MSK pathology Flashcards
Connective tissue disease? e.g.?
Autoimmune - inflammatory diseases characterised by presence of auto-antibodies
e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, scleroderma, dermatomyositis
Rheuamatoid arthritis? Marker? Histology?
Inflammation of joints
* Marker = rheumatoid factor, auto ab against Fc IgG
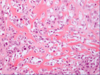
* Histo = lots of lymphocytes + plasma cells in synovial tissue

Phases of rheumatoid arthritis?
* Acute phase = inflammatory granulaion tissue (pannus) + hyperplastic synovium
* Chronic phase = fibrosis, deformity
SLE dx? Histo?
Dx: ANA+, anti double-stranded DNA, biopsy
Histo = chronic inflammation (lymphocytes + plasma cells)
Examples of metabolic MSK diease? (3)
Pagets, osteomalacia, crystal arthropathies
Crystal arthropathy? What process involves urate production?
gout, uric acid (end-product of purine synthesis)
* Urate formed in DNA replication as guanine and adenine are purine based
Causes of hyperuricaemia? (2)
* Increased production e.g. idiopathic,enzyme defect (Lynch Nyhan syndrome), cancer, psoriasis
* Reduced excretion (most common cause of gout) - drug side effect e.g. thiazide diuretics
Ax crystal arthropathy?
Crystals in joints causing inflammatory reaction
Pathological findings crystal arthropathy?
* Cytology – joint fluid shows needle-shaped crystals
* Histology – amorphous eosinophilic debris (giant cells), will not see crystals, another form of crystal arthropathy that can look similar = pyrophosphate arthropathy

What is another form of crystal arthropathy not involving urate crystals?
Calcium pyrophosphate = pseudogout or chondrocalcinosis
Pseudogout s/s?
* Usually asymptomatic (ncidental finding on x-ray)
* Can experience some joint pain
Cytology pseudogout?
Crystals are bigger, coarser and more rhomboid in shape (in contrast to urate crystals)

Paget’s disease of bone?
* Abnormality of bone turnover
* Increased osteoclastic activity
* Paradoxically – more bone but not normally structured (so often weaker, patients prone to develop fractures with minor trauma)
Ax Paget’s disease of bone?
Cause uncertain: possible genetics, viral infection (paramyxovirus, measles, RSV)
Pathological finding paget’s disease?
* Osteolytic (less dense)
* Burnt out

s/s Paget’s disease of bone? (4)
Secondary malignancy?
* Pain
* Enlargement + abnormal shape
* Increased metabolism (heat)
* AV shunt can lead to HF
Secondary malignancy = osteosarcoma
phases of bone fracture?
Initial phase - haematoma, inflammatory cells, cytokine release
1 week - callus, organised haematoma, remodelling bone
2-3 weeks - woven bone deposited perpendicular to cortical bone, cartilage deposition at fracture site
Effects of metastatic bone disease? (3)
* Most are osteolytic – loss of bone
* Prostate is osteosclerotic (more dense) – areas of opacity
* Remember myoloma/plasmacytoma - malignant proliferation of plasma cells, causes bony lesions
Avascular necrosis? Ax?
bone infarction (often asymptomatic until very end stage)
* Ax: trauma, alcohol, dysbarism, steroid injection, sickle cell, infection
Morphology avascular necrosis? Histology?
wedge-shape dinfarct (usually subcortical)
* Histo: creeping substitution (new bone growing over dead bone)

Osteoarthritis?
Degenerative bone disease
Features of osteoarthritis?
* Cartilage cracks (fibrillation) - reduced joint space
* Subchondral cysts
* Osteocytes - new bone formation at side
* Sclerosis


Ganglion cyst - space with myxoid material. Secondary inflammatory changes

Giant cell tumour