Quiz Flashcards
(86 cards)
The threshold for the detection of odors is ___ and adaptation to odors occurs ____.
A)high, quickly
B)high, slowly
C)low, quickly
D)low, slowly
C)
The axons of the olfactory neurons pass through the foramina of the _____ to synapse with mitral or tufted cells in the ____.
A)cribiform plate, olfactory tract
B)cribiform plate, olfactory bulb
C)nasal bone, olfactory tract
D)nasal bone, olfactory bulb
B)cribiform plate, olfactory bulb
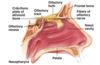
Which cells proliferate to replace lost olfactory cells?
A)basal cells
B)mitral cells
C)olfactory hairs
D)tufted cells
Feedback: Correct Answer
A)basal cells

Which of the following is NOT true of olfactory neurons?
A)The axons of the olfactory neurons combine to form the olfactory nerves.
B)The olfactory neurons synapse with cells in the olfactory bulb.
C)Olfactory neurons have receptors that react with odorants dissolved in fluid.
D)Olfactory neurons are uni-polar neurons.
Feedback: Correct Answer
Olfactory neurons are uni-polar neurons
Which region of the olfactory cortex is involved in conscious perception of smell?
A)intermediate olfactory area
B)lateral olfactory area
C)medial olfactory area
D)superior olfactory area
lateral olfactory area
The olfactory cortex is in the frontal lobe within the lateral fissure of the cerebrum. It is divided into three areas, the intermediate, lateral, and medial olfactory areas

Which region of the olfactory cortex is connected to the limbic system?
A)intermediate olfactory area
B)lateral olfactory area
C)medial olfactory area
D)
The medial olfactory area is connected to the limbic system, and thus is responsible for visceral and emotional reactions to odors.
Which region of the olfactory cortex aids in modifying sensory information in the olfactory bulb?
A)intermediate olfactory area
B)lateral olfactory area
C)medial olfactory area
D)superior olfactory area
medial olfactory area
The intermediate olfactory area projects axons along the olfactory tract back to the olfactory bulb and thus modulate activity in the olfactory bulb.medial olfactory area
Where within the nasal cavity is the olfactory epithelium located?
A)anterior and lateral portion of the nasal cavity
B)posterior and lateral portion of the nasal cavity
C)inferior portion of the nasal cavity
D)superior portion of the nasal cavity
superior portion of the nasal cavity

Which type of papillae have no taste buds associated with them?
A)circumvallate
B)filiform
C)foliate
D)
There are more filiform papillae then the other types of papillae, however they do not have taste buds.

Which type of papillae have the most sensitive taste buds associated with them?
A)circumvallate
B)filiform
C)foliate
D)fungiform
Feedback: Foliate papillae are most numerous in children and decrease with age.

How many primary tastes have been identified?
A)4
B)5
C)7
D)400
Feedback: Correct Answer
5
Which of the following cranial nerves does not transmit taste sensation?
A)Trigeminal (V) nerve
B)Facial (VII) nerve
C)Glossopharyngeal (IX) nerve
D)Vagus (X) nerve
Trigeminal (V) nerve
The majority of taste sensation is transmitted via the facial and glossopharyngeal nerves. The vagus nerve transmits some taste sensation from the epiglottis. The trigeminal nerve does not transmit taste sensation, however it does transmit tactile sensation from the tongue.

Identify the location of the taste area of the cortex.
A)precentral gyrus
B)postcentral gyrus
C)thalamus
D)temporal lobe.
postcentral gyrus
Feedback: The nerves carrying taste sensation enter into the medulla oblongata where they decussate and extend to the thalamus. From the thalamus the neurons project to the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe.

Which of the following primary tastes do not cause depolarization of the gustatory through a G protein mechanism?
A)bitter
B)sweet
C)salty
D)umami
Feedback: The salt sensation is a result of the opening of sodium channels and thus the diffusion of sodium into the cell, resulting in depolarization.
C)salty

Which of the following primary tastes do not require a substance to bind to a receptor on the gustatory hairs of taste cells?
A)salty
B)bitter
C)sweet
D)umami
Feedback: Correct Answer
A)salty

Which of the following describe the relationship between olfaction and gustation?
A)Gustatory hairs can also detect odorants.
B)Olfactory hairs can also detect tastants.
C)Olfactory sensations provide information about a substance that may be thought of as taste.
D)There is no relationship between the olfactory and gustatory senses.
Olfactory sensations provide information about a substance that may be thought of as tas
Which taste sensation is the most sensitive?
A)bitter
B)salty
C)sweet
D)umami
A)bitter
the bitter sensation has the lowest threshold or is the most sensitive. This low sensitivity may be protective in nature as many poisonous substances are bitter.
Which muscle closes the eyelid when it contracts?
A)inferior rectus
B)levator palpebrae superioris
C)orbicularis oculi
D)superior oblique
orbicularis oculi
Two skeletal muscles control the eyelid: the levator palpebare superious which elevates the lid and the orbicularis oculi which closes the lid.

Two skeletal muscles control the eyelid: the levator palpebare superious which elevates the lid and the orbicularis oculi which closes the lid.
levator palpebrae superioris

Which of these extrinsic eye muscles is NOT controlled by the oculomotor nerve?
A)inferior oblique
B)inferior rectus
C)medial rectus
D)superior oblique
Feedback: The superior oblique muscle is innervated by the trochlear (IV) nerve.
superior oblique
Which of these extrinsic eye muscles is controlled by the trochlear nerve?
A)inferior rectus
B)medial rectus
C)superior oblique
D)superior rectus
C)superior oblique
The superior oblique muscle is innervated by the trochlear (IV) nerve. The inferior rectus, the medial rectus, and the superior rectus are all innervated by the occulomotor (III) nerve.
Identify the three layers of the eye in from the outer most layer to the inner most layer.
A)fibrous tunic, nervous tunic, vascular tunic
B)fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, nervous tunic
C)nervous tunic, fibrous tunic, vascular tunic
D)vascular tunic, fibrous tunic, nervous tunic
Feedback: Correct Answer
B)fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, nervous tunic

What eye layer is referred to in the quote “Don’t fire until you see the whites of their eyes”?
A)conjunctiva
B)choroid
C)retina
D)sclera
D)sclera

The transparent anterior portion of the outer eye coat, which allows light rays to enter the interior of the eye is the
A)conjunctiva
B)cornea
C)iris
D)sclera
The cornea is an avascular transparent structure that covers the anterior of the eye.






























