Pleural Disease Flashcards
1
Q
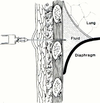
Pleural Anatomy
A
- 2 layers made of mesothelial cells
- Visceral pleura ⇒ lines lungs
- Parietal pleura ⇒ lings chest wall
- Normal pleural fluid production ~ 16.8 nl/day for 70 kg adult
- Fluid flows from visceral to parietal pleura
- Lymphatic drainage ~ 470 cc/day
- 28x more than production
- No fluid in pleural space normally
2
Q
Pleural Effusion
Definition
A
Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.

3
Q
Pleural Effusions
Pathophysiology
A
-
↑ fluid accumulation
Entry of fluids into pleural space:- ↑ systemic venous pressure
- ↑ pulmonary venous pressure
- ↑ permeability of pleural vessels
- ↓ pleural pressure
- ↓ microvascular oncotic pressure
-
↓ fluid removal
Blockage of lymphatics:- Central lymphatic obstruction
- Obstruction of lymphatic channels at pleural surface by tumor
4
Q
Transudates
Characteristics
A
Light’s Criteria

5
Q
Exudates
Characteristics
A
Light’s Criteria

6
Q
Transudates
Etiologies
A

7
Q
Exudates
Etiologies
A

8
Q
Pleural Fluid
Analysis
A
- Cell count and differential
- Chemistry
- Proteins, LDH, albumin, amylase, pH, glucose
- Obtain concurrent serum values
- Gram strain and culture
- Cytology
- Other tests as indicated
- Lipids, fungal culture, triglycerides, Ig
9
Q
Pleural Effusion
History
A
- Asymptomatic
- Dyspnea ⇒ d/t compression of underlying lung
- Pleuritic CP ⇒ see w/ some exudative effusions
10
Q
Pleural Effusion
Physical Exam
A
- ↓ tactile fremitus
- Dullness to percussion
- ↓ or absent breath sounds
- Tracheal shift to contralateral side w/ very large effusion
- Tubular breath sounds, egophany (E to A changes)
11
Q
CHF Related
Pleural Effusions
A
- Most common cause of transudates
- D/t ↑ pulmonary venous pressures from LV dysfunciton
- Usually bilateral, R > L
- Thoracentesis often not needed
- Unless atypical or fail to resolve w/ medical treatment
12
Q
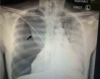
Image 1
A
Left-sided Massive Pleural Effusion
With contralateral shift of mediastinum and trachea.
Most common cause of non-traumatic massive pleural is cancer.
13
Q
Parapneumonic Effusions
Definition
A
Exudative effusions in setting of bacterial PNA or lung abscess.
- Often very high WBCs and LDH levels
- Effusion on same side as PNA
14
Q
Uncomplicated Paraneumonic Effusion
Characteristics
A
- Negative gram stain and culture
- pH > 7.30
- Glucose > 40
- Resolves w/ simple abx treatment of PNA
15
Q
Complicated Parapneumonic Effusion
A
- pH < 7.20
- Glucose < 40
- Requires chest tube or surgical drainage for resolution