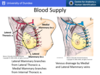
Sem 1 - D - Thoracic Wall - Thoracic Skeleton, Ribs & Joints, Resp Movements & Muscles, Blood Supply/ Drainage & Breast Flashcards
Which structures make up the thoracic cage? (bony structures)
12 thoracic vertebrae each with a pair of ribs coming anteriorly from it (24 ribs in total then) Sternum Clavicles x2 Scapula x2 Calvicles articulate with the sternum anteriorly and scapula posteriorly

In the thoracic cage, there is a superior and inferior thoracic aperture What makes up both superior and inferior thoracic apertures?
Superior thoracic aperture - T1 vertebral body, 1st pair of ribs and their costal cartilages and the superior border of the manubrium Inferior thoracic aperture - T12 vertebral body, 11th and 12th pairs of ribs, costal cartilages of ribs 7 to 10 and the xiphersternal joint (technically xiphoid process is in the inferior thoracic aperture)
What do the superior and inferior thoracic apertures allow for? What is the costal cartilages of rib 7-10 collectively known as?
Superior thoracic aperture allows for passage of structures between thorax and neck/upper limb Inferior thoracic aperture allows for passage of structures between thorax and abdomen Costal cartilages of ribs 7-10 = costal margin

Recap What forms the superior and inferior thoracic apertures? What do they allow for the passage of?
Superior - T1 body, 1st pair of ribs & costal cartilages, superior border of manubrium - passage of structures between thorax and neck/upper limb Inferior - T12 body, 11th &12th pairs of ribs, costal cartilages of ribs 7-10 and xiphersternal joint - passage of structures between thorax & abdomen

WHat is the costal margin again?
This is the joining of the costal cartilages from ribs 7-10 Both costal margins join to form the infrasternal angle
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/403/flashcards/11907403/jpg/ppngjpgpng-166019DC12F2DA7FD58.jpg

Black - superior articular process Maroon - lamina Orange - spinous process Yellow - transverse process Green - pedicle Blue - vertebral canal Red -transverse costal facet Purple - superior costal facet Pink- inferior costal facet
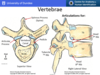
What does the superior and inferior costal facets articulate with? What does the superior articular process articulate with? What does the transverse costal facet articulate with?
Superior costal facet - articulates with head of the rib of the same number Inferior costal facet - articulates with the head of the rib of the below Superior articular process - articulates with the inferior articular process of the vertebrae above Transverse costal facet - articulates with the tubercle of the rib

Ribs can be split into two distinct groups: * Classification - which depends on the bony features of the rib * Type - which depends on the ribs connection with the sternum What are the three different types of ribs? Explain how they are different?
Three types of ribs True ribs - ribs 1-7 - attach directly to the sternum via their own costal cartilage False ribs - ribs 8-10 - attach indirectly to sternum with their costal cartilages uniting with the costal cartilages of the ribs above Floating ribs - ribs 11 and 12 -no connecting to sternum

Now have discussed the different types of ribs (true, false and floating), lets talk about the classification of ribs which is based on their bony features Classification can be split into Typical and atypical Which ribs are typical and which are atyical?
Typical ribs - ribs 3 to 9 Atypical ribs - ribs 1,2 and 10,11,12
What makes a rib a typical rib
Rib has a head, neck, tubercle and body
Describe the head of a typical rib? What does the neck of a typical rib connect?
Head of a typical rib - wedge shaped with a superior articular facet and an inferior articular facet separated by the crest of the head * Superior articular facet articulates with the inferior costal facet of the vertebrae above * Crest of the head articulates with the IV disc * Inferior articular facet articulates with the superior costal facet of the vertebrae of the same number Neck of a typical rib - connects the head of the rib to the body of the rib at the tubercle
Describe the tubercle of a typical rib?
Tubercle has an * Articular part for the transverse process of the rib of the same number * Non-articular part for the attachment of the costotransverse ligament

What is the most curved part of the rib known as? What is the costal groove?
The costal angle is the most curved part of the rib The costal groove is a groove on the internal surface of the inferior border of the rib - the groove exists for the protection of intercostal vessels and nerves

Describe how rib 1 is an atypical rib?
The head of the rib only has one articular facet as it only articulates with the transverse process of vertebra T1 - C7 vertebrae does not have a costal facet Rib 1 does not have a costal angle Also has groove for subclavian vessels on the superior surface (subclavian artery and vein) separated by the scalene tubercle
What does the scalene tubercle serve for the attachment of? Is the subclavian artery or vein groove more posterior?
Serves for the attachment of the anterior scalene muscle Subclavian artery groove is more posterior Subclavian vein groove is more anterior

What makes the second rib an atypical rib?
It has a tuberosity on the upper surface for the attachment of the serratus anterior muscle

What makes ribs 10-12 atypical?
They all have a single facet on the head as they only articulate with the vertebrae of the same number Ribs 11 and 12 also short with no neck or tubercle

Along the lateral border of the sternum are a number of costal grooves – this is where the ribs will articulate Sternum is split into the manubrium, body and xiphoid process What is another name for the sternal angle? Which part of the sternum do each of the ribs articulate?
Sternal angle aka manubriosternal joint
Rib 1 - articulates at superior manubrium
Rib 2 - articulates at sternal angle
Rib 3-6 - articulate along body of the sternum
Rib 7 - articulates at the xiphisternal joint

The intervertebral joints consist of the facet joint and the intervertebral discs What makes each of these joints? What type of joint are each of these joints? What is another name for the facet joint?
Facet joints - * formed by superior articular process of vertebrae articulating with inferior articular process of vertebra above * It is a synovial plane joint * Also known as zygapophysial joint Intervertebral disc - * between two vertebral bodies * this is a secondary cartilagenous joint
The sternocostal joints also have different types of joint What type of joint exists between rib 1 and the sternum? What type of joint exists between ribs 2-7 and the sternum?
Rib 1 and the sternum - primary cartilagenous joint Ribs 2-7 and the sternum - synovial plane joints
Interchondral joints are between costal cartilages They exist between ribs 6-7,7-8 and 8-9 WHat type of joint are these? What type of joint exists between ribs 9 and 10?
INterchondral joints - synovial plane joints Joint between rib 9 and 10 - fibrous joint
The two costovertebral joints are between * the head of the rib and the vertebrae * the tubercle of rib and the vertebrae What are the participants in the joint of the head of the rib? What are the participants in the joint at the tubercle of the rib? What is this joint also known as?
Head of the rib - superior articular facet with inferior costal facet of rib above Crest of head of rib - with IV disc Inferior articular facet with superior costal facet of rib of the same number Tubercle articulates with transverse costal facet - costotransverse joint

If a line were drawn between the costovertebral joints (between head of rib and tubercle articulations with vertebrae) , the axis of the line is far more lateral in the upper ribs (ribs 1-6) and far more posterior in the lower ribs (ribs 7-12) This axis causes a difference in the movement of the ribs during inspiration * What direction do upper ribs move on inspiration? * What is the name for this movement? What direction do lower ribs move on inspiration? * What is the name for this movement?
Upper ribs move in an anterior direction on inspiration due to more lateral axis between costoverebtral joints- described as a PUMP HANDLE MOVEMENT Lower ribs move in a lateral direction on inspiration (due to more posterior axis between costovertebral joints) - described as a BUCKET HANDLE MOVEMENT

What are the changes in dimensions of the thoracic cavity during inspiration? What is the primary muscle of inspiration at rest?
The sternum and upper ribs move anteriorly and superiorly
The lower ribs move laterally
The diaphragm (primary muscle of inspiration at rest) descends Thoracic cavity increases in size, vertically, horizontally and laterally