George's Quiz Flashcards
(26 cards)
The condition that occurs if the eyeball is too long, or if the cornea or lens is optically too strong is called A) astigmatism. B) hyperopia. C) myopia. D) presbyopia. E) strabismus
myopia. Myopia is the condition that occurs if the eyeball is too long or if the cornea or lens is optically too strong. Astigmatism is a type of refractive error, where the cornea is not uniformly curved so light rays are not focused at a single point.
Which of these parts of the eye normally NEVER has melanin present? A) choroid B) ciliary body C) iris D) retina E) vitreous humor
vitreous humor Feedback: Incorrect Answer: The vitreous humor of the eye does not contain pigment. The retina does contain melanin.
Olfactory neurons A) are always unipolar neurons. B) are replaced every two months. C) have axons that contain olfactory vesicles. D) synapse directly with association neurons. E) all of these
B) are replaced every two months. Feedback: Incorrect Answer: Olfactory neurons synapse with mitral cells or tufted cells, both of which then relay olfactory information to the brain through olfactory tracts and synapse with association neurons.
When ciliary muscles contract, A) tension is increased on the suspensory ligaments. B) the choroid is pulled toward the lens. C) the lens gets flatter. D) the focal point moves closer to the lens. E) all of these
the choroid is pulled toward the lens.
Axons from the nasal retina project to the __________ side of the brain; axons from the temporal retina project to the __________ side of the brain. A) same, same B) same, opposite C) opposite, same D) opposite, opposite
Axons from the nasal retina project to the opposite side of the brain; axons from the temporal retina project to the same side of the brain.
Which type of papillae have the most sensitive taste buds associated with them? A) circumvallate B) filiform C) foliate D) fungiform
Foliate papillae are most numerous in children and decrease with age.
Identify the location of the taste area of the cortex. A) precentral gyrus B) postcentral gyrus C) thalamus D) temporal lobe
postcentral gyrus Feedback: The nerves carrying taste sensation enter into the medulla oblongata where they decussate and extend to the thalamus. From the thalamus the neurons project to the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe.
Which muscle raises the upper eyelid when it contracts? A) levator palpebrae superioris B) orbicularis oculi C) superior oblique D) superior rectus
levator palpebrae superioris
Which of the following statements about nerve fibers of the optic nerves is true? A) The nasal fibers from both retinas crossover at the optic chiasm. B) The temporal fibers from both retinas crossover at the optic chiasm. C) The nasal fibers from the left and the temporal fibers from the right retina crossover at the optic chiasm. D) The nasal fibers from the right and the temporal fibers from the left retina crossover at the optic chiasm.
The nasal fibers from both retinas crossover at the optic chiasm. The right and left optic nerves are connected to each other at the optic chiasm. The nasal (medial) fibers crossover at the optic chiasm, however the temporal (lateral) fibers project to the brain on the same side of the body without crossing.
The right and left optic nerves are connected to each other at the optic chiasm. The nasal (medial) fibers crossover at the optic chiasm, however the temporal (lateral) fibers project to the brain on the same side of the body without crossing.
constriction of the pupil Depth of focus is the greatest distance through which an object can be moved and still remain in focus on the retina. The depth of focus is greater when the diameter of the pupil is small.
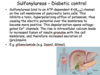
Identify the labeled structure in the diagram. A) aqueous humor B) choroid coat C) retina D) vitreous humor

The retina is the innermost layer of the eye. That retina contains both pigment as well as the photoreceptors.

optic tract
Feedback: The retina consists of three layers of cells: the photoreceptors, the bipolar cells, and the ganglion cells. The ganglion cells unite at the optic disc and exit the eye via the optic (II) nerve.
Which of the following is the passageway between the middle ear and the pharynx?
A)eustachian tube
B)external auditory meatus
C)oval window
D)semi-circular canals
eustachian tube
The eustachian tube (also called the auditory tube) allows for the equilibration of pressure between the outside air and the middle ear cavity.
Which of the following is located within the vestibule of the ear?
A)crista ampullaris
B)helicotrema
C)macula
D)organ of Corti
macula
The vestibule, along with the semi-circular canals, function in balance. The macula is a sensory structure within the utricle and the saccule of the vestibule

The receptor cells for hearing, hair cells, are located within the
A)macula
B)organ of Corti
C)utricle
D)vestibule
The organ of Corti rests on the basilar membrane and supports the hair cells that detect sound.
organ of Corti, or spiral organ, is the receptor organ for hearing and is located in the mammalian cochlea. This highly varied strip of epithelial cells allows for transduction of auditory signals into nerve impulses’ action potential.[1] Transduction occurs through vibrations of structures in the inner ear causing displacement of cochlear fluid and movement of hair cells at the organ of Corti to produce electrochemical signals.[2]


This is the vestibule of the inner ear. The vestibule is involved in balance, primarily in evaluating the position of the head in relationship to gravity.
Ivabradine
•selectively inhibits the pacemaker If current in a dose-dependent manner. Blocking this channel reduces cardiac pacemaker activity, slowing the heart rate and allowing more time for blood to flow to the myocardium
Blocks the If channel from the inside when the channel is in the open state as the drug is lipophilic

Vepramil
Decrease entry of calcium and delay the depolarization of SA and AV nodal cells
By decreasing the influx of calcium, Verapamil prolongs the effective refractory period within the AV node and slows AV conduction in a rate-related manner

drug that induces a neuronal inhibition
This opening leads to a increased conductance to chloride ions, which produces membrane hyperpolarization, this induces a neuronal inhibition

Bronchodilators

Salbutamol/Sal/F

β- 2 Receptors


commonly used in treating asthmatics
•Ipratropium is commonly used in treating asthmatics. Sensory nerve endings are present in the lining of the airways and when activated release Ach which in turn activate muscarinic receptors (G proteins) inducing constriction and narrowing of the airways. Muscarinic receptor antagonists act to inhibit constriction of airways leading to relaxation of smooth muscle cells

River Blindness
- Onchocerciasis also known as river blindness or Robles disease is second most common infectious disease to cause blindness and is a parasitic disease caused by the filarial worm Onchocerca volvulus
- It is not the nematode (round worm), but its endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis (bacteria), that causes the severe inflammatory response that leaves many blind
- The parasite is transmitted to humans through the bite of a black fly of the genus Simulium. The larval nematodes spread throughout the body. When the worms die, their Wolbachia symbionts are released, triggering a host immune response that can cause severe itching, and can destroy optical tissue in the eye
- After mating, the female adult worm can release up to 1000 microfilariae (early stage of life cycle) a day