Embryology 3 Flashcards
What is a summary for the development of the respiratory system?
1) Tubular outgrowth from foregut (oesophagus)
2) This outgrowth will develop into the trachea and lung buds
3) Trachea will seperate from oesophagus and lung buds will proliferate
4) Proliferating lung buds will invaginate laterally into the pleural cavities, so forming visceral and parietal pleural and the pleural cavity
5) Meanwhile, transverse septal ‘shelf’ will begin to develop between thorax and abdomen, below the pleural cavities
6) This shelf is composed of 4 components, which fuse to form the diaphragm
7) But sometimes things go wrong with the embryonic tracheal, lung and diaphragmatic formation which results in congenital abnormalities

When does folding of the embryo occur?
Week 3
What does folding give rise to?
Gut tube

What does the gut tube form from?
Endoderm

What does the trachea and lungs form from?
Foregut
What is step 1 in development of the respiratory system?
Development of the trachea and the lungs
When does development of the trachea and the lungs occur?
Week 4 of gestation
Where does the development of the trachea and lungs begin from?
Ventral wall of foregut
What is A?

Hindgut
What is B?

Yolk sac
What is C?

Foregut
What is D?
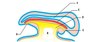
Primitive gut
What is E?

Notochord
What is F?

Neural tube
What is the process of the development of the trachea and lungs?
1) Respiratory primordium starts as a median outgrowth (diverticulum) - laryngotracheal groove - from vental part of the foregut
2) Diverticulum (part of endoderm) becomes invested (covered) with mesoderm on its outside and enlarges to form trachea and lung buds
3) A septum (oesophagotracheal septum) develops between the oesophagus and trachea, completely seperating them
What is the diverticulum part of?
Endoderm
What does the diverticulum become covered by to form the trachea and lung buds?
Mesoderm
What is the median outgrowth called that goes on to form the trachea and lung buds?
Laryngotracheal groove (diverticulum)
What septum develops between the oesophagus and trachea to completely seperate them?
Oesophagotracheal septum
When is the development of the trachea and lung buds completed?
Week 8

What sometimes happens to the oesophagotracheal septum?
It does not completely seperate the trachea and the oesophagus
What are examples of diseases due to the septum not completely seperating the trachea and oesophagus?
Fistula
Atresia

What is a fistula?
Abnormal or surgically made passage between a tubular organ and the body surface, or between two hollow or tubular organs