SM 183a - Lung Cancer Flashcards
What kind of lung cancer is this?
How do you know?
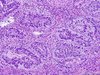
Adenocarcinoma
Glandular structures are present
(Simple columnar epithelium)

A biopsy of squamous cell carcinoma will show…
Keratin pearls

True or false:
Lung cancer has the highest annual incidence of cancer among men and women in the United States
False
It is the leading cause of cancer death, but not the leading new diagnosis
What is Pemberton’s Sign?
What might it indicate?
Pemberton’s sign:
A person’s face turns bright red when they raise their arms
Concerning for a tumor in the chest that is compressing the SVC
Where are squamous cell carcinomas usually located?
Centrally
Near the hilum, can create cavitary lesions
Paraneoplastic syndromes are most often associated with what type of lung cancer?
Small cell lung cancer
Pareneoplastic syndrome = altered immune system response to a neoplasm, can caus systemic, non-metastatic effects
What is the treatment for small cell carcinoma?
- Limited stage
- Chemotherapy + radiation
- Curative intent
- Extensive stage
- Chemotherapy + immunotherapy
- Palliative intent
What kind of lunc cancer is this?
How do you know?
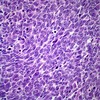
Small cell lung cancer
Small, densely packed blueish cells with neuroendocrine differentiation

What kinds of lung cancers cause central tumors?
Usually smoking-related tumors
- Squamous cell
- Small cell
- Sometimes adenocarcinoma
What is the goal of treatment for stage I-III lung cancer?
Curative intent
May involve surgery, surgery + chemo, surgery + chemo + other
How do you identify a site for biopsy when working up a patient with suspected lung cancer?
Use imaging to determine whether there is a chance it has metastasized
If so, biopsy that site - this will aid in staging
What are the most common sites of metastatic lung disease?
- Pleura
- Bone
- Brain/spine
- Liver
- Adrenal glands
What are the 3 mainstays of treatment for stage IV lung cancer?
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy: Molecular targets
- Immunotherapy: Stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells
What kinds of lung cancers cause peripheral tumors?
Adenocarcinoma
Large cell carcinoma
Most patients with lung cancer present with state ____ disease
Most patients with lung cancer present with state 4 (metastatic) disease
What is the difference in presentation between tumors that cause SVC syndrome and pancoast tumors?
Tumors that cause SVC syndrome are likely obsructing the superior vena cava
Pancoast tumors are apical, and result in nerve impingement
What is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in America?
Lung cancer
How is lung cancer diagnosed?
- Tissue sampling is required
- Biopsy a distant site if metastatic disease is suspected
- Usually performed if imaging/other signs are concerning
Where are adenocarcinomas usually located?
May be central or peripheral
What is the goal of treatment for stage IIIC/IV lung cancer?
Palliative
Most conduive to personalized therapy based on molecular and PDL1 analysis
What kind of lunc cancer is this?
How do you know?

Squamous cell carcinoma
- Squamous cells present
- Flat-ish, scaly appearance
- Can see keratin pearls
(A subset of NSCLC)

What are the signs of pancoast tumor?
Depends on the site of involvement, but may include…
- Shoulder pain
- Brachial plexus abnormalities
- Horner’s syndrome
- Hoarseness
- Due to impingement of laryngeal nerves
_________ lung cancer occurs almost exclusively in smokers
Small cell lung cancer occurs almost exclusively in smokers
What kinds of lung tumors have neuroendocrine differentiation?
Small cell tumors
Carcinoid tumors


