SM 179a - Viral Infections Flashcards
How can adenovirus be prevented?
Oral, live, nonattenuated vaccine for types 4, 7, 21
Separate vaccines given separately
Reserved for military recruits (not available to the public)
What kind of nucleic acid does parainfluenza virus (PIV) have?
(-)ssRNA
Whart are the roles of hemaglutinin and neuraminidase in influenza pathogenesis?
Hemaglutinin and neuraminidase play a major role in inluenza A
-
Hemaglutinin
- Binds sialic acid
- Limits species transfer
-
Neuraminidase
- Role in viral release in propagation
What are the signs and symptoms of 2019-nCoV?
Fever
Cough
Shortness of breath
Myalgias, confusion, headache, sore thorat, rhinorrhea
What is antigenic drift?
What causes it?
A minor change based on mutations in a viral genome
Due to mistakes made by RNA polymerase
Which virus is most likely to cause a “barking cough” in children?
PIV 1 and PIV 2
Barking cough = croup, most often occurs in children
Which viruses are most likley to cause pneumonia in adults?
When I have pneumonia, I-RAPSS myself in blankets
- Influenza
- RSV
- Adenovirus
- PIV
- SARS-CoV
- Sin nombre
Why do so many viruses affect the human respiratory tract?
The respiratory tract is in direct contact with the environment
What animals are associated with MERS-CoV?
Camels
Bats
Humans
How is RSV transmitted?
Respiratory droplets or fomities
What animal is linked to novel-Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)?
Bats
Unclear secondary animal source
What is the most effective prevention for influenza?
What is the efficacy?
Flu vaccine
Efficacy = 20-60%
What kind of nuleic acid does rhinovirus have?
Non-segmented ssRNA
Influenza C causes disease in __________
Influenza C causes disease in children
Adults have protective immunity
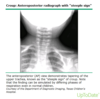
What is the “steeple sign?”
Which virus/clinical syndrome is it associated with?
The steeple sign is a radiographic finding associated with croup, usually caused by PIV 1 or PIV 2
What animals were associated with SARS-CoV infection?
Palm civet
What complication of influenza are people younger than 19 receiving long-term aspirin therapy at risk for?
Reye syndrome
Vomiting, confusion, may progress to coma
Which country is the origin of the majority of MERS-CoV cases?
Saudi Arabia
Which viruses are most likely to cause pneumonia in children?
- RSV
- PIV
- Influenza
- Rhinovirus*
- Measles*
- CMV*
* = Not likely to cause pneumonia in immunocompetent adults
Describe the clinical presentation of RSV
- Children and older or immunocompromised adults
- Lower respiratory tract
- Pneumonia or bronchiolitis
- Lower respiratory tract
- Everyone else
- Upper respiratory tract (less severe)
May lead to airway reactivity similar to asthma and decreased lung function
Where does baloxavir act?

Site 1
Inhibits mRNA synthesis - prevents viral protein synthesis
Baloxavir is a cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor

Where in the human body does RSV replicate?
What areas are typically infected?
Replicates in the nasopharynx
Infects the bronchial epithelium - Infection is restricted to the lungs
Which influenza medication is a neuraminidase inhibitor?
What does it do?
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
Prevents the release of new virions from infected cells
Where are outbreaks of adenovirus likely to occur?
Close quarters
Dorm rooms, military barracks, etc
How is adenovirus transmitted
Aerosol droplets
Direct inoculation
Fecal-oral
What is the treatment for RSV?
Supportive
Ribavirin may have some benefit in adults, but do not use in children
Where in the body is rhinovirus likely to cause infection?
Why?
Upper respiratory tract (not lower)
Does not replicate well at high temperatures
What is the treatment for adenovirus?
- Supportive: Most cases are self-limiting
- Antivirals
- If disease is severe: pneumonia, organ-invasive
- Cidofovir (very nephrotoxic)
- Brincidofovir
- If disease is severe: pneumonia, organ-invasive
What kind of nucleic acid doe HCoV have?
Nonsegmented ssRNA
How is influenza diagnosed?
PCR aka molecular assay (preferred)
Rapid antigen detection (not as good)
Run the test of you suspect flu (fever, sore throat, cough, myalgia)
What are the two major drugs used to treat influenza?
What are their mechanisms of action?
-
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) - This one is better
- Neuraminidase inhibitor
- Prevents the release of new virions from infected cells
-
Baloxavir (Xofluza)
- Cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor
- Prevents viral mRNA synthesis
How is influenza transmitted?
- Spread via respiratory droplets and fomites
- Invades ciliated epithelial cells of the URI
Does the flu vaccine help us keep up with antigenic drift or antigenic shift?
Antigenic drift
How is SARS-CoV spread?
Person to person or via droplets
Some people are “super spreaders”
What is the function of the SH protein in RSV?
Inhibits apoptosis
Which patient popoulation should NOT recieve the flu vaccine?
- Cancer patients recieving chemotherapy
- Persons with AIDS (CD4 count <200)
- Recipients of a lung transplant
- Persons with egg allergies
- None of the above
e. None of the above
Everyone should get the flu vaccine!
Airway obstruction in croup is greatest during…
Inspiration
Symptoms of croup arise from….
Inflammation and obstruction of the subglottic structures
What is the treatment for PIV?
Supportive
Which influenza medication inhibits mRNA synthesis?
Baloxavir (Xofluza)
Cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor
(But Oseltamivir is usually used instead)
Where does oseltamivir act?

