3:
- Significant stiffness and pain at extreme ROM. No midrange pain
- Xrays show severe dorsal osteophyte >50% joint space nrrowing
Grade 4:
- significant stiffness and pain at extreme ROM AND pain at mid-range
- x-rays: same as grade 3
List some differentials for failed treatment of ankle sprain (i.e. missed concommitant injuries/pathology)
- injury to the anterior process of calcaneus
- injury to the lateral or posterior process of the talus
- injury to the base of the 5th metatarsal
- osteochondral lesion
- injuries to the peroneal tendons
- injury to the syndesmosis
- tarsal coalition
- impingement syndromes
Indications for 1st MTP arthrodesis in HV:
CP
Down’s
Ehler-Danlos
RA
Gout
Severe DJD
What is the mechanism for injury to the superior peroneal retinaculum?
Dorsiflexion & inversion
During reflexive contraction of the peroneal muscles