renal anatomy Flashcards

…
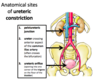
where do ureters travel?
pass from retroperitoneum through false pelvis into true pelvis
what seperates false pelvis from true pelvis?
pelvic inlet
pelvic floor?
levator ani
perineum?
compartment between pelvic floor and skin
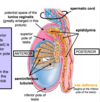
route of ureters?
* pass anterior to the common iliac vessels + enter pelvis
* run anteriorly (along the lateral walls of the pelvis)
* At level of ischial spine, turn medially to enter posterior aspect of bladder
* enter posterior bladder wall in an inferomedial direction

are ureters retroperitoneal?
Yes until they reach the true pelvis - sub-peritoneal
where can ureter be found in females?
Males?
* Females = runs inferiorly to uterine tubes + uterine artery (water under the bridge)
* males = runs inferiorly to vas deferens

…
where do arteries entering the pelvis branch from?
Veins drain?
Internal iliac artery
internal iliac vein
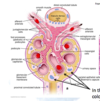
what forms the “trigone” of the bladder
the 2 ureteric orifices and internal urethral orifice
what rests on top of the bladder?
making it…?
visceral peritoneum
* a subperitoneal organ
which muscle forms main bulk of the bladder wall?
function? (2)
detrusor muscle
* encircles ureteric orifices to prevent reflux or urine when bladder contracts
* in males, forms internal urethral sphincter which contracts during ejaculation to prevent reflux of semen into bladder
which sphincter is found in males but not females?
internal urethral sphincter
what is the most anterior organ in the pelvis?
bladder

what is the most dependent part of pelvic cavity?
pouch of douglas (rectouterine) in female
rectovesical pouch in male
2 routes of catheterising patient’s bladder? (2)
* urethral
* suprapubic (bladder has to be full otherwise will pierce peritoneum)

…

…

…
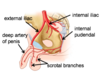
route of sperm?
* produced in seminiferous tubules
* stored in epididymis
* travels to vas deferens
* combines with seminal gland behind bladder to form ejaculatory duct
* prostatic urethra passes through prostate
* spongy urethra passes thru corpus spongiosum
spermatic cord?
contains testicular artery, testicular vein, vas deferens, lymphatics, nerves (smooth muscle + somatic for cremaster muscle)

…
excess fluid in tunica vaginalis?
hydrocele