Skin Flashcards
What is an Ephelis? What is the histology?
Ephelis
- Freckle
- Histo
- Normal density of melanocytes
- Increased melanin pigment in basal keratinocytes
What are the differences between an ephelis and a cafe au lait spot?
- Ephelis (freckle)
- Vary with sun exposure
- Normal density melanocytes
- Increased melanin in basal keratinocytes
- Cafe au lait
- Larger
- Independent of sun exposure
- Increased melanocytes
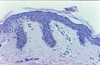
What disease process is pictured below?

Lentigo
Lentigo
- Location
- Gross appearance
- Microscopic appearance
- Location
- Hands
- Face
- Mucous membranes
- Gross appearance
- Macules or patches
- independent of sun
- Microscopic appearance
- Hyperplasia of melanocytes in basal layer (linear)
Junctional Nevus
- Gross appearance
- Microscopic appearance
- Gross appearance
- Usually flat
- Microscopic appearance
- Nests of melanocytes
- Epidermal - dermal junction
- Little or no mitosis

Compound Nevus
- Gross appearance
- Microscopic appearance
- Gross appearance
- Raised
- Microscopic appearance
- Nests of melanocytes:
- At dermal - epidermal junction
- Deeper in dermis
- Nests of melanocytes:

Intradermal Nevus
- Gross appearance
- Microscopic appearance

- Gross appearance
- Raised
- Microscopic appearance
- Cluster of dermal melanocytes
- No nest nature

Mature Nevus
- Gross appearance
- Microscopic appearance
- Gross appearance
- Raised??
- Microscopic appearance
- Deeper melanocytes have fusiform shape
Maturation of nondysplastic nevi

Maturation sequence of nondysplastic melanocytic nevi.
- A, Normal skin shows only scattered dendritic melanocytes within the epidermal basal cell layer.
- B, Junctional nevus.
- C, Compound nevus.
- D, Dermal nevus.
- E, Dermal nevus with neurotization (extreme maturation). Nevi may exist at any stage in this sequence for variable periods of time, although many are believed to progress through this sequence.
What increases cancer risk in congenital nevi?
Size
Large = increased melanoma risk
Blue Nevus
- Gross appearance
- Microscopic appearance

- Gross appearance
- heavily pigmented
- Microscopic appearance
- non nested dermal infiltrates
- dermal fibrosis
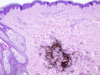
What percent of people with Dysplastic Nevus Syndrome have melanoma by age 60?
50%
What are the microscopic characteristics of Dysplastic Nevi?

- Lentiguous hyperplasia
- melanocytes begin to replace basal layer
- Cytologic / nuclear atypia
- Melanin incontinence
- released by dead melanocytes
- Linear / lamellar fibrosis in dermis
- surrounding rete pegs

What are the first and second stages of growth in melanomas?
- Radial growth
- Horizontal spread
- Unable to metastasize
- Vertical growth
- Nodular appearance
- Metastatic potential
What disease process is pictured below?

Seborrheic keratosis

dark keratin-filled surface plugs (inset)
benign basaloid cells
prominent keratin-filled “horn” cysts, some of which communicate with the surface (pseudo-horn cysts).
What disease process is pictured below?

Acanthosis Nigricans
- Micro
- •Hyperkeratosis
- •Papillomatosis
- •undulating enlarged dermal papilla
- •Slight basal cell hyperpigmentation
- •No melanocytic hyperplasia

What disease process is pictured below?

Fibroepithelial polyp
- Gross:
- Flesh colored
- Pedunculated

What may be associated with fibroepithelial polyps?

- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Intestinal polyposis
- Increased in pregnancy
What is the makeup of an Inclusion Epidermal Cyst?
- Wall
- Normal epidermal epithelium
- Filled with
- Laminated keratin

What is the makeup of a Pilar / Tricholemmal Epidermal Cyst?
- Wall
- Hair follicular epithelium
- Filled with
- Homogenous keratin

What is the makeup of a Dermoid Epidermal Cyst?
- Wall
- normal epidermal epithelium
- Small hair follicles budding out from wall
- Filled with
- laminated keratin
(just like inclusion but with hair follicles)

What is the makeup of a Steatoma Simplex Epidermal Cyst?
Sebeceous cyst
- Wall
- Similar to sebaceous duct
- Lobules budding from wall
What is the mutation and inheritance pattern resulting in Steatocystoma multiplex Epidermal Cyst?
Mutation in keratin 17
AD

What disease process is pictured below?

Cylindroma
“Turban Tumor”























































