SM 164a - Radiology Flashcards
What usually causes blunting of the costophrenic angles?
Pleural Effusion
What heart abnormality might cause unilateral left hilar enlargement?
Pulmonary valve stenosis
What are the chest x-ray findings of pulmonary edema?
- Enlarged cardiac silhouette
- Enlarged, ill-defined pulmonary vessels
- Bilateral airspace opacities
- Pleural effusions
Where are the borders of the secondary pulmonary lobule (SPL)?
Interlobular septa, containing pulmonary veins and lymphatics
What is atelectasis?
Collapse of airspaces.
The term encompasses mild (subsegment) to whole lung collapse
List some common examples of lung pathologies that cause with centrilobular opacities on chest x-ray.
What structures are affected by these diseases?
- Pulmonary edema
- Bronchiolitis
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
These pathologies affect the bronchioles and intralobular artery (structures in the central portion of the SPL)
What is lobular pneumonia?
What would you see on a chest x-ray?
Pneumonia that encompasses an entire lobe/majority of a lobe of the lung
- Uniform area of lung infection (no patchiness)
- Infection is bound by a fissure
Which structures in the hila is enlarged in sarcoidosis?
Lymph nodes
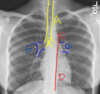
What structure is arrow #4 pointing to?

Pulmonary Arteries

Describe the appearance of a pleural effusion on chest x-ray
Blunting of the costophrenic angles on the frontal or lateral view
What is structure E?

Pulmonary Hila

What would you see on a chest radiograph if there were a pneumonia or mass in the medial aspect of the lingula?
The left heart border (left ventricle border) would be obscured
Which lobes can be thought of as the posterior lobes?
Lower lobes
Which structures in the hila are enlarged in pulmonary hypertension?
Main and central pulmonary arteries
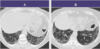
What is the most likely diagnosis?

A. Pneumonia
B. Pulmonary edema
C. Lobar collapse
D. Pneumothorax
D. Pneumothorax

What chest x-ray findings are you looking for when you assess the pleura?
- Costophrenic angles on frontal and lateral view
- Should be sharp; blunted in pleural effusion
- Lateral view is more sensitive for the detection of pleural fluid
List some common pathologies that cause with interlobular septal thickening (on CT) and Kerley B lines (on Chest x-ray).
Interlobular septal thickening is caused by thickening of the outer connective layer of the secondary pulmonary lobule
- Interstitial pulmonary edema
- Lymphatic carcinomatosis
Affect structures in the periphery of the SPL (pulmonary veins and lymphatics)
Describe the appearance of a tension pneumothorax on a chest x-ray
- Shift of the mediastinum
- Depression of the diaphragm
- Collapse of the lung
In which direction is a lateral view chest x-ray taken?
From right to left
How can one differentiate the interlobular septal thickening in pulmonary edema vs. lymphangitic carcinomatosis?
Pulmonary edema = bilateral, smooth
Lymphangitic carcinomatosis = unilateral, smooth early, nodular later on
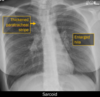
Which lobe(s) are collapsed?

Right middle lobe and right lower lobe
The right heart border and diaphragm border are obscured; caused by a lesion in the bronchus intermedius

In a normal, healthy person, on an inspiratory frontal radiograph, the lungs extend to the ____th rib posteriorly and the ___th rib anteriorly
In a normal, healthy person, on an inspiratory frontal radiograph, the lungs extend to the 10 th rib posteriorly and the 6th th rib anteriorly
List 3 key features of a normal lung x-ray
- Equal density, approximately equal size
- The bronchi and vessels are very visible centrally
- The outer peripher of the lungs are clearer than the center
- You should not see the peripheral bronchioles clearly

What pathology might cause the fissures of the lungs to be seen easily?
Lobar pneumonia