SM_238b: Cancer of the Penis Flashcards
Describe epidemiology of penile carcinoma
Epidemiology of penile carcinoma
- Consistently low annual incidence rates among industrialized countries
- Prevalence rates are higher in non-industrialized countries
- Principally in uncircumscribed men
- Neonatal circumcision virtually eliminates risk of invasive squamous cell carcinoma but not CIS
- Adult circumcision does not decrease risk
- Most common between 50-70 years of age
- African American = Caucasian, Asian American lower, and Hispanic American higher
____ and ____ are risk factors for penile cancer
HPV and chronic inflammation are risk factors for penile cancer

Describe signs and symptoms of penile carcinoma
Signs and symptoms of penile carcinoma
- Erythematous precursor lesion
- Visible and palpable mass: glans (60%), prepuce (23%), shaft (9%)
- Large and/or atypical appearing wart
- Frank ulceration
- Carcinoma in situ
- Exophytic mass or ulceration
- Pain
- Periodic bleeding
- Purulent discharge
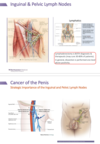
- 40-80% have palpable inguinal nodes
- Metastases to lung, liver, bone, brain in 1-10% of patients on presentation
Describe pitfalls of clinical staging of penile cancer
Pitfalls of clinical staging of penile cancer
- 30-60% of palpable nodes are secondary to reactive lymphadenitis: infection, chronic inflammation
- Up to 60% of palpably normal groins harbor metastatic disease
- 95% of patients with untreated nodal metastases die within 3 years
Penile cancer most commonly develops from ____, most are ____, half are ____, and half are related to ____
Penile cancer most commonly develops from mucosal surface of the glans of penis or inner prepuce, most are squamous cell carcinoma, half are HPV linked, and half are related to chronic inflammatio

Metastatic cancer to penis presents with ____, ____, ____, ____, and ____
Metastatic cancer to penis presents with priapism, palpable mass, pain, hematuria, and urethral bleeding

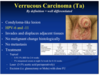
This is ___ of penis

This is squamous cell carcinoma of penis

Survival for squamous cell carcinoma of the penis is ____
Survival for squamous cell carcinoma of the penis is presence or absence of inguinal lymph node involvement

HPV has ____ and ____ oncoproteins
HPV has E6 and E7 oncoproteins
- E6: prevents p53 from making damaged cells commit suicide
- E7: binds to Rb and prevents it from stopping damaged cells from growing

____ is a surrogate marker for HPV 16
P16INKA4 is a surrogate marker for HPV 16

Squamous cell carcinoma of penis involves overexpression of ___
Squamous cell carcinoma of penis involves overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)

Patients with squamous cell carcinoma of penis who are HPV+ have ___ survival
Patients with squamous cell carcinoma of penis who are HPV+ have greater survival
Gardasil is a ___ valent vaccine
Gardasil is a 9 valent vaccine
Describe premalignant penile lesions
Premalignant penile lesions
- HPV related: carcinoma in situ (erythroplasia of Queyrat and Bowen’s disease), Bowenoid papules, giant condyloma accuminatum (Bushke-Lowenstein tumor), warty / basiloid / mixed PeIn
- Non-HPV related: lichen sclerosus, cutaneous penile horn, leukoplakia, pseudoepitheliomatous / keratotic / micacenous balanitis / differentiated PeIN
Describe Bowen’s disease / erythroplasia of Queyrat
Bowen’s disease / erythroplasia of Queyrat
- Considered premalignant lesions or CIS of penis
- Bowen’s occur mainly on shaft, erythroplasia occurs on glans / prepuce
- Bowen’s not associated with visceral malignancies
- Progression to squamous cell carcinoma occurs in 10%
- Treatments vary

Bowenoid papules are ___
Bowenoid papules are a variant of penile intraepithelial neoplasia

Giant condyloma acuminata is ___
Giant condyloma acuminata is Bushke-Lowenstein tumor
This is ___

This is undifferentiated pelvic intraepithelial neoplasia

Lichen sclerosis involves ____ and ____
Lichen sclerosis involves meatal stenosis and urethral stricture

This is a ____

This is a cutaneous penile horn

This is ___
This is leukoplakia of the penis

This is ____

This is pseudoepitheliomatous, keratotic, and micaceous balanitis

This is ___

This is differentiated penile intraepithelial neoplasia