Pulm SAS and Misc. Review Flashcards
Equations are in the lectures for which they are relevant (143 cards)
Is the following consistent with hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
Upper lobe nodules
Yes
Community acquired pneumonia with dense consolidation is most likely caused by…

- H. influenzae*
- S. pneumoniae*
If a patient with this CT had a history of smoking but no other exposures or significant laboratory findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?

IPF
Idiopathic = no clear cause of the lung disease

Is the following consistent with a UIP pattern on HRCT?
Diffuse ground glass
No
Is this consistent with sarcoidosis?
Occurs exclusively in smokers
No
You are rounding on the pulmonary consult service and asked to evaluate a patient with an abnormal chest CT. The CT shows diffuse interlobular septal thickening. This radiographic abnormality can be caused by pathology in which structures?
Lymphatics and pulmonary veins

Would uremia cause anion gap nor non-anion gap metabolic acidosis?
Anion gap metabolic acidosis
Which fungal pneumonia is characterized by “halo sign” on CT?

Aspergillosis
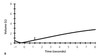
The patient with the solid flow-folume loop has isovolume flows that are _____ compared to a healthy lung (dotted line)

The patient with the solid flow-folume loop has isovolume flows that are high compared to a healthy lung (dotted line)
This is indicative of restrictive physiology
You are caring for a mechanically ventilated patient in the ICU with pneumonia. She is deeply sedated and paralyzed. Her tidal volume is set to 600 mL and her RR is 10. What happens if you change her settings to a tidal volume of 200 mL and a RR of 30?
A. You have lowered V̇A
B. Nothing, V̇E is unchanged
C. You have lowered V̇D
D. You have increased V̇E
A. You have lowered V̇A
Is the following consistent with hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
Lymphocystic infiltrate
Yes
For mechanically ventilated patients, we try to keep transpulmonary pressure < 25 – 30 cmH2O to not injure the delicate alveolar capillary barrier.
You are managing a patient whose Palv (plateau pressure) is set to 20 cm H2O. Over the course of the day, he develops large bilateral pleural effusions
What is true about the patient’s management?
A. Palv can likely be safely raised
B. Palv should be lowered
C. Palv should be kept the same
A. Palv can likely be safely raised
- The patient has pleural effusion - fluid in the pleural space
- Alveolar pressure should be raised to compensate
Transpulmonary pressure = Palv - Pip
Normal: 20 - (-5) = 25
This paient: 20 - (some number >-5) = <25
Palv should be increased in order to maintain transpulmonary pressure
What drug is most often implicated (as far as this module goes) in drug-induced ILD?
Amiodarone
Any patient with an abnormal HRCT who is taking amiodarone can be assumed to have drug-induced ILD
How does hypoalbuminemia cause edema?
Hypoalbuminemia = few proteins in the serum, resulting in low oncotic pressure in the capillaries. This can cause leakage of fluid out of the capillaries into the interstitium, leading to edema
Is this pattern nodular or reticular

Nodular

In a patient with hypersensitivity pneumonitis, what would you expect to find on lung biopsy?
Loosly formed, non-caseating granulomas

If this x-ray is from a 68-year-old male in the MICU with septic shock following cholangitis has this chest x-ray. He is refractory to oxgyen, does not have elevated filling pressures, and is not taking drugs toxic to the heart.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
If he had the exact same thing without the cholangitis, what would be the most likely diagnosis?

Most likely = ARDS
Most likely if no inciting incident = Acute Interstitial Pneumonia
(AIP = Idiopathic ARDS)

Pathologic findings of loosely formed, non-caseating granulomas would increase suspicion for which ILD?
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP)
Neutrohpilic exudate in a pleural effusion is associated wtih…
Infection (ex: bacterial pneumonia)
Which PH group affects location C?

Group 3 - Pulmonary Hypertension Owing to Lung Disease

What is lymphangitic carcinomatosis?
Dilation of lymphatic channels
May indicate widespread malignancy or pulmonary venous hypertension
A patient is experiencing pulmonary edema. The edema fluid is low in proteins
What is causing the edema?
If the edema fluid is low in proteins, fluid is leaking out of the microvasculature due to high intravascular hydrostatic pressure
Proteins are prevented from crossing the intact endothelial barrier, resulting in low-protein fluid in the interstitial space
Is vomiting associated with metabolic acidosis or metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis (chloride responsive)
Which PH group affects location A?

Group 4 - Chronic Thromoboembolic Pulmonary HTN