Site 3
Prevents the release of new virions from infected cells
Oseltamivir is a neuraminidase inhibitor

Is there a vaccine for RSV? Why not?
No vaccine :(
Reinfection is common and immunity does not persist
Bronchiolitis is an infection of the _________________
Bronchiolitis is an infection of the
terminal bronchiolar epithelial cells
Who should we treat for influenza?
- Peopel with severe symptoms
- Anyone hospitalized
- People at high risk for complications
- Children ≤ 2 years old
- Adults ≥ 65 years old
- Pregnant women
- Obese patients
- People with chronic medical conditiosn
- People <19 recieving long-term aspirin therapy
- People with immunosuppressive conditions
Which influenza medication prevents the release of new virions from infected cells?
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
Neuraminidase inhibitor
Influenza B causes severe disease in __________
Influenza B causes severe disease in elderly and at risk people
What disease is caused by PIV 3?
Lower respiratory tract infection in children (pneumonia)
Which types of PIV cause croup?
PIV 1, PIV2
Which respiratory virus might also cause bilateral conjunctivitis?
Adenovirus
What is hantavirus cardio-pulmonary syndrome?
Initial fever followed by the abrupt onset of acute pulmonary edema and shock
Which virus does not utilize the respiratory tract for transmission and estabilishment of infection
- Measles virus
- Varicella-Zoster virus
- Ebola virus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Sin Nombre Virus
c. Ebola virus
Note: All herpes viruses utilize the respiratory tract to establish infection
What kind of nucleic acid does adenovirus have?
dsDNA
List the possible presentations of adenovirus
- Common cold
- Pharyngitis
- Pharyngitis + conjunctivits
- Bronchitis
- Pneumonia
- Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis
- Bilateral conjunctivitis, painful corneal opacities
Who is most likely to be infected by PIV?
- Children
- PIV 1 and PIV 2 -> Croup, otitis media, pharyngitis, cold
- Adults
- Common cold
- Older adults
- Pneumonia
- Immunocompromised
- Severe disease: pneumonia w/ high mortality
What feature of its genome allows influenza to undergo antigenic shift?
Segmentation of the genome
Which clinical syndrome is most closely associated wtih PIV?
Croup (laryngotracheobronchitis)
What is the treatment for rhinovirus?
Supportive
Vitamin C may reduce symptoms
Zinc therapy may reduce symptoms
Why does SARS coronavirus prefer the lung?
SARS CoV binds the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE-2) receptor, which is found in the lung
Which influenza medication is a cap-dependent endonulease inhibitor?
What does it do?
Baloxavir (Xofluza)
Inhibits viral mRNA synthesis
(But Oseltamivir is usually used instead)
What kind of nucleic acid does the influenza virus have?
(-)ssRNA
Which viruse are most likley to cause croup?
PPIMA
- PIV1
- PIV2
- Influenza
- Measles
- Adenovirus
PIV = parainflenza virus
The influenza virus is shed for ________ days prior to symptoms and up to ________ days after symptom onset
The influenza virus is shed for 1-2** days prior to symptoms and up to **5 days after symptom onset
Immunocompromised individuals may shed for months
Describe the clinical features of influenza
The following symptoms may last 3-5 days
- Fever
- Myalgias
- Sore throat
- Non-productive cough
- Pneumonia if v. severe
Only ~50% of patients with the flu have all 4 symptoms
What are the 2 important virus particle proteins in RSV?
-
SH protein
- Inhibits apoptosis
-
F (fusion) protein
- Mediates the fusion of infected cells together to form syncytia
Influenza A causes disease in __________
_________ are the main reservoir
Influenza A causes disease in humans, mammals, and birds
Aquatic birds are the main reservoir
Which viruses are most likely to cause the common cold?
Oh CRRAP I have a cold
- Coronavirus
- Rhinovirus
- RSV
- Adenovirus
- PIV
What is antigenic shift?
What causes it?
A major change in the viral genome due to re-assortment of segments of RNA
This leads to completely new N and H combinations, which can lead to high infectivity or virulence.
What is the function of the F protein in RSV?
F protein = Fusion protien
Mediates the fusion of infected cells together to form syncytia
How is rhinovirus transmitted?
Aerosol droplets
Contaminated hands or surfaces
Which viruses are most likely to cause pharyngitis?
A RICH *ECH* (clears throat)
- Adenovirus
- Rhinovirus
- Influenza
- CMV
- HSV
- EBV
- CMV
- HIV
What disease is caused by PIV 4?
Common cold
Pneumonia in immunocompromised persons
Describe the disease outbreaks caused by adenovirus 14
Sporadic outbreaks of severe diseases and pneumonia
List some of the most serious complications of influenza?
- Secondary bacterial pneumonia
- Exacerbations of cardiopulmonary conditions
- Viral myocardidits
- Viral encephalitis
- Reye syndrome (in children taking ASAs ex: asprin)
- Severe vomiting, confusion, may progress to coma
What disease does HCoV cause?
Common cold
Which viruses are most likely to cause tracheobronchitis?
- Influenza
- Parainfluenza (PIV)
Which influenza undergoes both antigenic drift and antigenic shift?
Influenza A
Which viruses are most likely to cause bronchiolitis?
- RSV
- hMPV
- Coronavirus
- Bocavirus
When should you start treatment for a suspected influenza infection?
While the results of PCR or rapid antigen testing are pending
(Treat empirically with osiltamivir)


