Quiz2 timmerman AntiEstrogens, Progestins, Androgens Flashcards
Antiestrogens
Important in the modification of?
What are the two major groups? Of drug types

Triphenylethylene Analogs
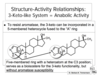
What structure is retained? But features what type of moeity that is critical for antiestrogenic activity?

Clomiphene
What bulky group does it have that gives it antagonist activity?
What isomer is the ant antagonist and what one is the agonist?

Clomphene
Employed to promote?
Form?
What SEs?

Tamoxifen
What isomer is used? What type of compound is it?
Used to treat?
form?

Selective estrogen Receptor Modulators
SERM
What are these trying to circumvent
What was developed?

SERMs
All approved drugs in this category exhibit?
Why have they been given the name SERM?

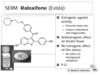
Raloxifene
What type of activity? And what two things does this help?
What effect on breast tissue?
No ___ effect on the uterus?
form?
Toremifene
Related to?
What reduces its anti-estrogenic potency?
Other SERMs in trials?

Fulvestrant Analog of what?
and Acolbifene has to be converted?

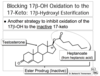
Triazole ___ inhibitors
2 of them
Prevent what?
What type of inhibitors?

Role of aromatase?

Role of Aromatase in Cancer?
Block conversion of?
Control?
Aid in?

What binds heme in Anastrozole and Letrozole

Anastrozole
Specific?
Tx of?

Letrozole
What does it do?
Tx of? Second line to?

Exemestane?
What is it?
Reversible or irreversible?
Tx of?

Phytoestrogens?

Phytoestrogens
Soy isoflavone B-glycosides are?

Phytoestrogens
What activity do they have?
The two hydroxyl groups?

Tx of Phytoestrogens?

Where is the focus of progesterone drug in the pathway?

Nat sources of Progestin
4
What is an important note about synthesized progestterone?

Semi and Bio synthetic sources of progestins?

Indications for progestins?

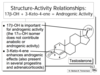
Pregnane nucleus what are the important features? For derivates

Key progesterone functional groups
What do they do?

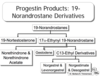
What are the two main progestin products?

Progestin Products: Progesterone and Derivatives
Starting at Nat Progestins then from there
What are synthetic products made from?

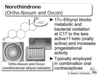
Progesterone
Prometrium
Duration? Due to?
Where from?
What places are susceptible for metabolism?

Progesterone: Metabolism to?
What is added and different?
What does it get metabolized by?
Addition at 6 you should know whay its metabolized to

Progesterone metabolism due to reduction
what is the product and where are the changes

Progesterone
Progestasert
Despite?
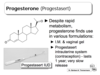
17a-Hydroxyprogesterone what is it?
Where is it produced?

Where is 17a-Hydroxyprogesterone in the Steroid Hormone Syn pathway

17a-Hydroxyprogesterone
Metabolism
what is teh same and what is different in comparison to progesterone metabolism
What does this limit?
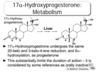
Blocking the Metabolism of 17a-Hydroxyprogesterone

Progestin Products: Progesterone Derivatives
3

Blocking 3-keto-4-ene metabolism and 6ahydroxyation
What aspects are improved?
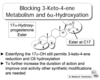
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
What SC is introduced? What does this cause?
Slow reduction of the keto and double bond 4-5

Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
at teh C6 position ___ is added and this decreases?
This blocks?

Medroxyprogesterone Acetate (Provera)
What does the liver do? Similar to ___ except for?
What is active?
What decreases reduction of 20-keto

Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
How is it active? Like what form?
What types are active how is this different?
What form provide contraception for 3 months?

Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
In Prempro
Used in combination with?

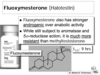
Megesterol Acetate
(Megace)
What on the B ring increases activtiy?
How much of oral dose is metabolized?
How does it differ from Medroxyprogesterone?
How does it block metabolism

Megesterol Acetate
Active in what form?
Acitivty similar to?
What decreases reduction of 20-keto?

Ethisterone and Analogues
_ derivative of what?