Pulmonary Blood Flow and Gas Exchange and Transport 1 Flashcards
How does alveolar ventilation and compliance change with height from the base to the apex?
Both of them decline
Why does compliance decline with height from the base to the apex?
Alveoli are more inflated at FRC at the apex, since the ones at the base are more compressed
What does the alveoli at the apex being more inflated than the ones at the base mean for changes in intrapleural pressure?
Changes in pressure brings about bigger changes in alveolar volume at the base

What does the pulmonary vein carry?
Oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
What does the pulmonary artery carry?
Deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
What are the 2 kinds of blood supply to the lungs?
Bronchial circulation
Pulmonary circulation
What is the purpose of bronchial circulation?
Supply the lungs with nutrients
What circulation supplies the lungs with nutients?
Bronchial circulation
What is bronchial circulation supplied via?
Bronchial arteries from systematic circulation to supply oxygenated blood to airway smooth muscle, nerves and lung tissue
What is the purpose of pulmonary circulation?
Gas exchange
What circulation is used for gas exchange?
Pulmonary circulation
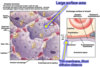
What does pulmonary circulation consist of?
Left and right pulmonary arteries originating from the right ventricle
What does pulmonary circulation do?
Carries entire cardiac output from right ventricle, supplying dense capillary network surrounding the alveoli and returns oxygenated blood to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein
What kind of system is the pulmonary circulation?
High flow, low pressure
How does air diffuse across membranes?
Down its partial gradiants

What does gas exchange occur due to?
Presence of partial pressures
Where is the partial pressure of oxygen highest?
In arterial circulation
Where is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide highest?
In venous circulation
What does the abbreviation “A” mean in regards to partial pressures?
Alveolar
What does the abbreviation “a” mean in regards to partial pressures?
Arterial blood
What does the abbreviation “v” mean with regards to partial pressures?
Mixed venous blood (such as pulmonary artery)
What does PaO2 mean?
Partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood
What does PACO2 mean?
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in alveolar air
What does mixed venous blood (v) reflect the values of?
Values in tissue