Pulm Clinical Medicine (except MDM) Flashcards
Describe the following for Pneumothorax:
- Percussion note:
- Breath sounds:
- Adventitious sounds:
- Fremitus:
Pneumothorax = air in the pleural space
- Percussion note: Hyperresonant
- Breath sounds: Decreased or absent
- Adventitious sounds: None
- Fremitus: Decreased fremitus
What conditions could cause B lines on ultrasound?
B lines are a marker of interstitial fluid or thickening of interstitial tissue
- Diffuse B lines = pulmonary edema
- Interstitial fluid
- Focal B lines = consolidation
- Fluid fills alveolar spaces, usually interstitial tissue is thickened
A patient has resonant percussion, vesicular breath sounds, normal fremitus, and rhonchi.
What is most likely wrong with the patient?
Chronic bronchitis
Rhonchi are caused by narrowing of the large airways
Adventitious breath sounds that are “countious, high-pitched, with a muscial quality and heard on ispiration” are most likely…
Stridor
What positions of comfort might indicate that a patient is in respiratory distress?
- Sniffing position
- Indicates upper airway obstruction (this is an emergency)
- Tripod breathing
- Optimizes the mechanics of breathing
Why is it important to collect “collateral information” when evaluating a patient with dyspnea?
Collateral information = information about changes to daily life that a patient makes to avoid dyspnea
Ex: They may resport little/no dyspnea, but what are they cutting out to avoid it?
Adventitious breath sounds that are “continous, high-pitched, with a musical quality, and loudest on expiration with an occasional squeek” are most likely…
Wheezes
What conditions would result in hyperresonance during percussion?
- More air in the chest cavity (lungs or pleural space)
- Emphysema
- Asthma
- Pneumothorax
What pathological changes cause wheezes on auscultation?
Narrowing or partial obstruction of intrathoracic (lower) airways
May be caused by asthma, bronchitis, bronchiolitis, or airway compression
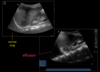
What sign is shown in this image?
What pathology does it indicate?

Shred sign
Indicates pneumonia
A patient has hyperresonant percussion, decreased breath sounds, and decreased fremitus.
What is most likely wrong with the patient?
Pneumothorax
- Air in the pleural space
- Hyperresonant percussion occurs when there is increased air space in the chest
If you hear bronchovesicular or bronchial breath sounds in abnormal places, what pathology might be present?
Consolidation
Due to pneumonia or pulmonary hemorrhage
In a normal lung:
-
Bronchovesicular: Large airspaces
- 1st and 2nd interspaces anteriorly
- Between the scapulae
-
Bronchial: Large airways
- Over the manubrium (if at all)
Describe the following for Pleural effusion:
- Percussion note:
- Breath sounds:
- Adventitious sounds:
- Fremitus:
Pleural effusion = fluid in the pleural space
- Percussion note: Hyporesonant
- Breath sounds: Decreased
- Adventitious sounds: None or possible pleural rub
- Fremitus: Decreased fremitus
Trachea may be shifted toward infolved side if a large area of the lung is affected
In a normal lung, where would you hear bronchovesicular breath sounds? Bronchial breath sounds?
- Bronchovesicular: Large airspaces
- 1st and 2nd interspaces anteriorly
- Between the scapulae
- Bronchial: Large airways
- Over the manubrium (if at all)
A patient has resonant percussion, vesicular breath sounds, normal fremitus, and crackles.
What is most likely wrong with the patient?
Pulmonary edema
- Crackles are caused by small airways popping open
- Resonance and fremitus are normal because fluid is in the interstitium, not in the pleural space or airspaces
What will you see on a normal ultrasound of the lung?
- Bright white, horizontally-sliding pleura
- A-lines (green)
- Comet tails (a few)

What will you see on ultrasound if the patient has a pneumothorax?
- Comet tails are abent
- No pleural sliding where the pneumothorax is
- The rest of the pleura will slide
- Lung point may be visible
- Boundary between normal lung and pneumothorax

What conditions would result in increased tactile fremitus?
- Things that increase the amount of fluid in the lungs
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary hemorrhage
If a patient is in respiratory distress, what signs can be seen in the neck?
Trapezius and sternocleidomastoid contraction
Tracheal tugging
What special tests can be performed to assess for consolidation of the lungs?
- Bronchophony
- Words will be louder than normal - “99”
- Whispered Pectoriloquy
- Intesnsification of whispered words - “1, 2, 3”
- Egophony
- Normal “ee” sounds will sound like a long “a”
If you hear stridor, what pathology is most likely present in the patient?
Upper airway obstruction
- Croup
- Laryngeal edema
- Airway compression
- Airway stenosis
What are the 4 key inputs that can drive dyspnea?
- Mechanoreceptors
- Chemoreceptors
- Neurohormonal uncoupling
- Psychosocial factors
Usually dyspnea is a combination of several of these factors
A patient presents with a cough. List the alarm sysmptoms that would warrant expedited or urgent evaluation
CHeWW-D CHESS
- Current/Former smoker with a New Cough
- Hemoptysis
- Wheezing and shortness of breath
- Weight gain
- Nocturnal Dyspnea
- Chest pain
- Hoarseness
- Peripheral Edema
- Trouble Swallowing
- Systemic (fever, weight loss)
Describe vesicular breath sounds
Normal breath sounds
- Heard over most of the lung field (except near large airways)
- Louder in inspiration than expiration