ENT Embryology Flashcards
what are pharyngeal (branchial) arches formed from?
developed from gill arches (remnants of fish gills)
When are pharyngeal (branchial) arches formed?
Develop cranial to caudal
Arch 1 – Day 22
Arch 2 + 3 – Day 24
Arch 4 + 6 – Day 29
(5 is missing because it doesn’t form in humans)
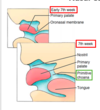
Pharyngeal apparatus? (3)
Function of clefts and pouches?
* Core pharyngeal arch (mesenchymal tissue)
* external pharyngeal cleft (ectoderm)
* internal pharyngeal pouch (endoderm)
Clefts and pouches seperate arches (external layer is cleft, internal layer is pouch)

What is each pharyngeal arch made up of? (4)
* Core of mesenchyme derived from paraxial and lateral plate mesoderm (musculature of the face)
* neural crest cells (skeletal components of face)
* cranial nerve
* Artery (aortic arch arteries)

…
What skeletal elements is first arch split into?
Maxillary process (cranial)
* maxilla
* zygomatic bone
* squamous portion of temporal bone
Mandibular process (caudal)
* formes meckel’s cartilage
* incus and malleous (ear)
* mandible
Muscles and nerves of 1st arch?
All muscles supplies by CN V3
* muscles of mastication
* anterior belly of digastric
* mylohyoid
* tensor tympani
* tensor veli palatini
Sensory supply to skin of the face
* V1 (opthalmic)
* V2 (maxillary)
* V3 (mandibular)
Skeletal elements of 2nd arch? (5)
* stapes (ear)
* styloid process of temporal bone
* stylohyoid ligament
* lesser horn of hyoid
* upper part of hyoid body
What is the cartilage of the 1st arch known as?
2nd arch?
1st arch = Meckel’s cartilage
2nd arch = Reichert’s cartilage
2nd arch muscles and nerves?
All musculature supplied by CNVII
* muscles of facial expression
* posterior belly of digastric
* stylohyoid (elevates tongue)
* strapedius
* auricular muscles
Skeletal components of 3rd arch?
* greater horn o fhyoid
* lower part of hyoid bone

Muscles and nerves of arch 3?
Supplied by glossopharyngeal (CN IX) nerve
* stylopharyngeus
* longitudinal pharyngeal muscle
Muscles of arch 4? (3)
Supplied by?
Cricothyroid
levator veli palatini
pharyngeal constrictors
* vagus (CN x) = same as arch 6
Muscles of arch 6?
Suppplied by?
Intrinsic laryngeal - moves inner vocal cords
Supplied by vagus (CN X) = same as arch 4
What do the pharyngeal clefts become?
1st cleft = external acoustic meatus
2 - 4th cleft = form cervical sinus (eventually disappears)
What happens if cervical sinus does not disappear during development?
Branchial fistulas + cervical cyst
What do pharyngeal pouches become?
1st pouch = middle ear, tympanic membrane, eustachian tube
2nd pouch = palatine tonsil
3rd pouch = inferior parathyroid gland, thymus
* the reason it is inferior is because it buds off
4th pouch = superior parathyroid gland, ultimobranchial body


…
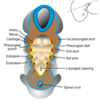
Development of the ear?
Inner ear
* balance (semicircular canals)
* hearing (organ of Corti)
Middle Ear
* tympanic cavity
* ossicles
External Ear
* External auditory meatus - 1st cleft
* auricle

What do otic vesicles give rise to?
What are they formed from?
Otic vesicles give rise to inner ear
* otic placode -> otic pit -> otic vesicle
What does utricular portion of inner ear give rise to?
Saccular portion?
Utricular = semicircular canals (balance)
Saccular = cochlear (hearing)
Development of cochlear duct?
Cochlear duct grows in spiral between 6-8 weeks
* surrounding mesnechyme becomes cartilaginous
* coil becomes origin of Corti (hearing)
Development of external ear?
* External auditory meatus -> dorsal part of first pharyngeal cleft
* Month 3 - epithelial cells proliferate to form Meatal Plug
* Plug dissolves in month 7 and contributes to ear drum
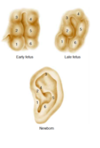
* 6 auricular Hillocks fuse to form auricle
(plug can lead to congenital deafness, can be surgically removed)